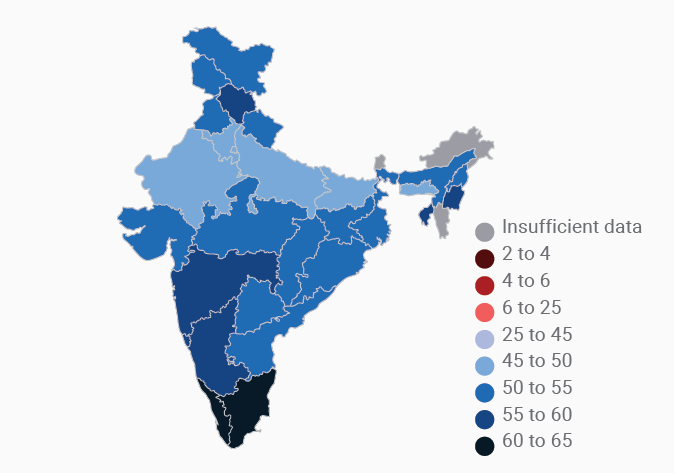
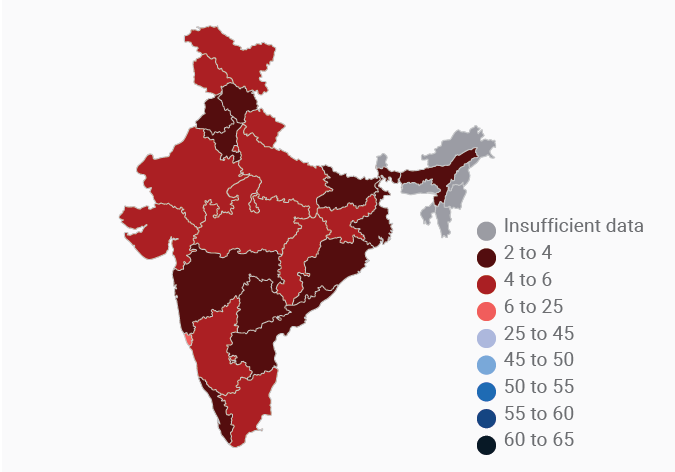
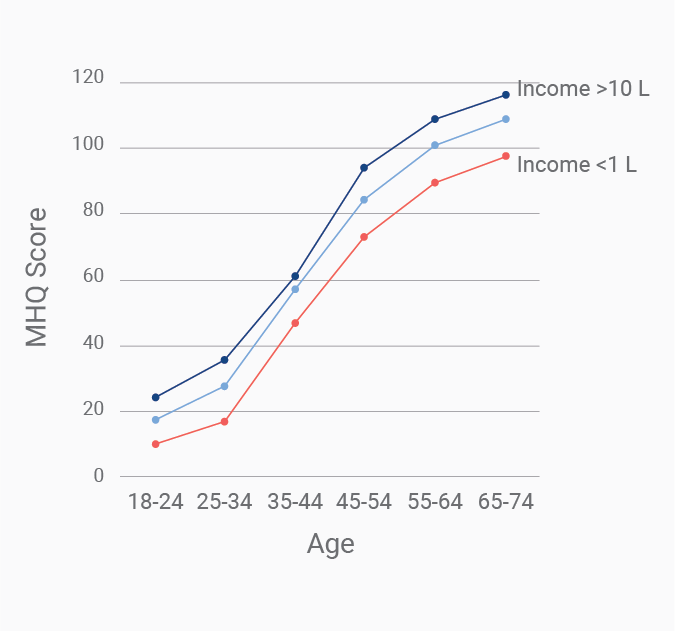
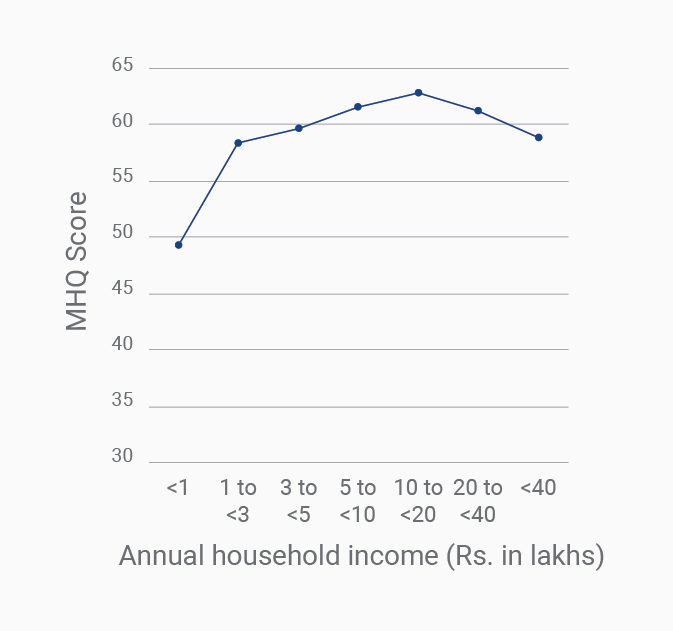
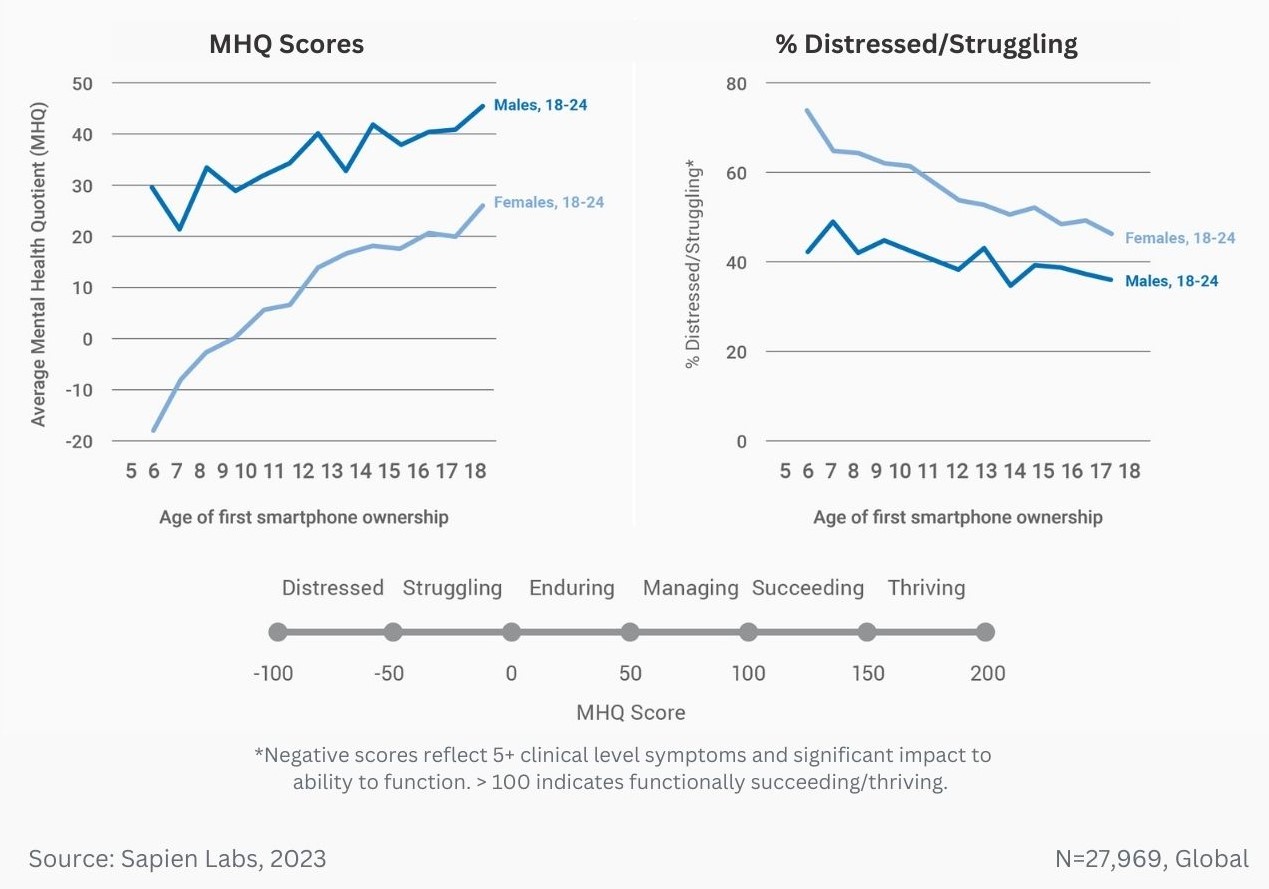
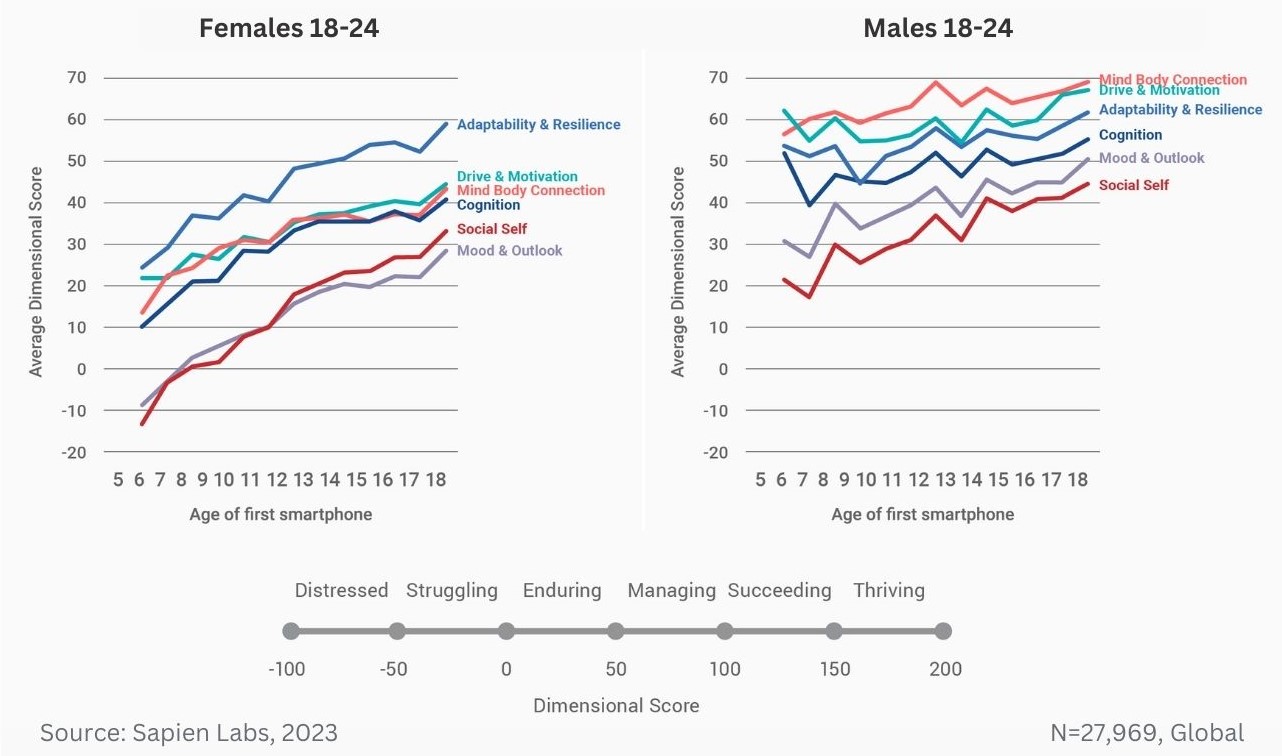
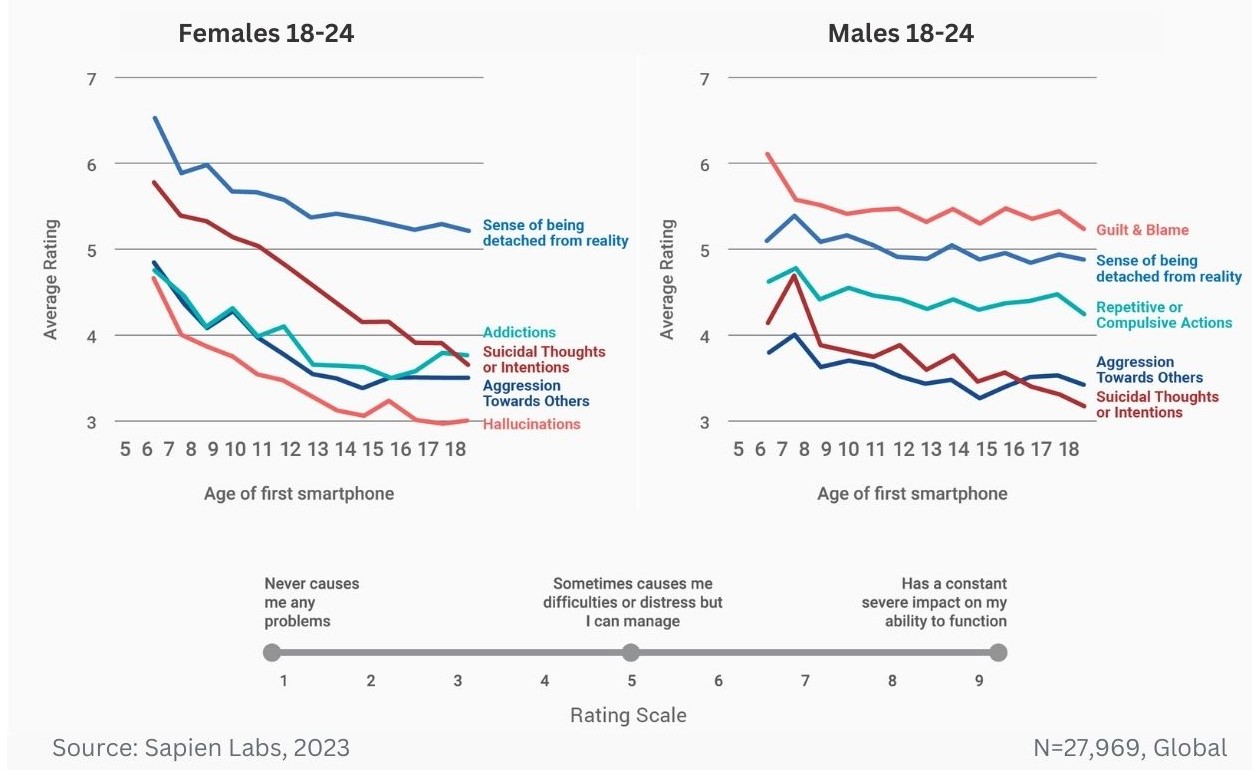
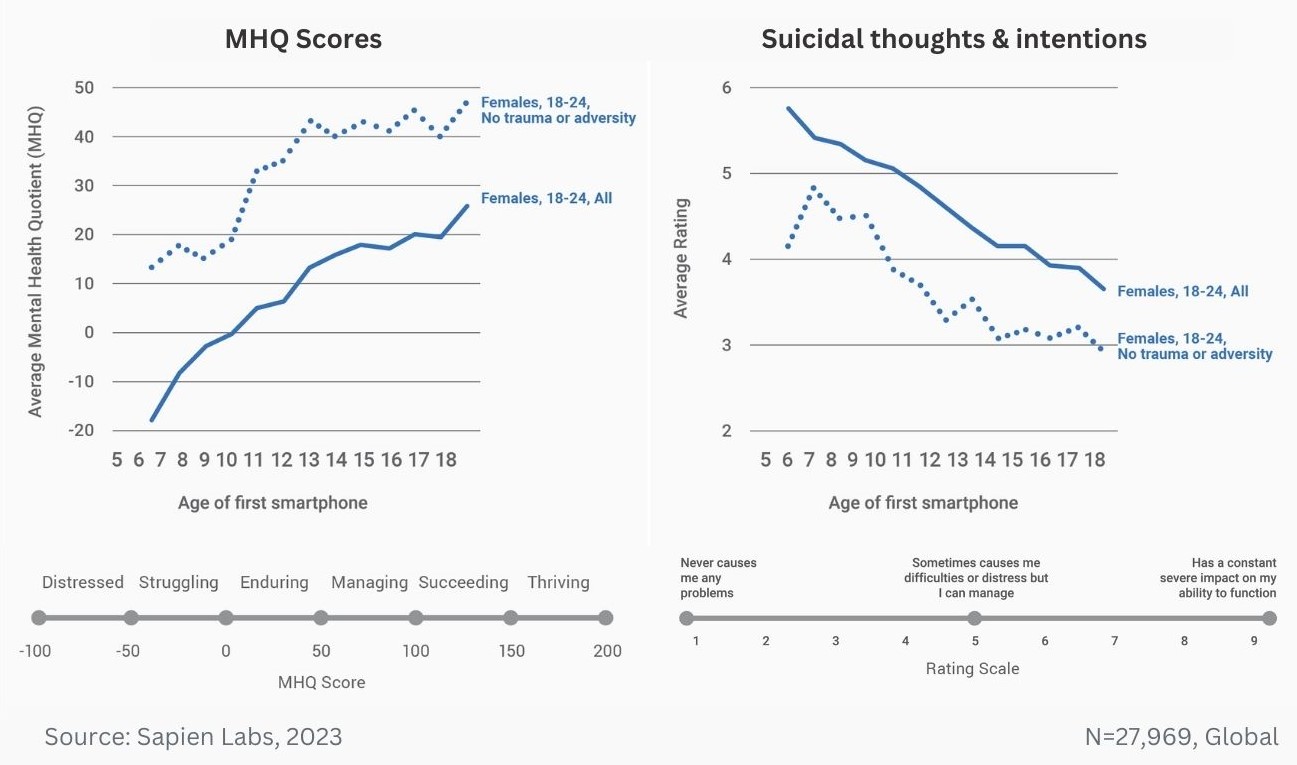
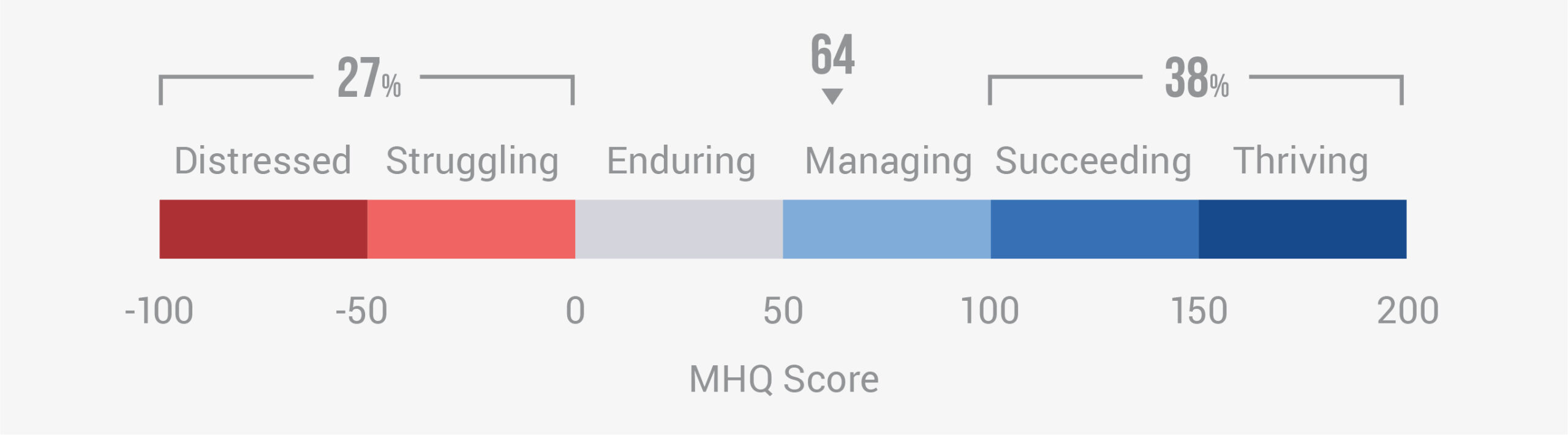
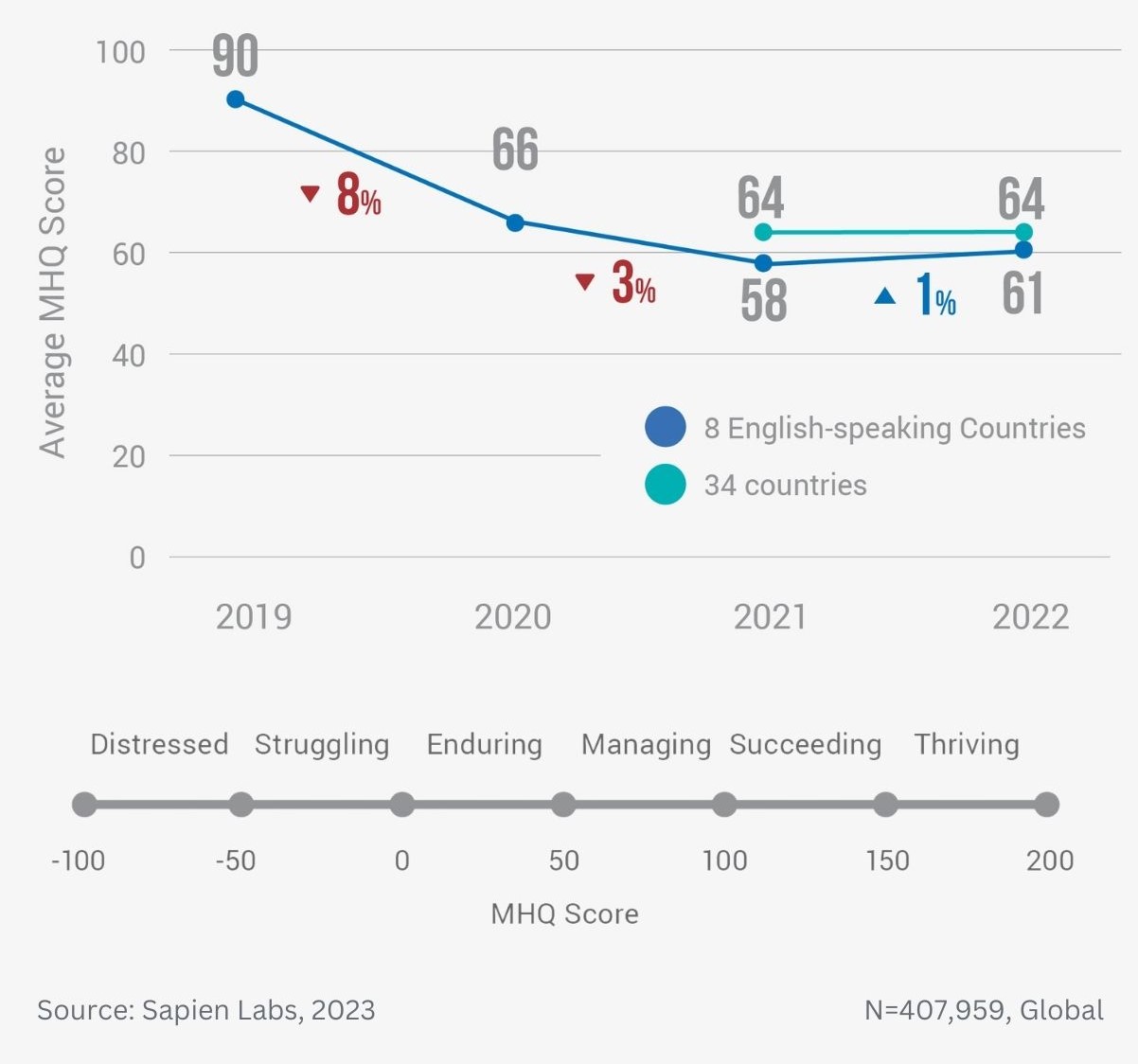
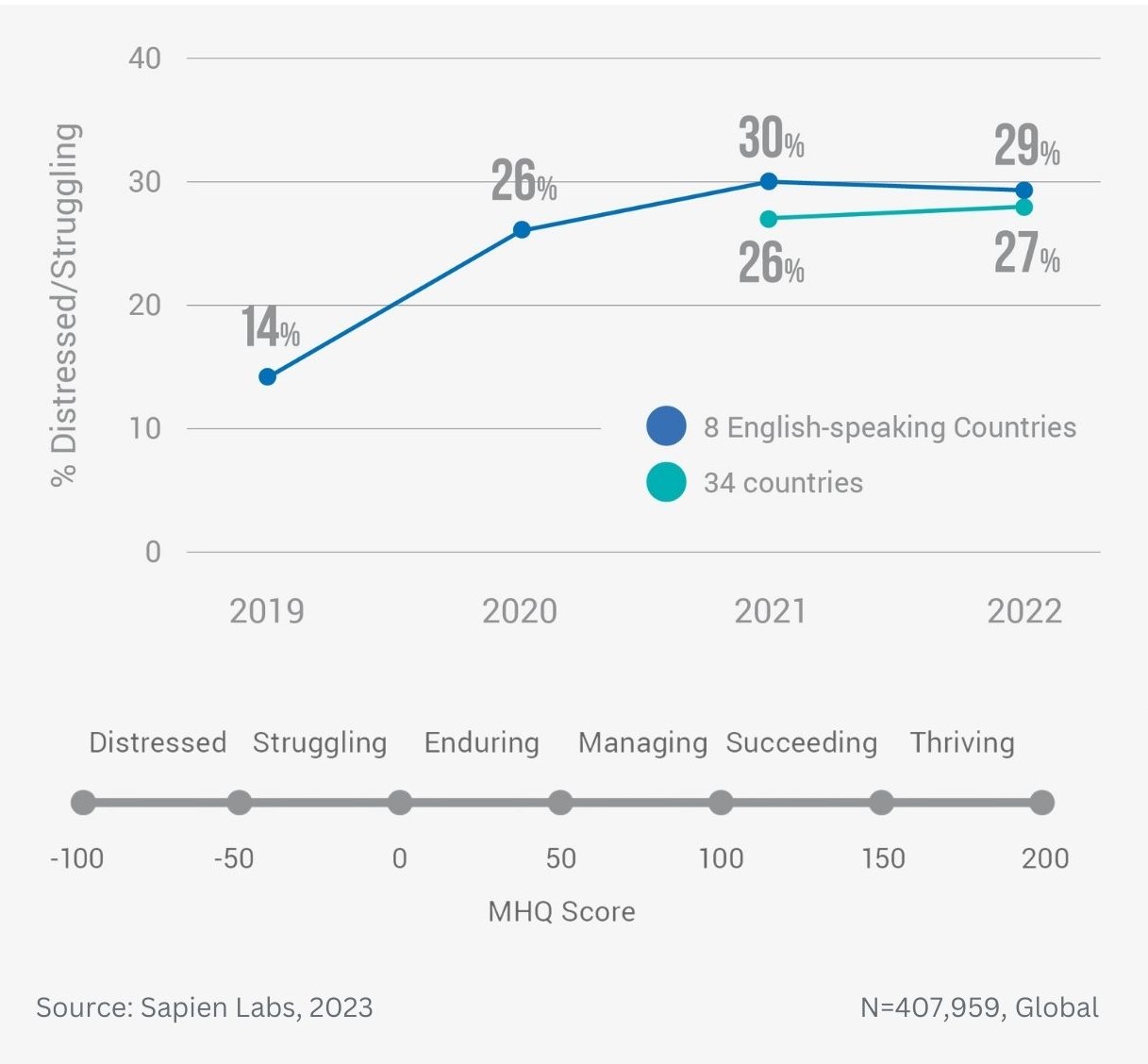
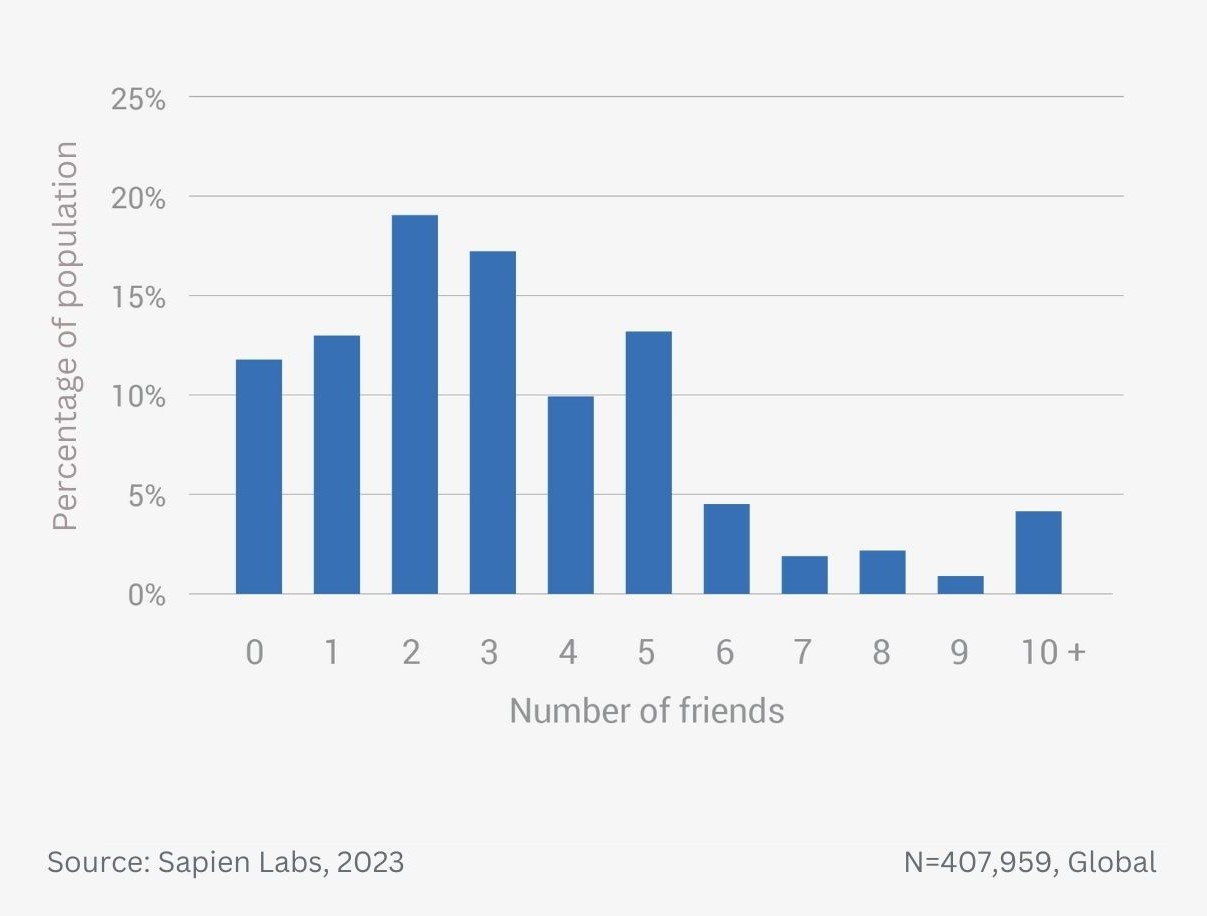
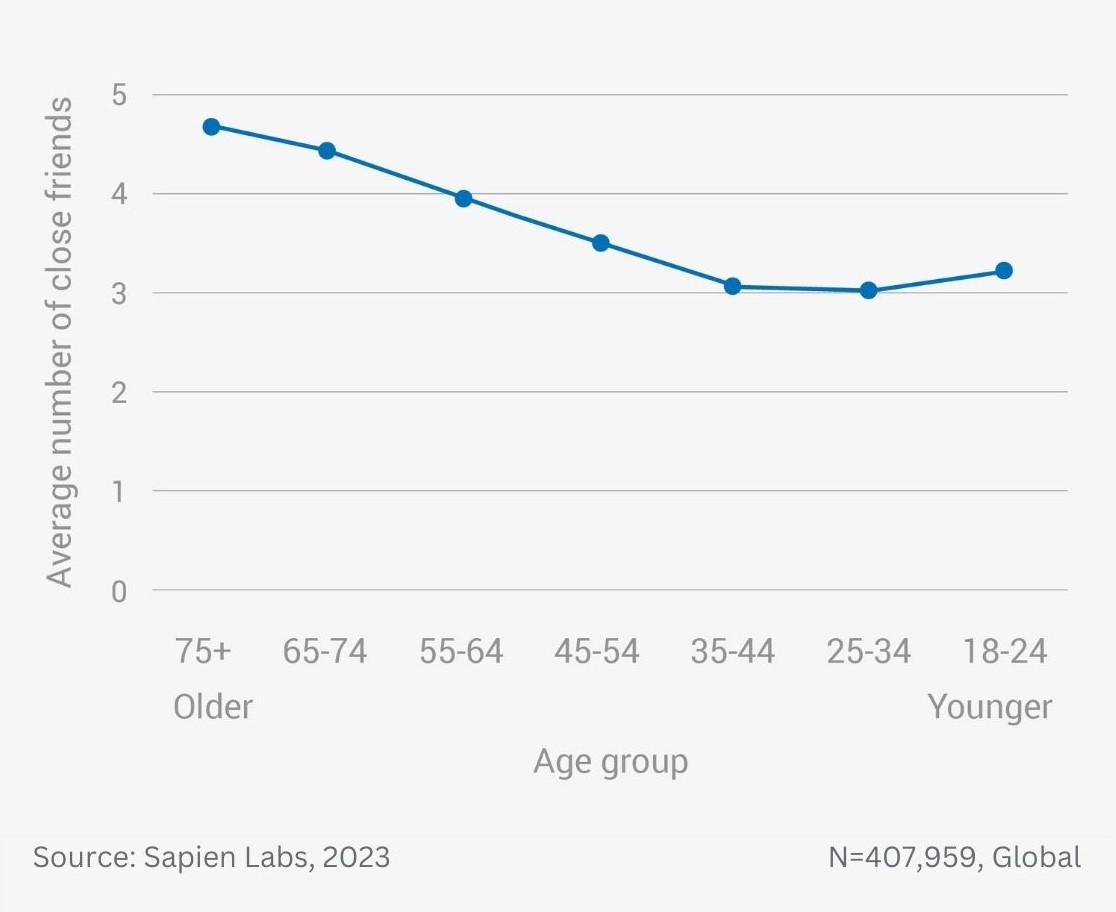
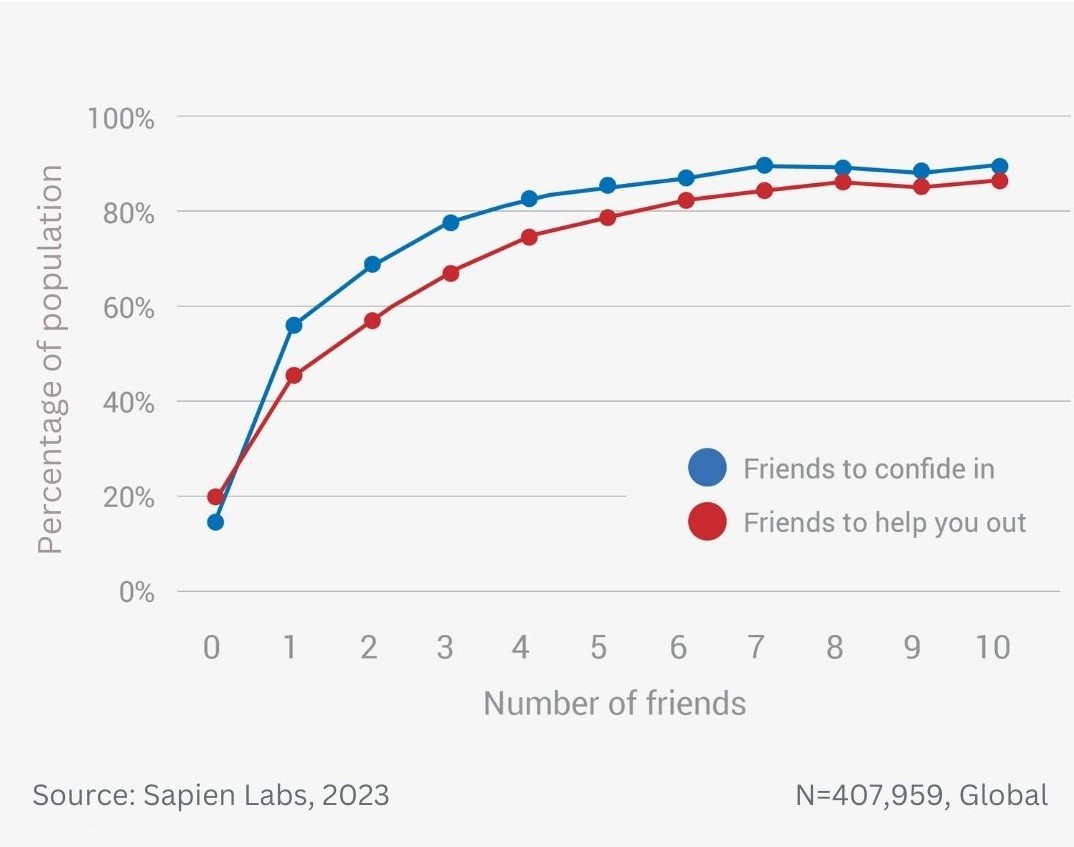
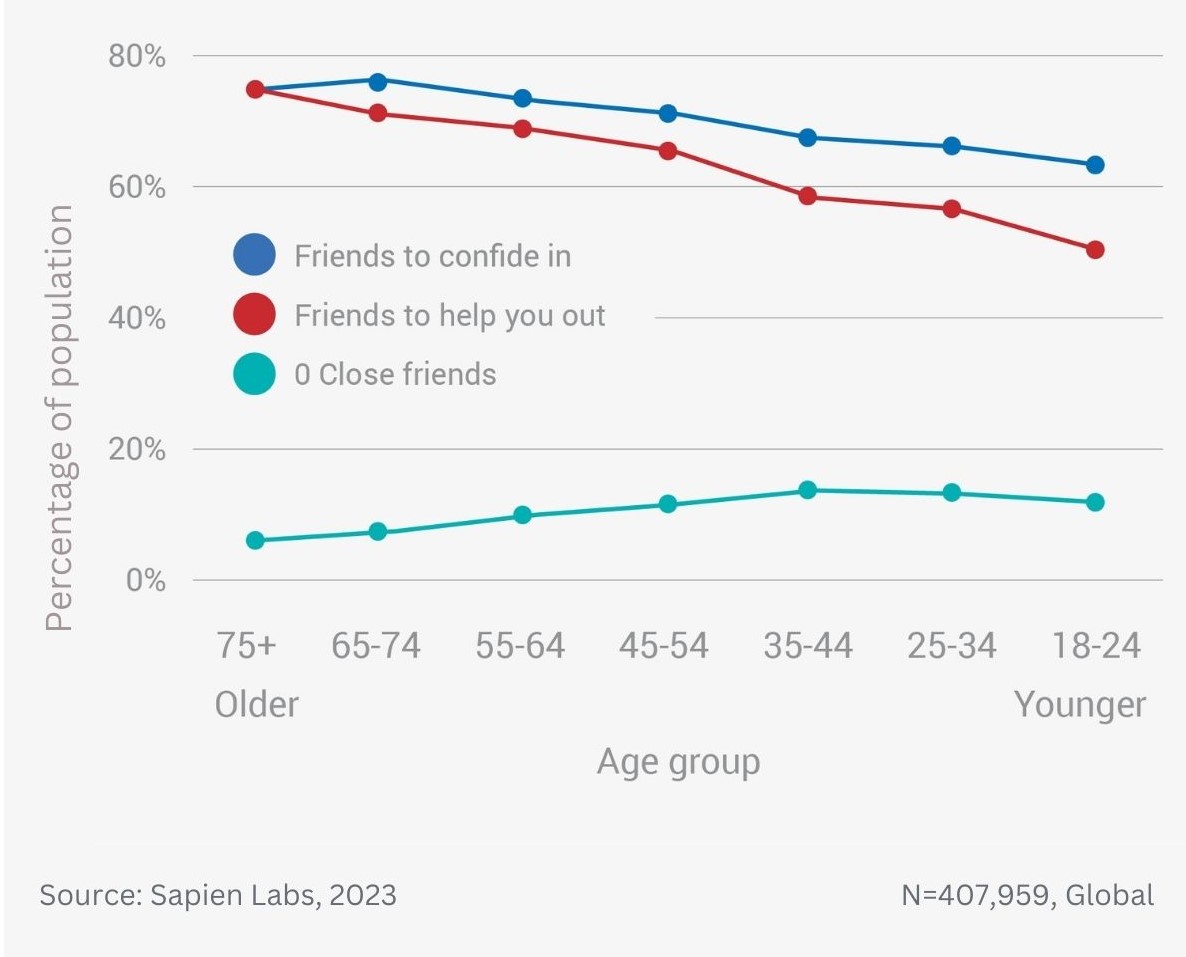
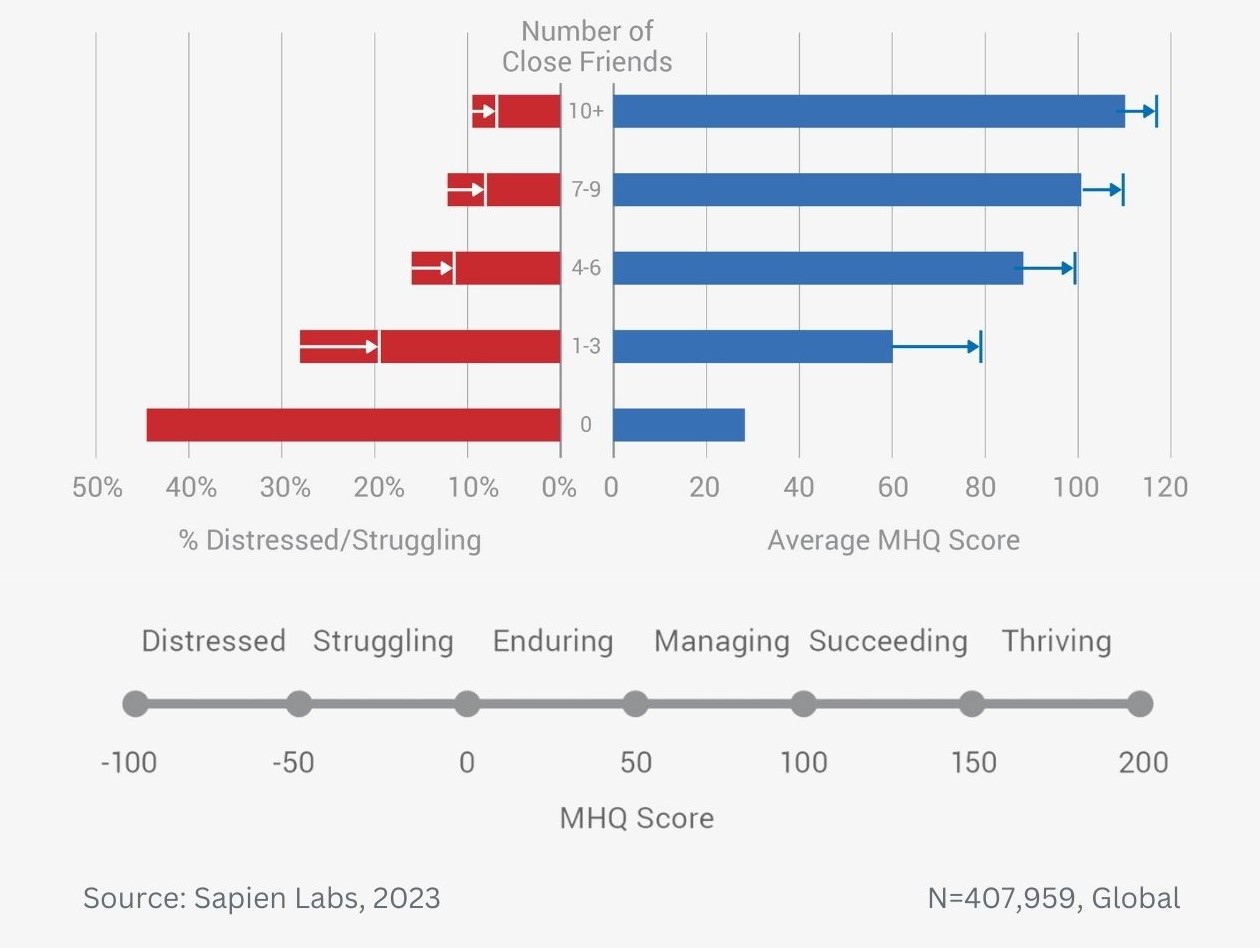
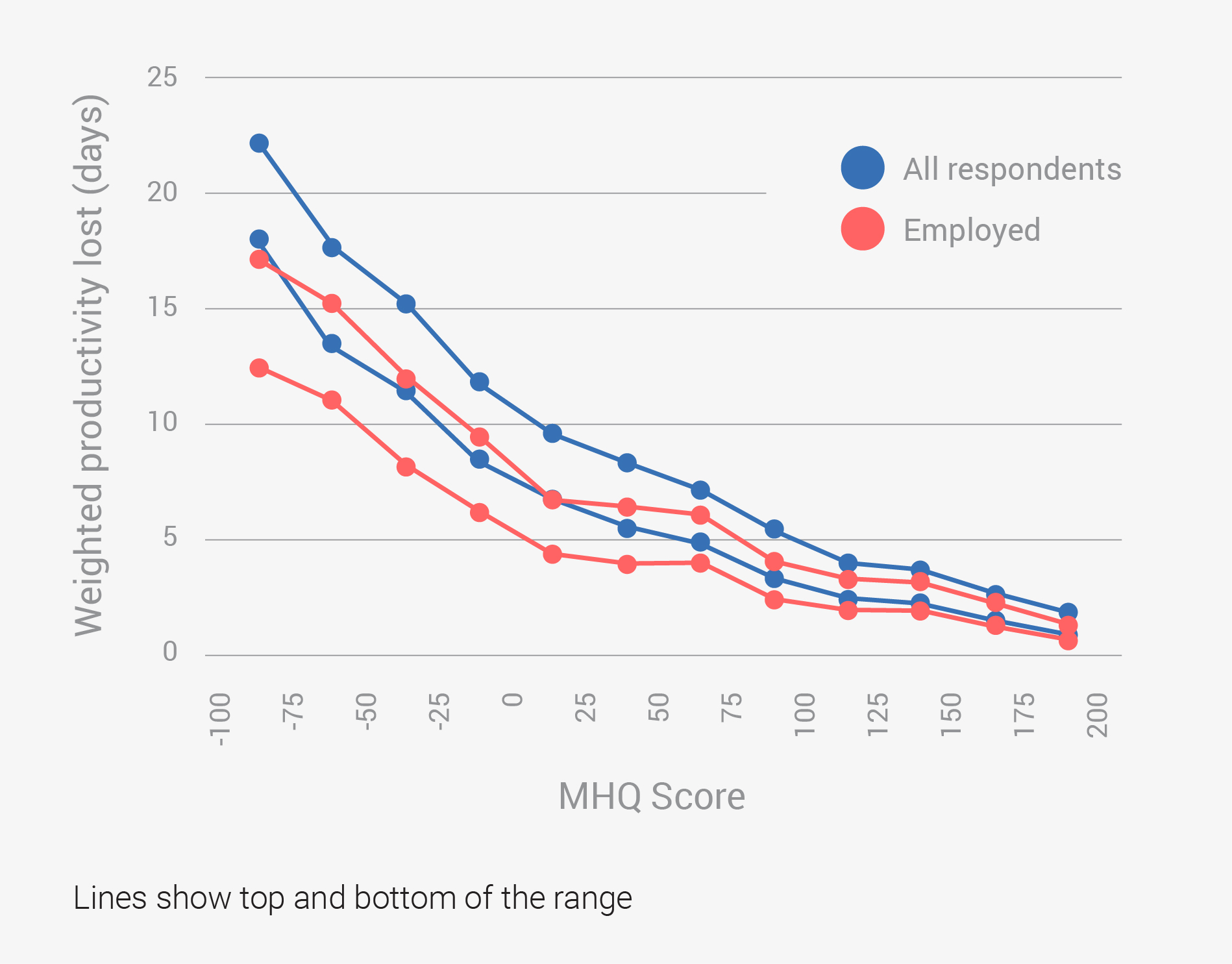
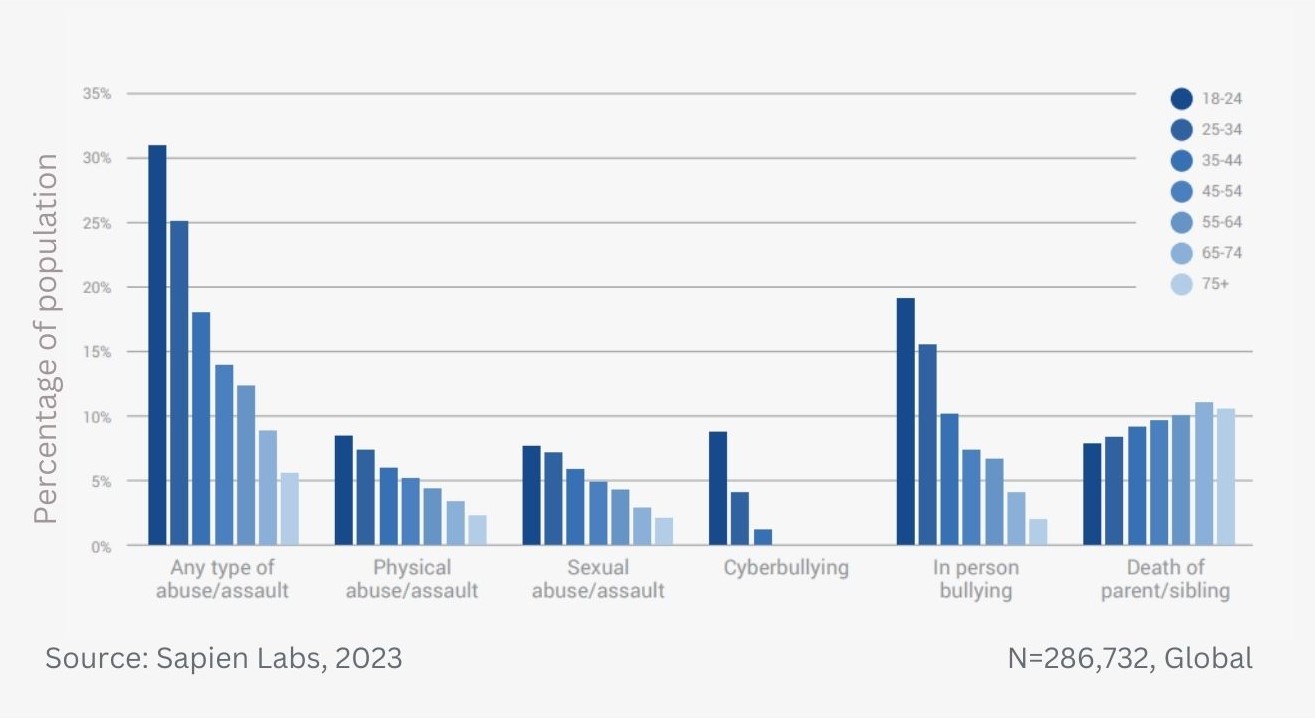
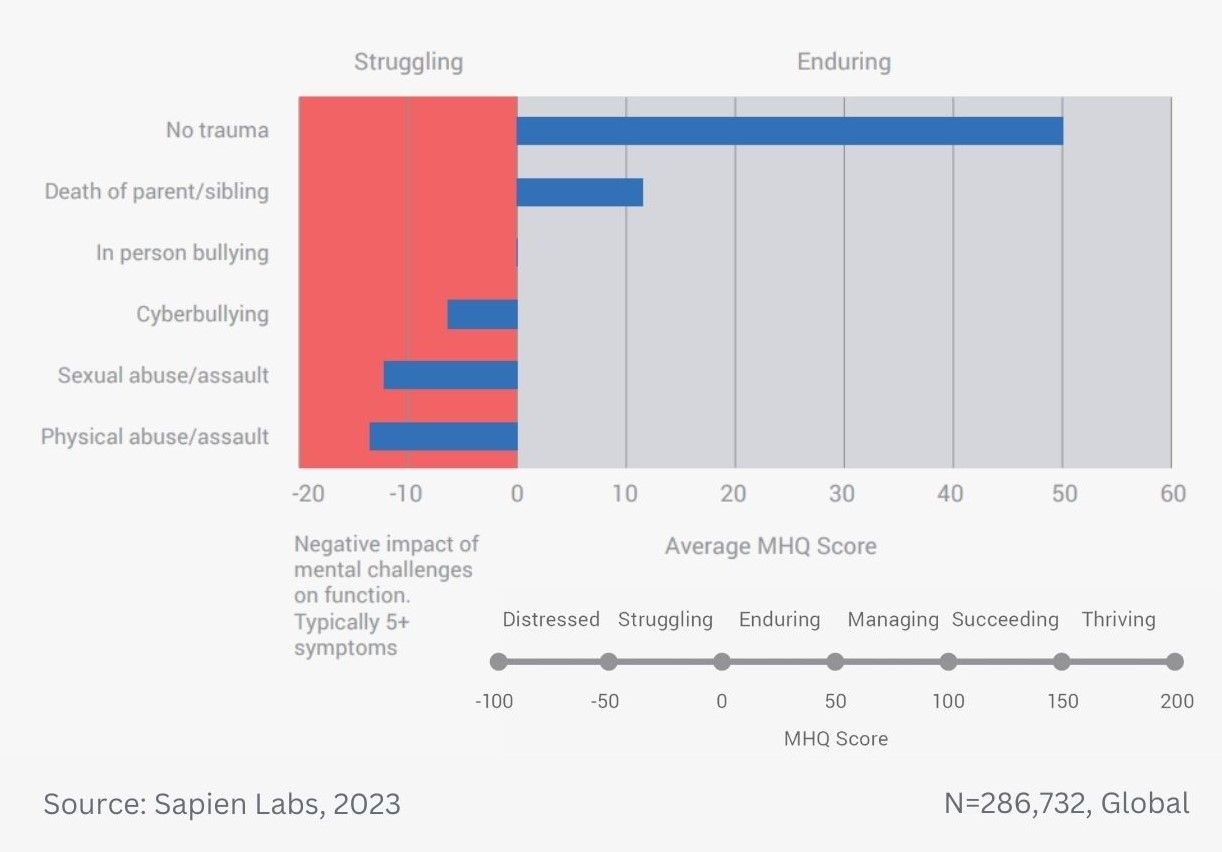
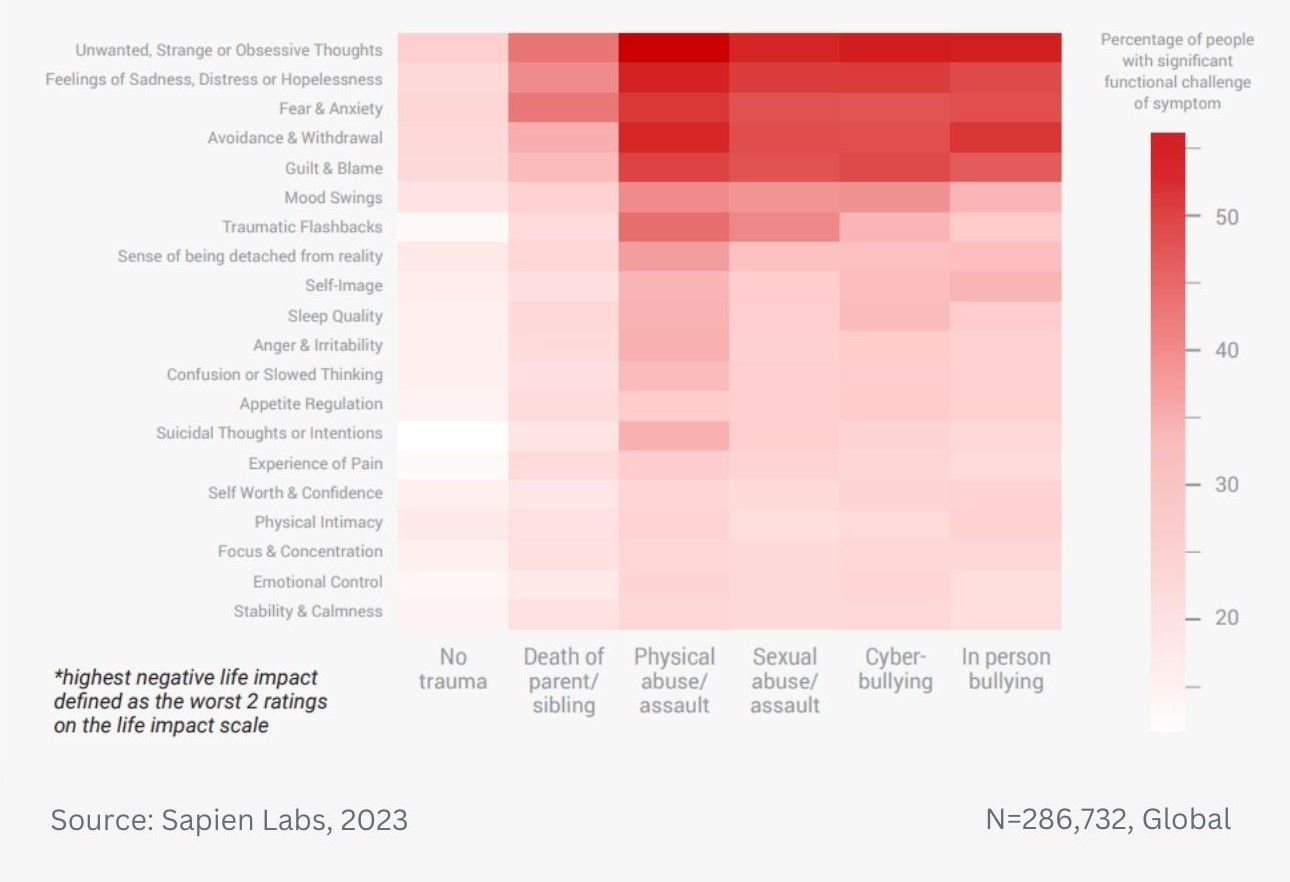
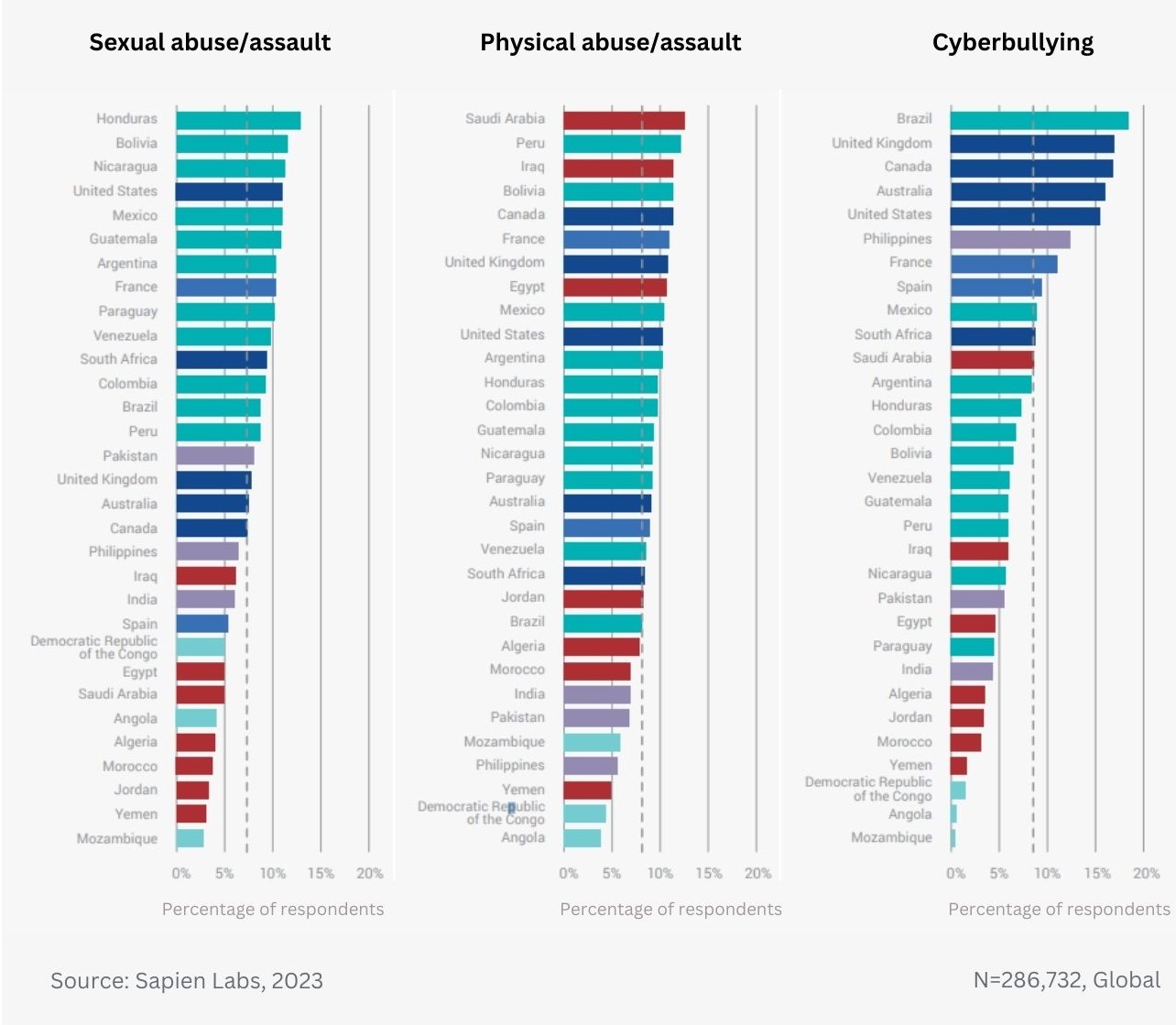
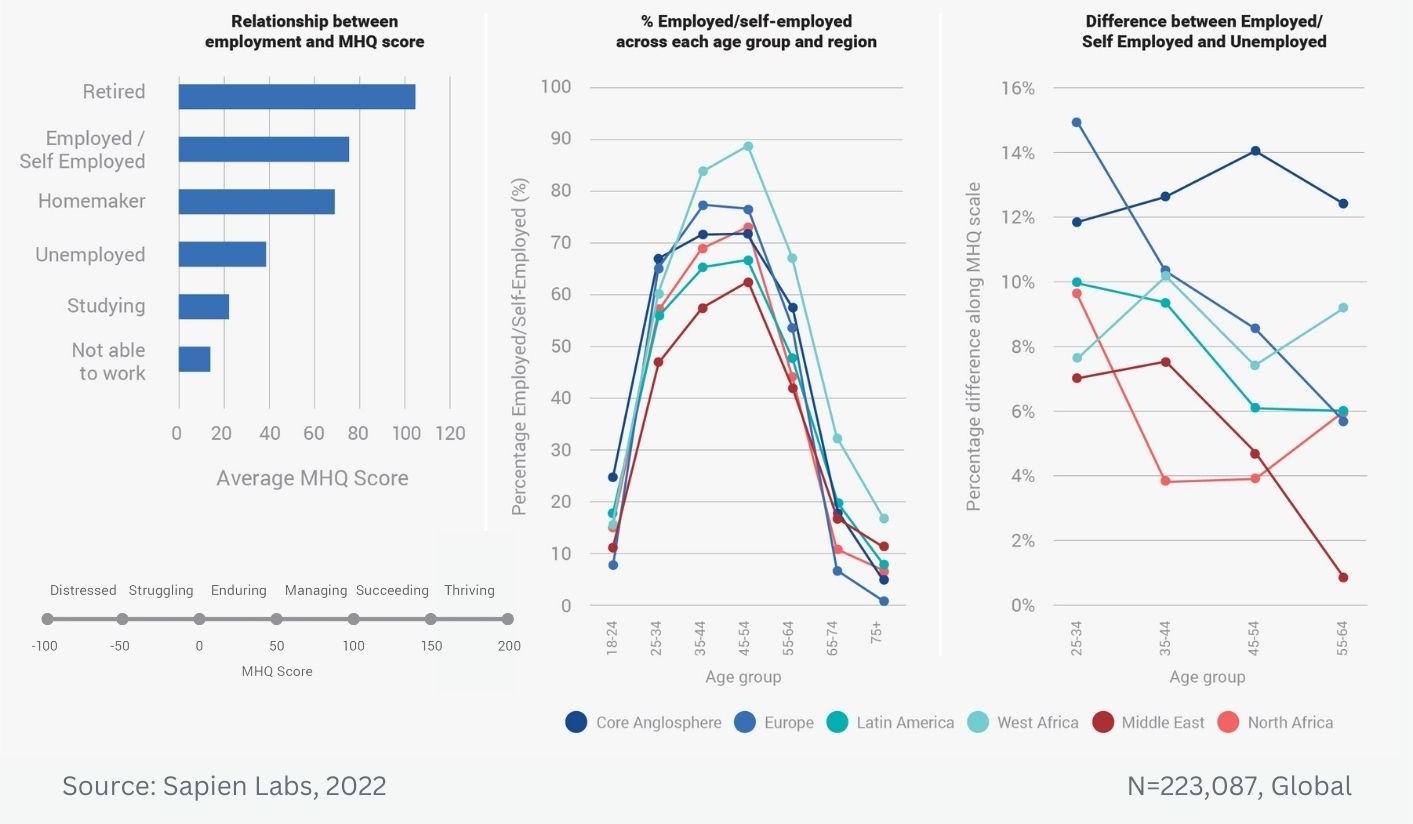
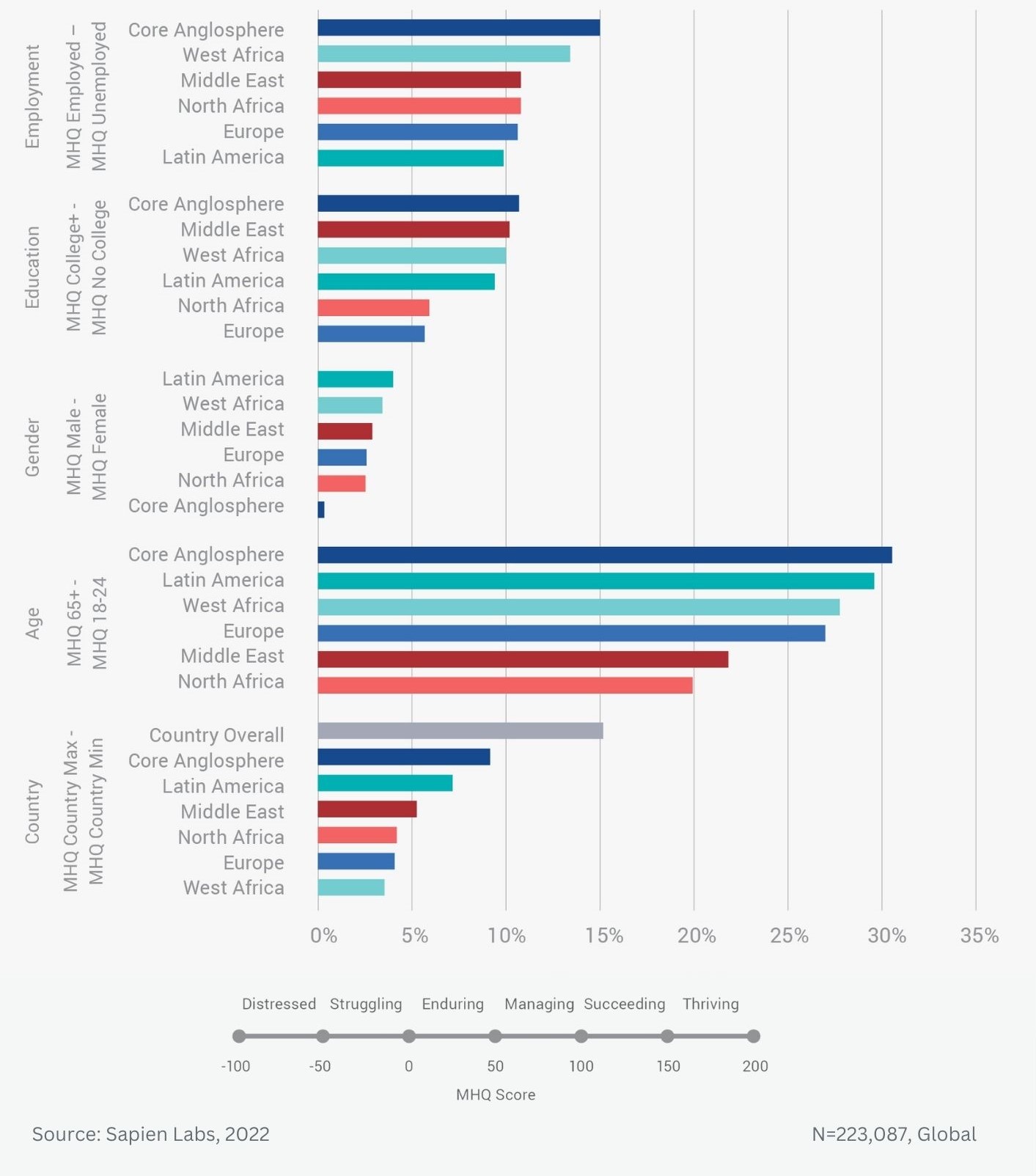
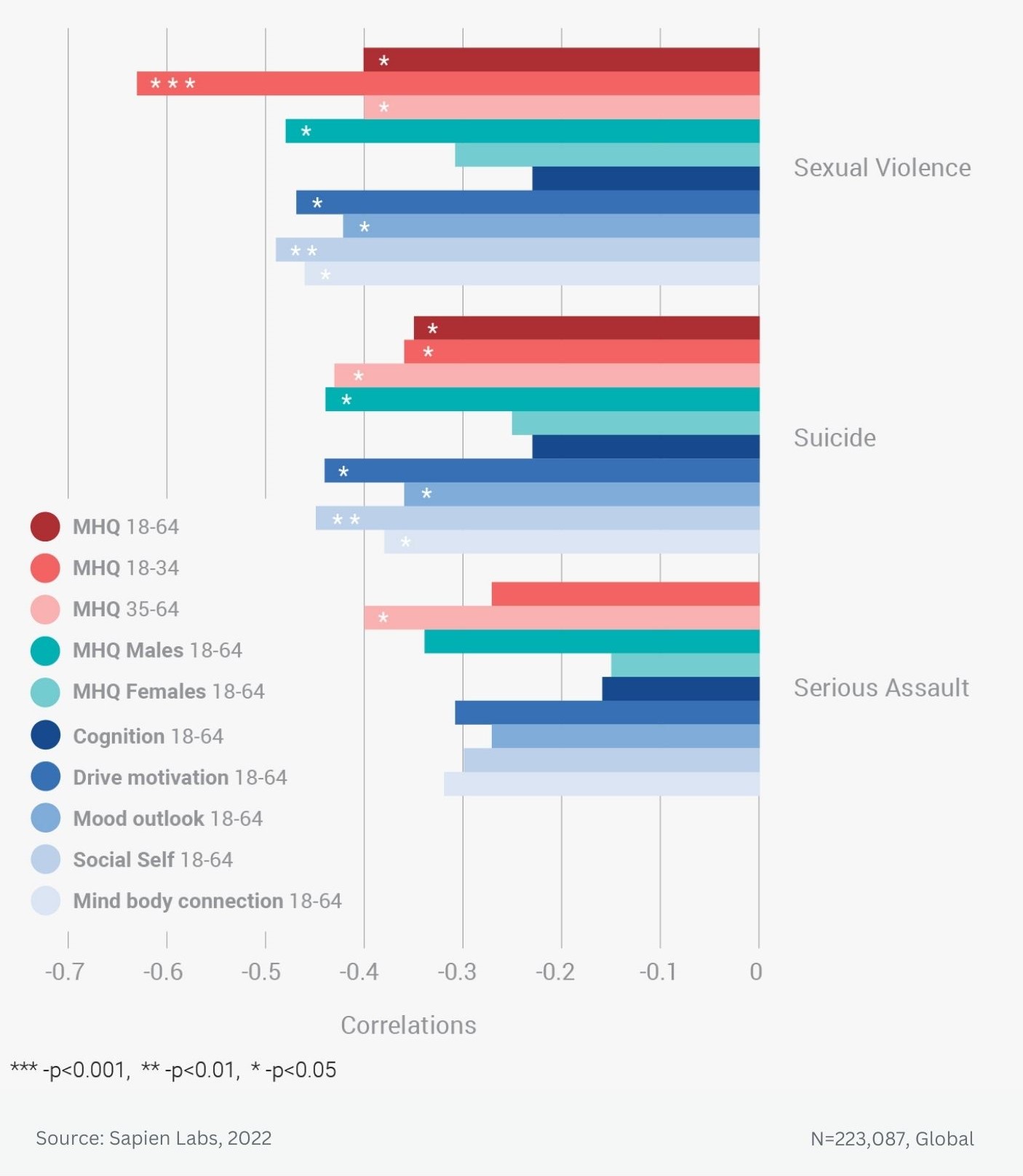
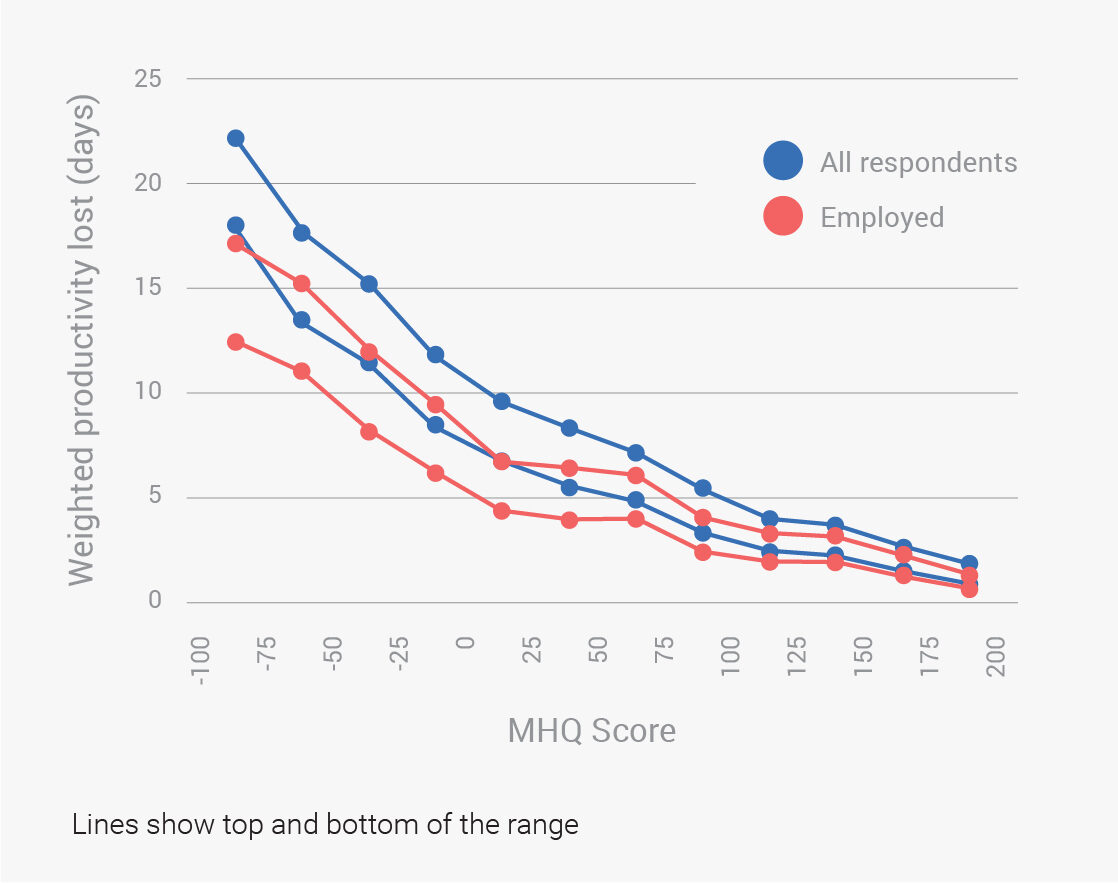
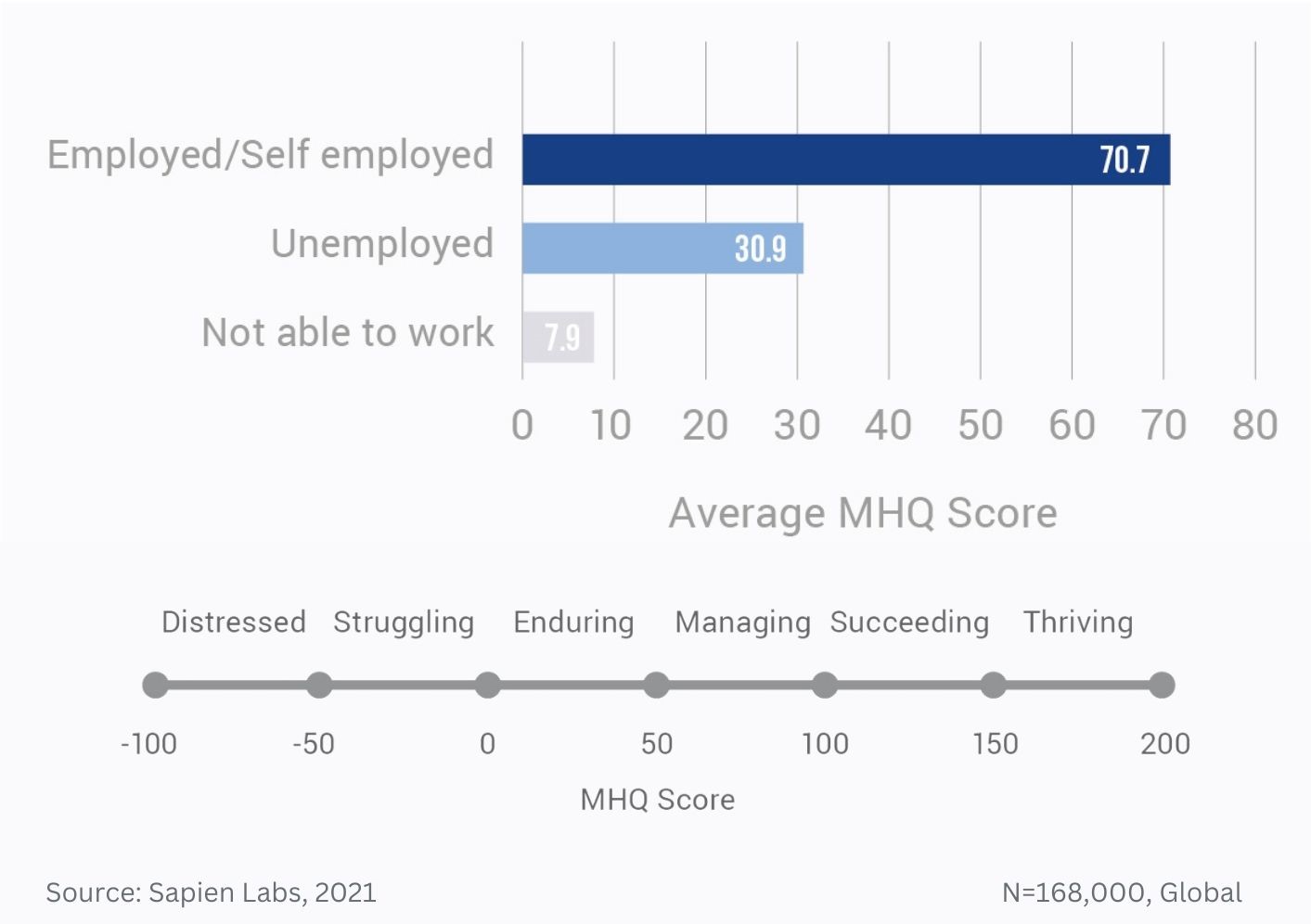
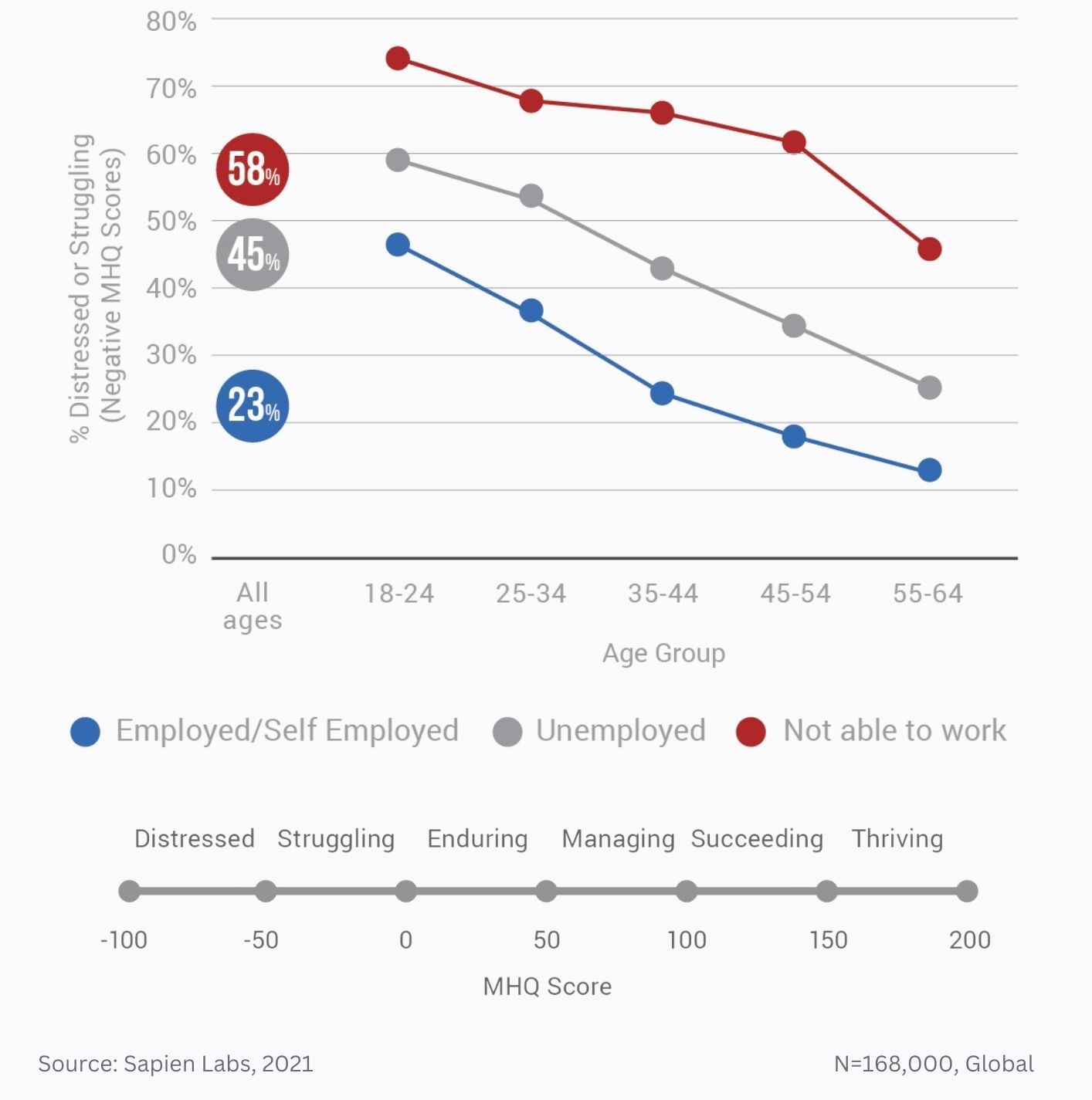
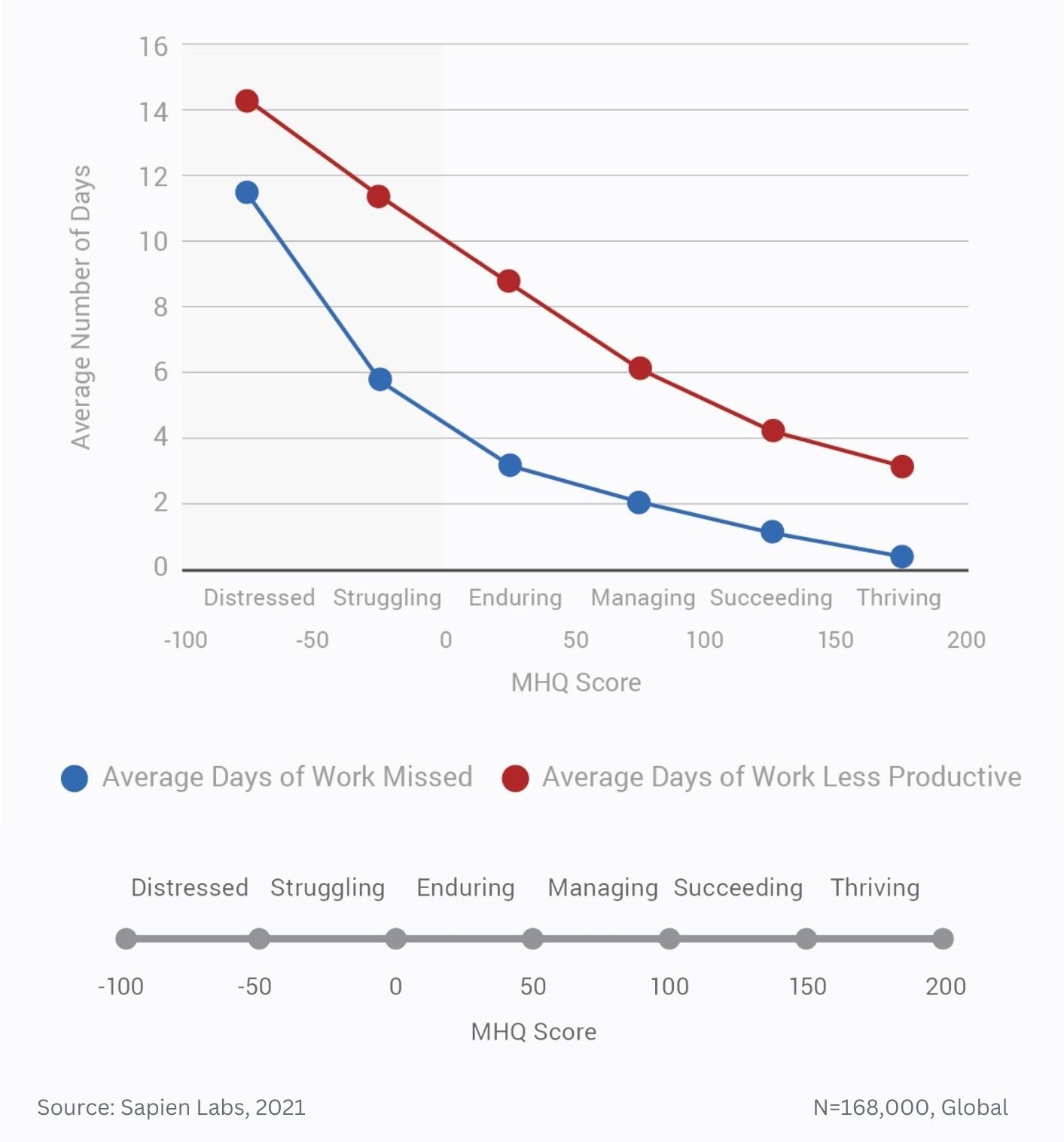
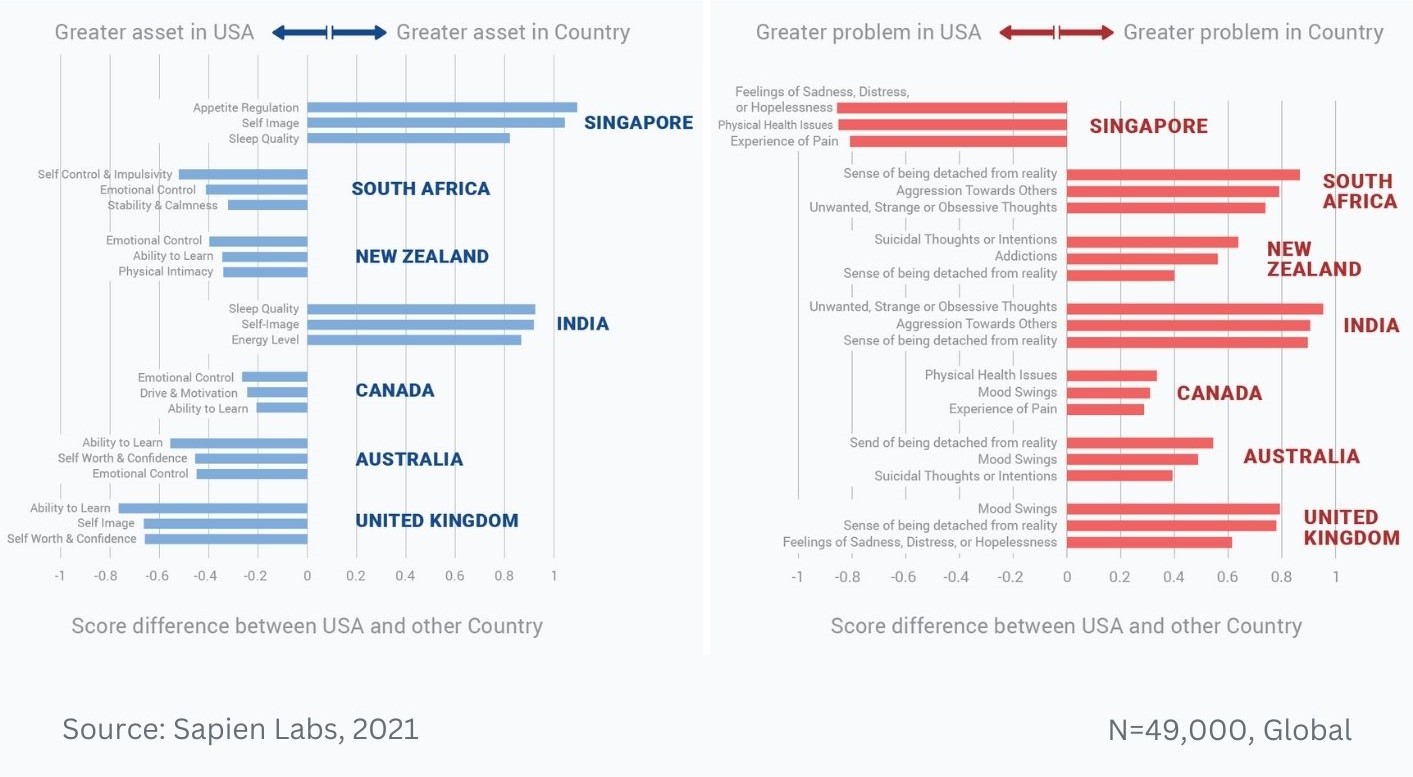
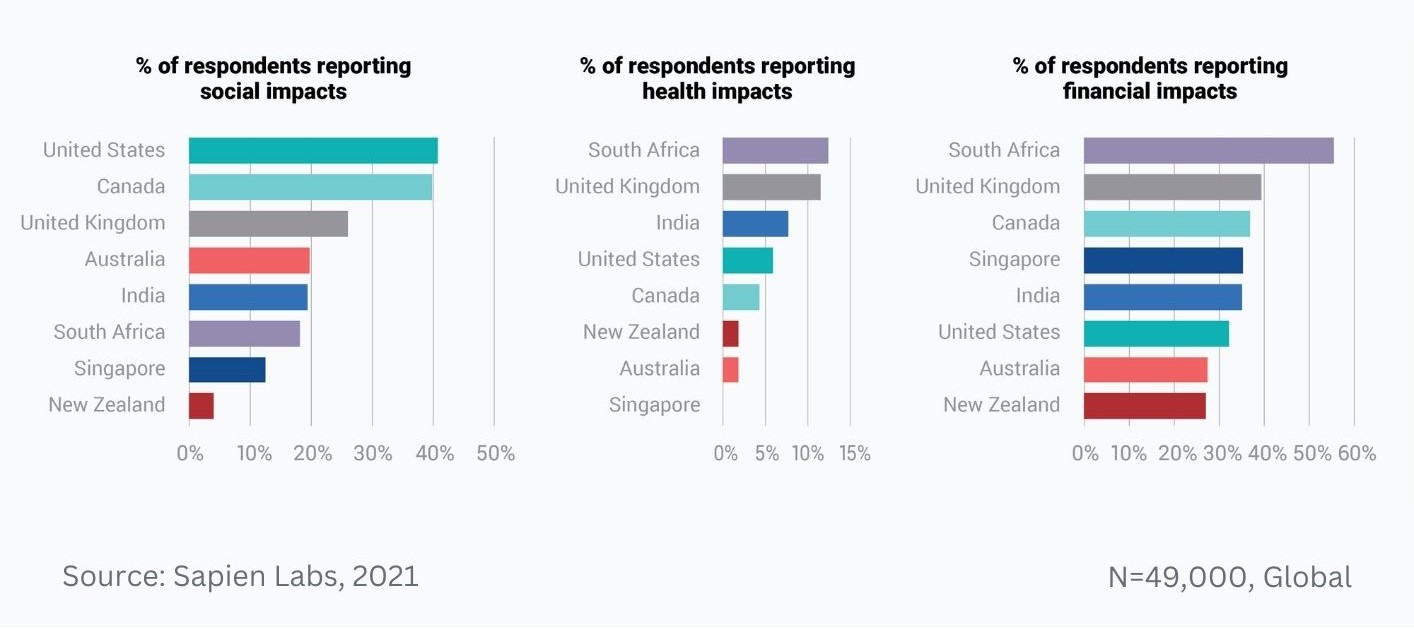
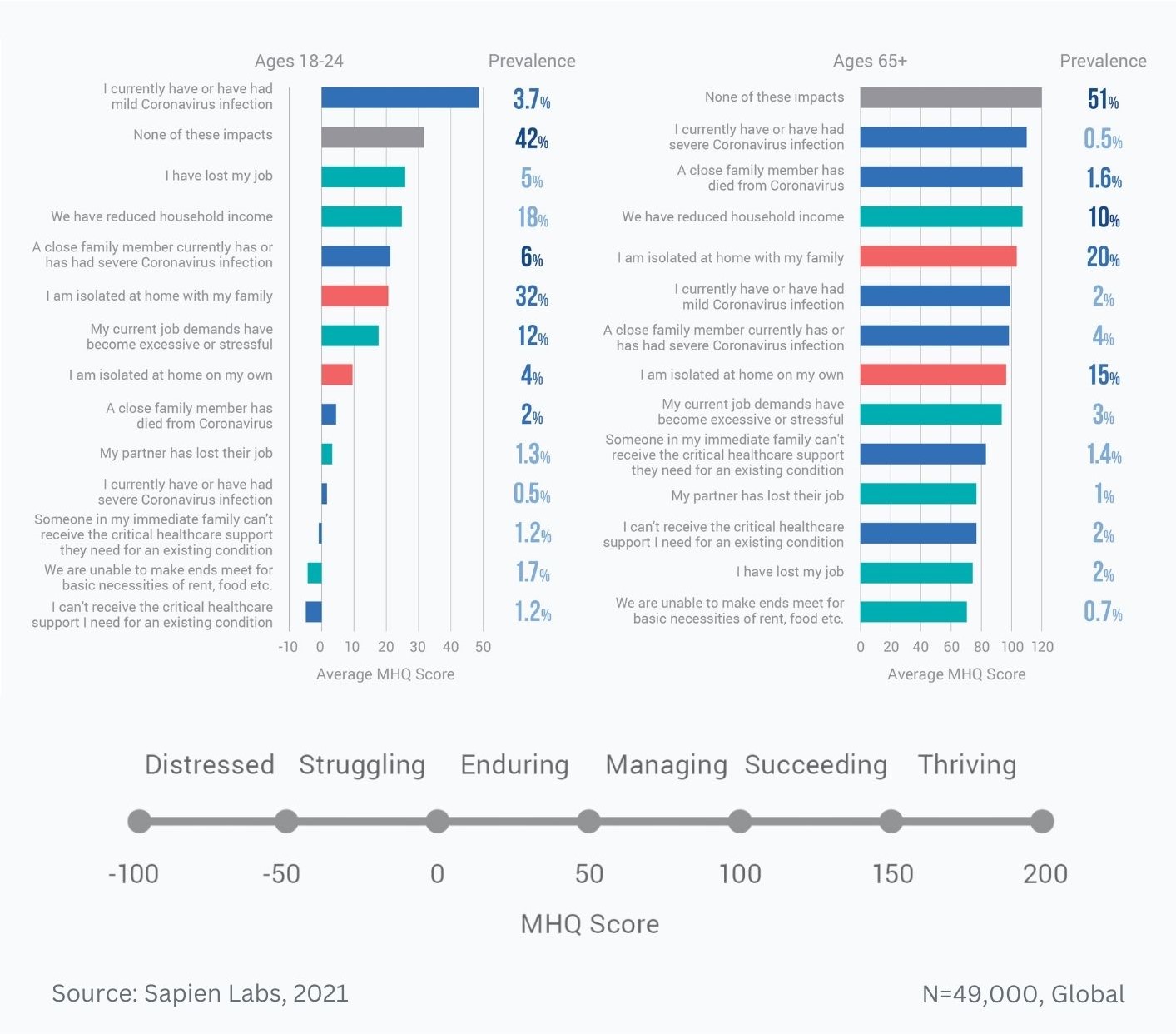
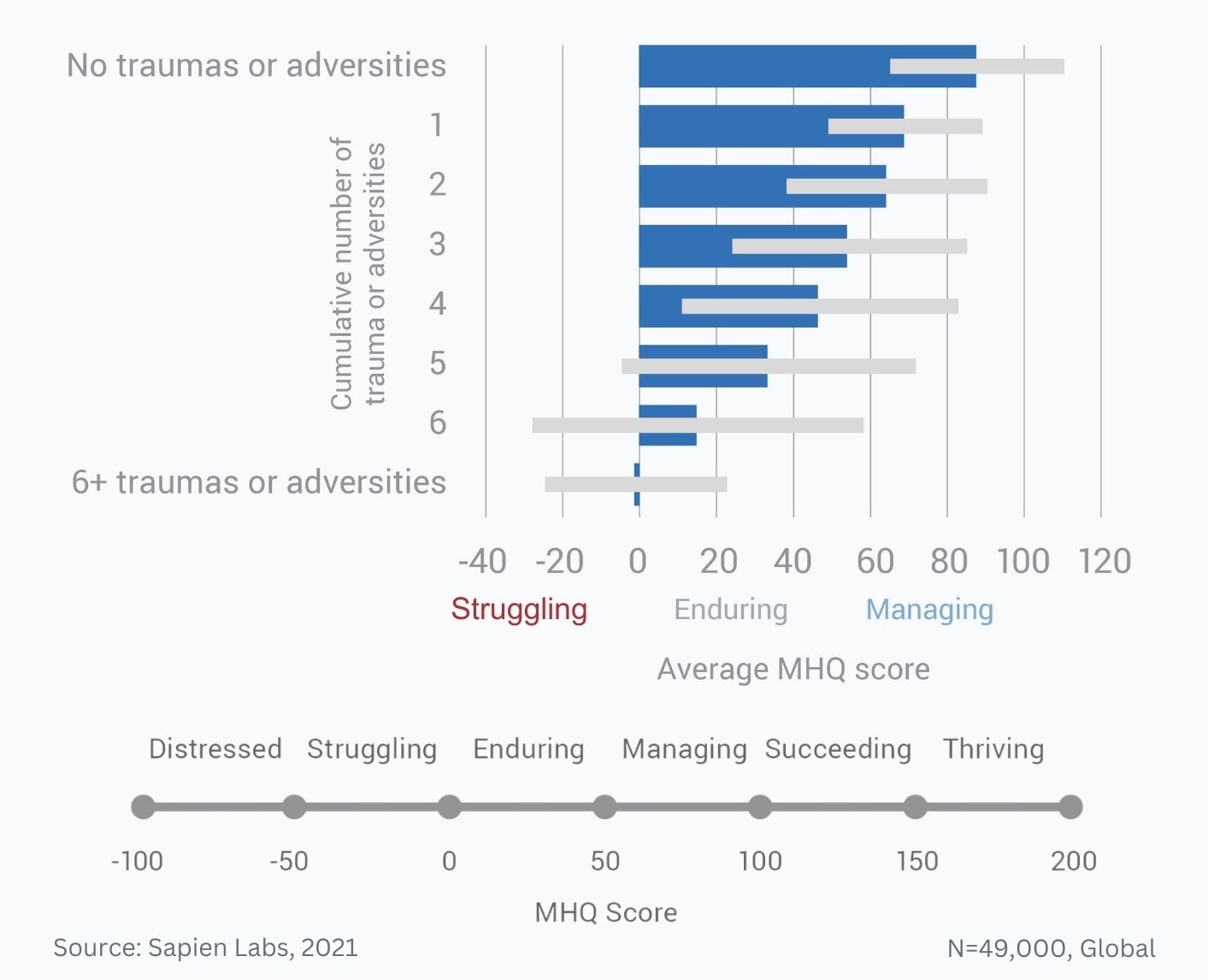
Data Gallery Tag: Mental Health Quotient
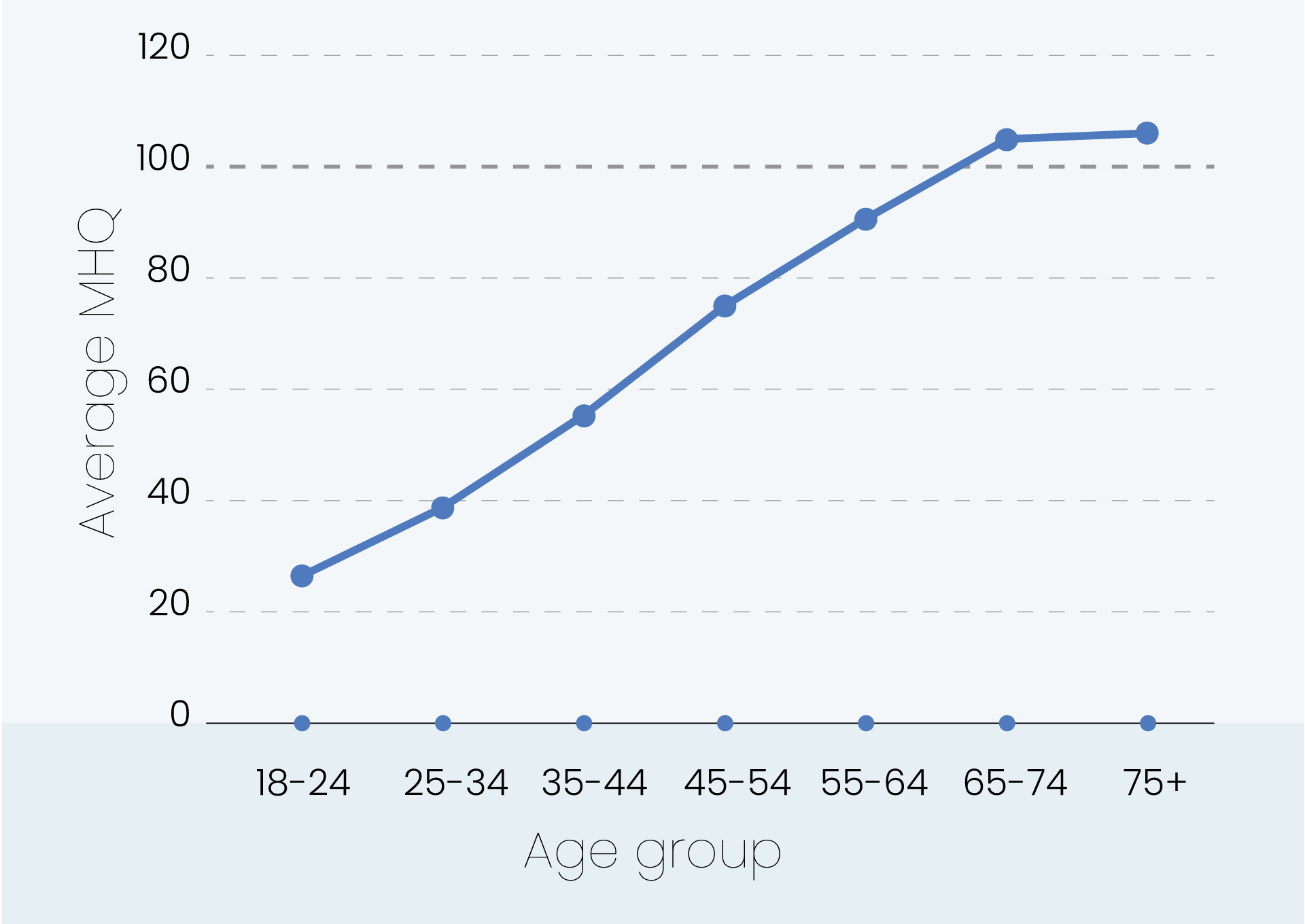
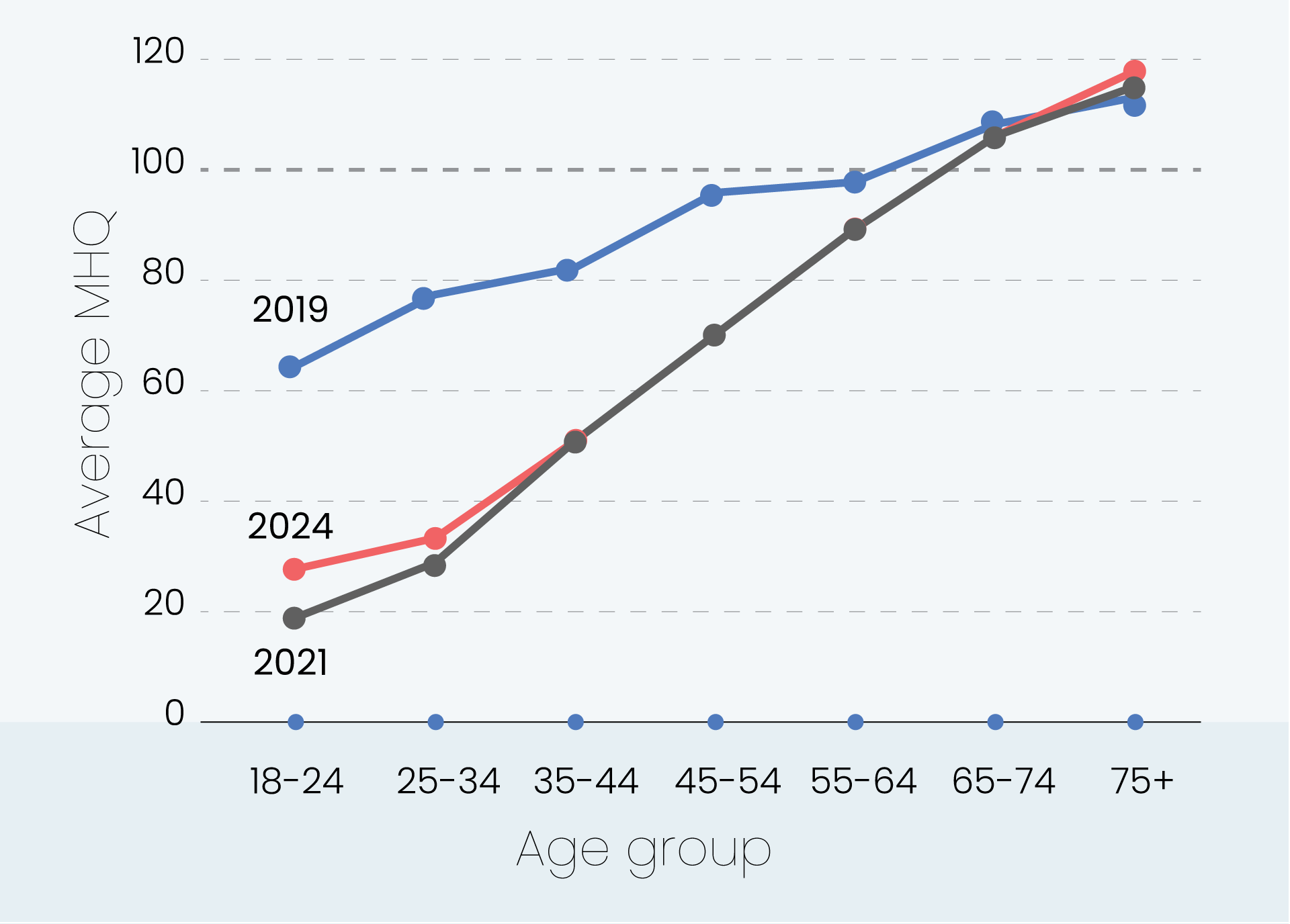
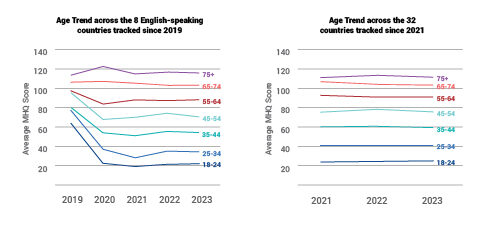
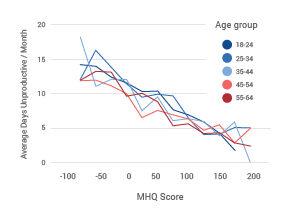
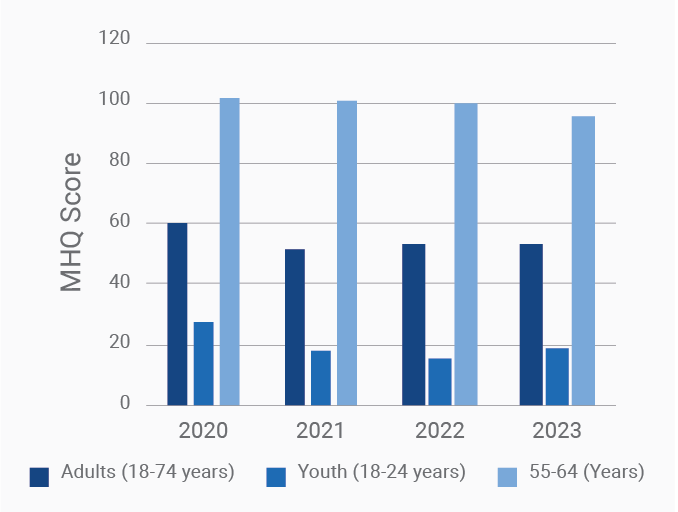
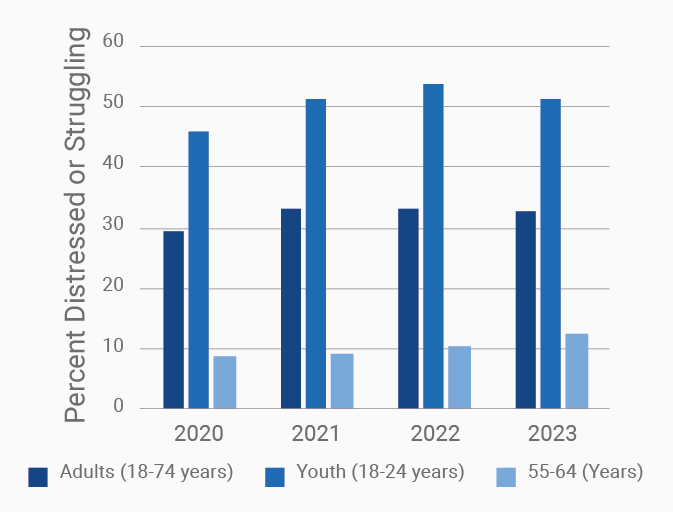
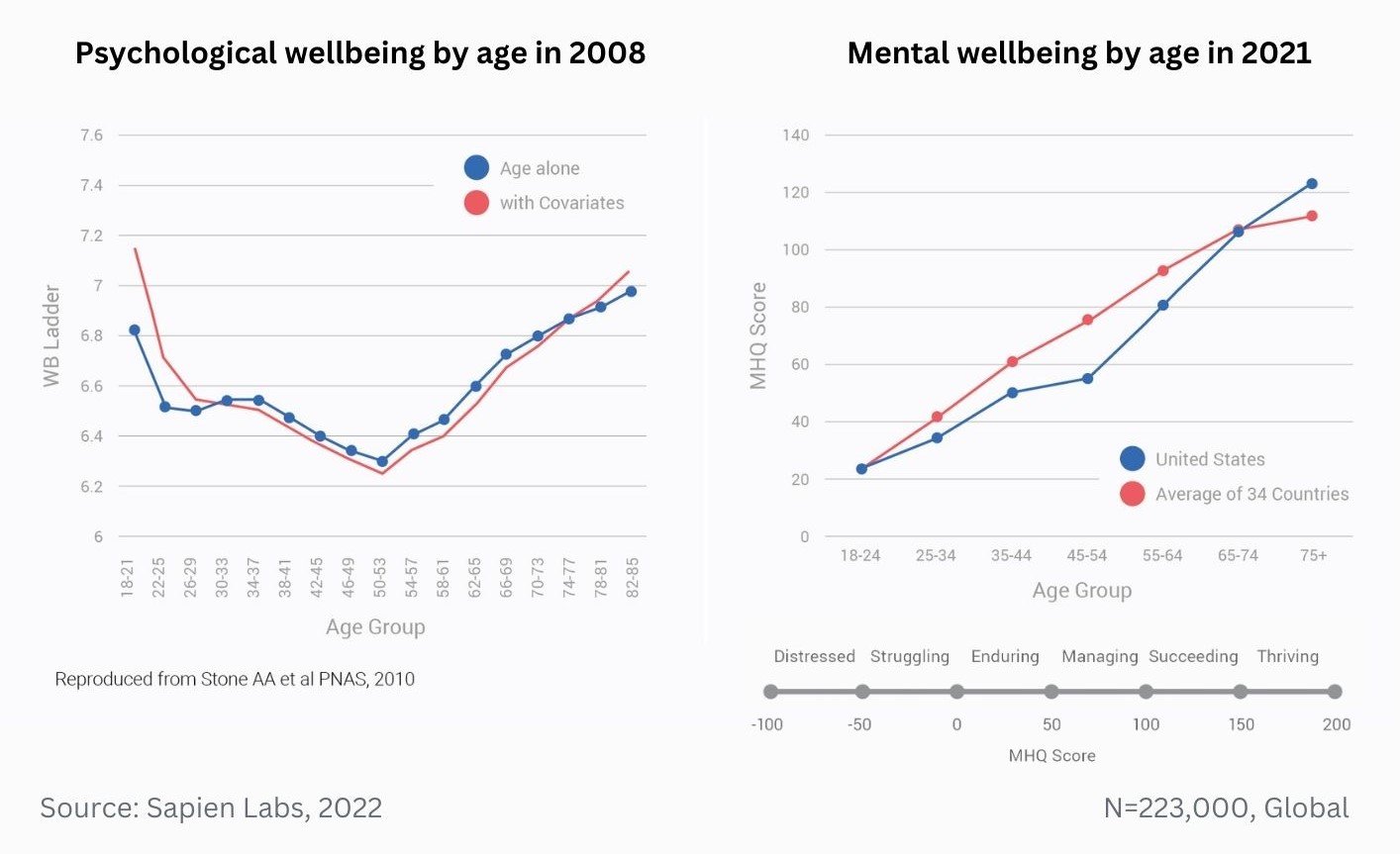
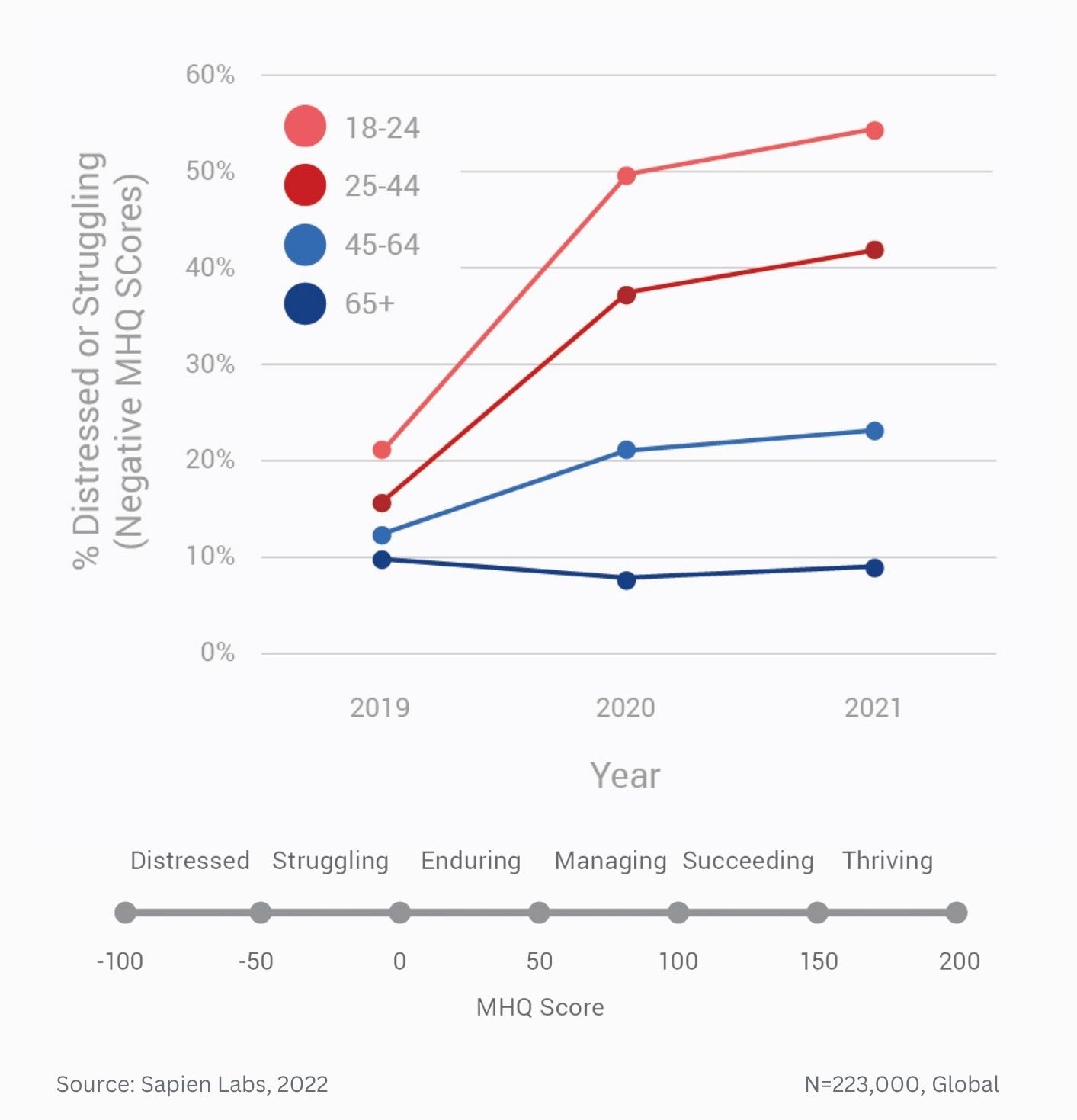
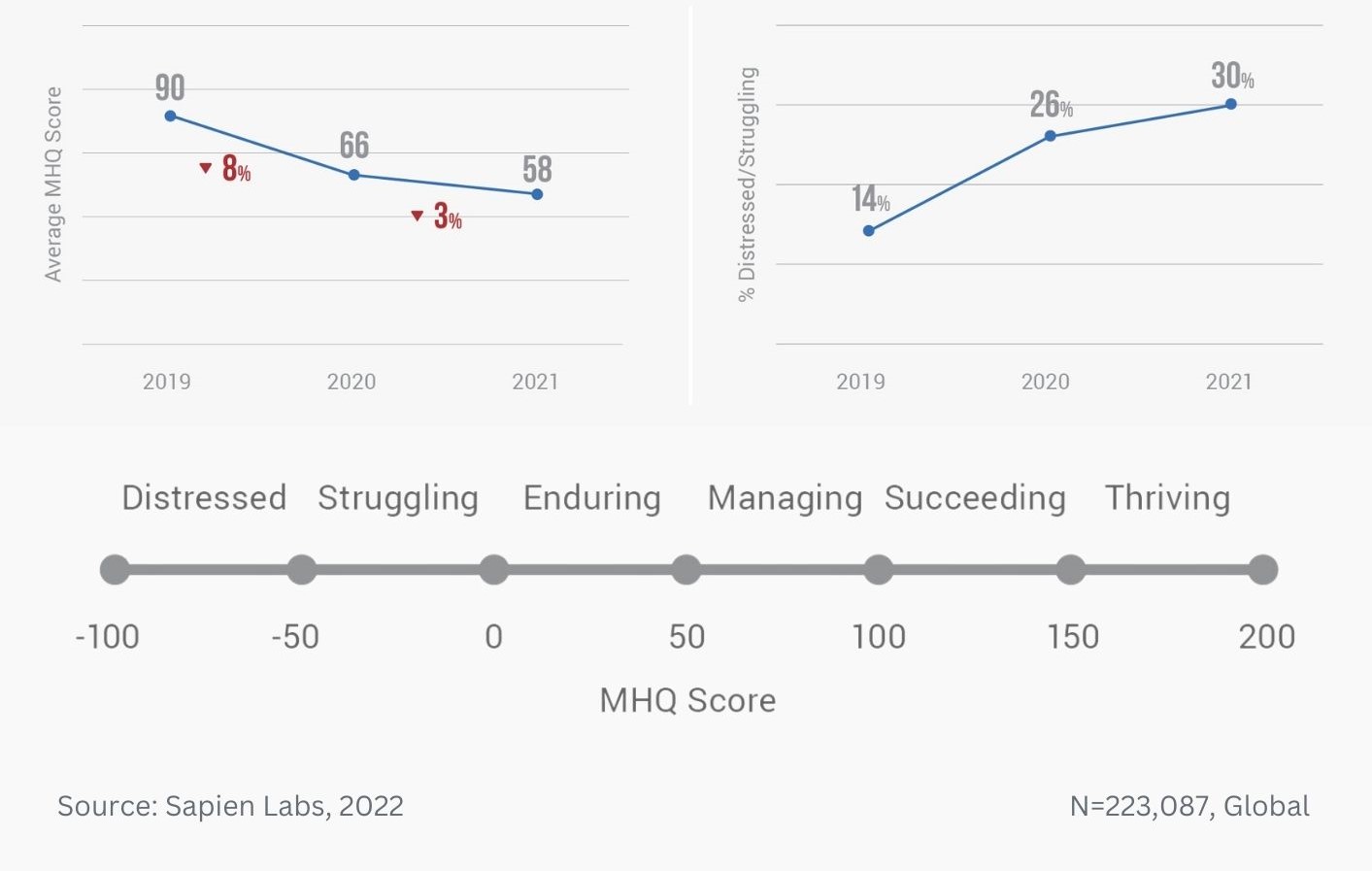
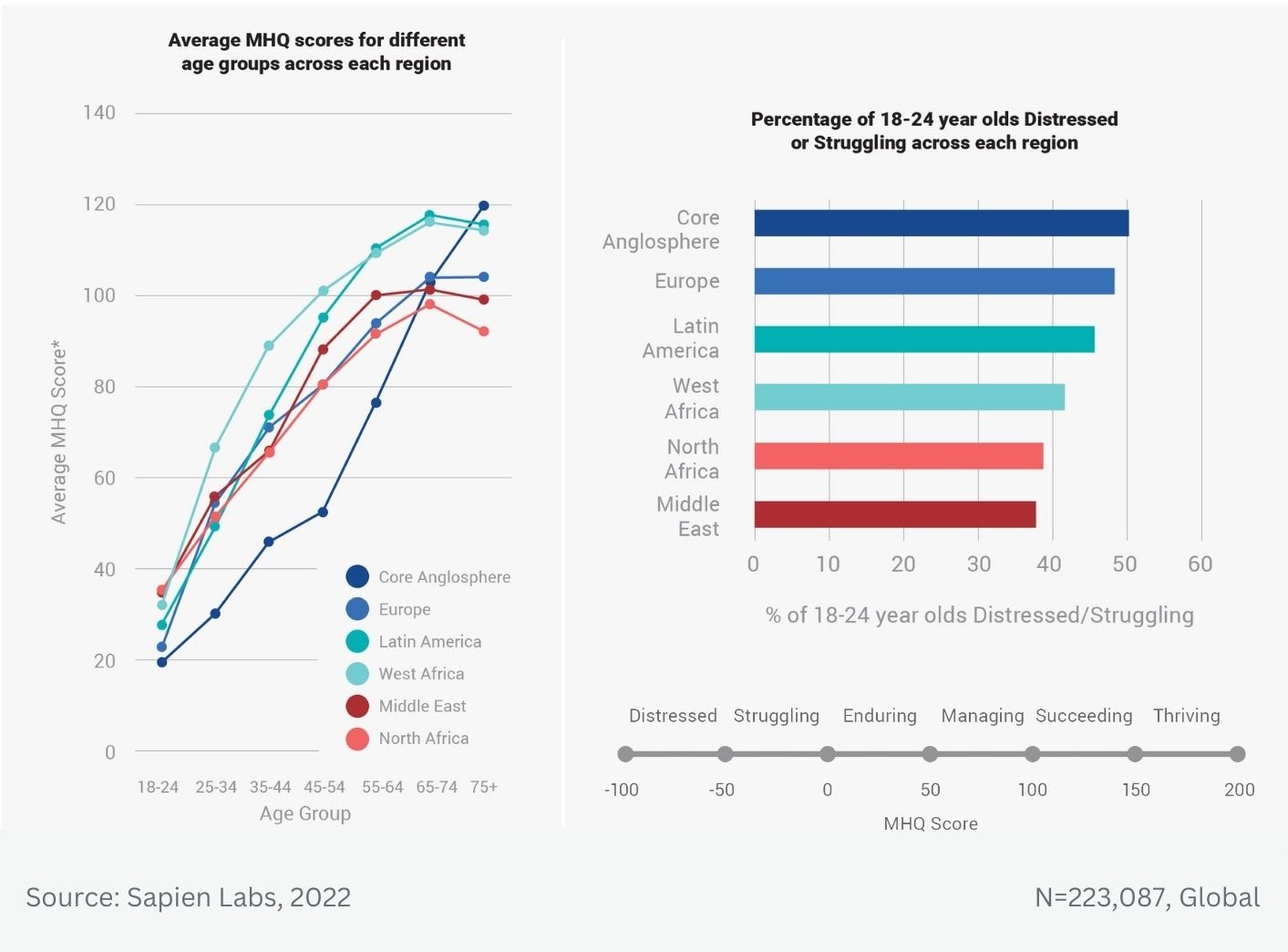
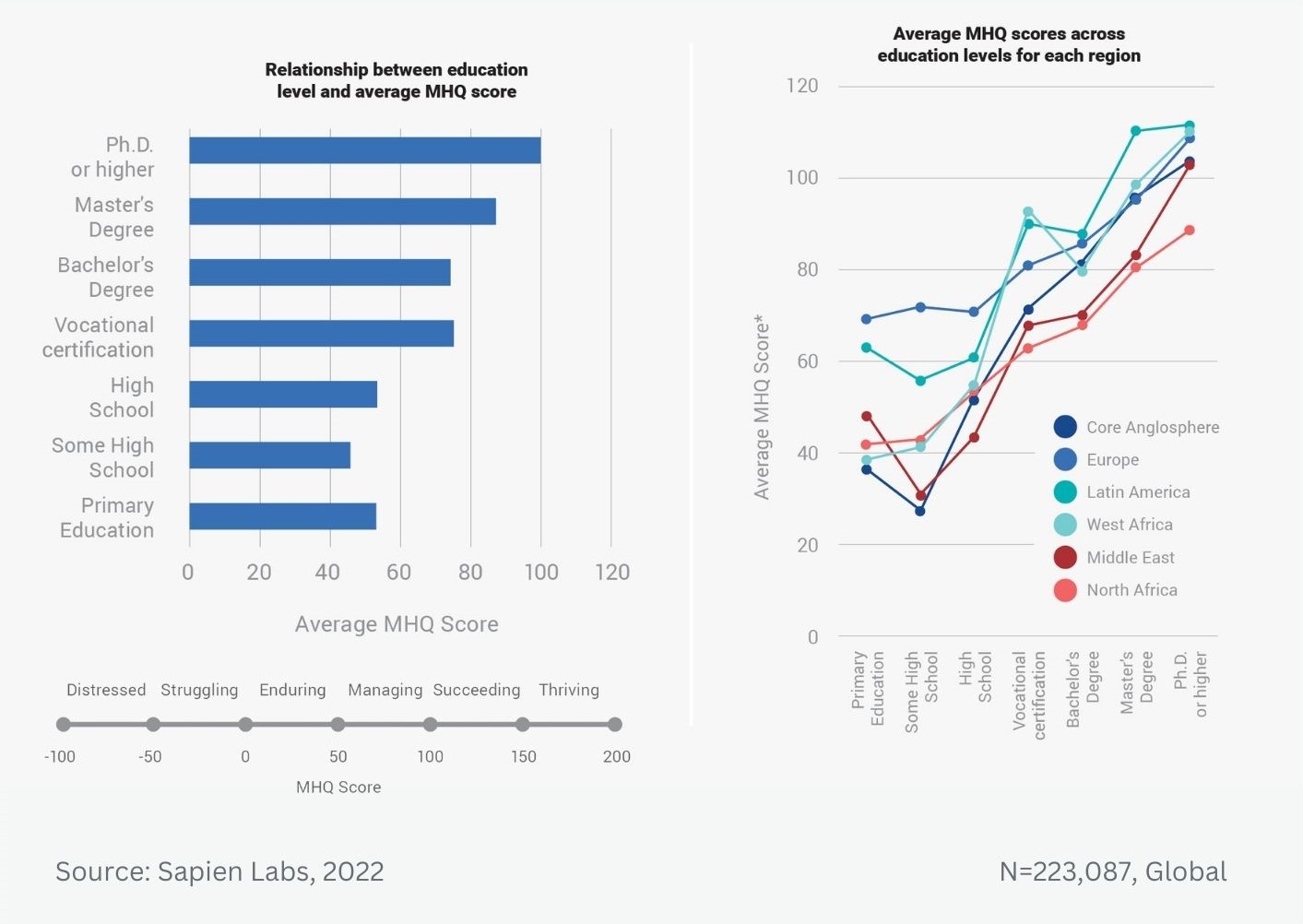
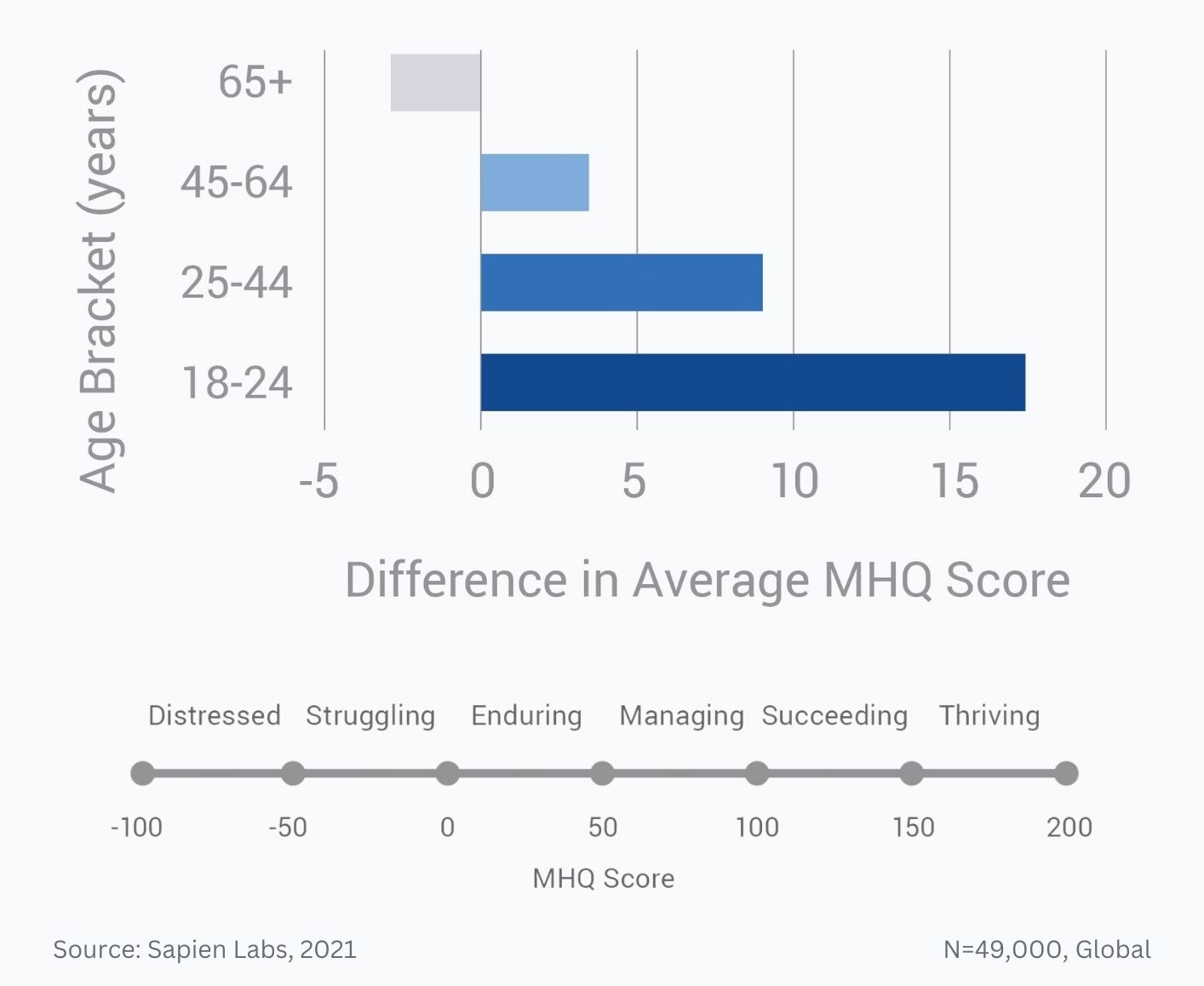
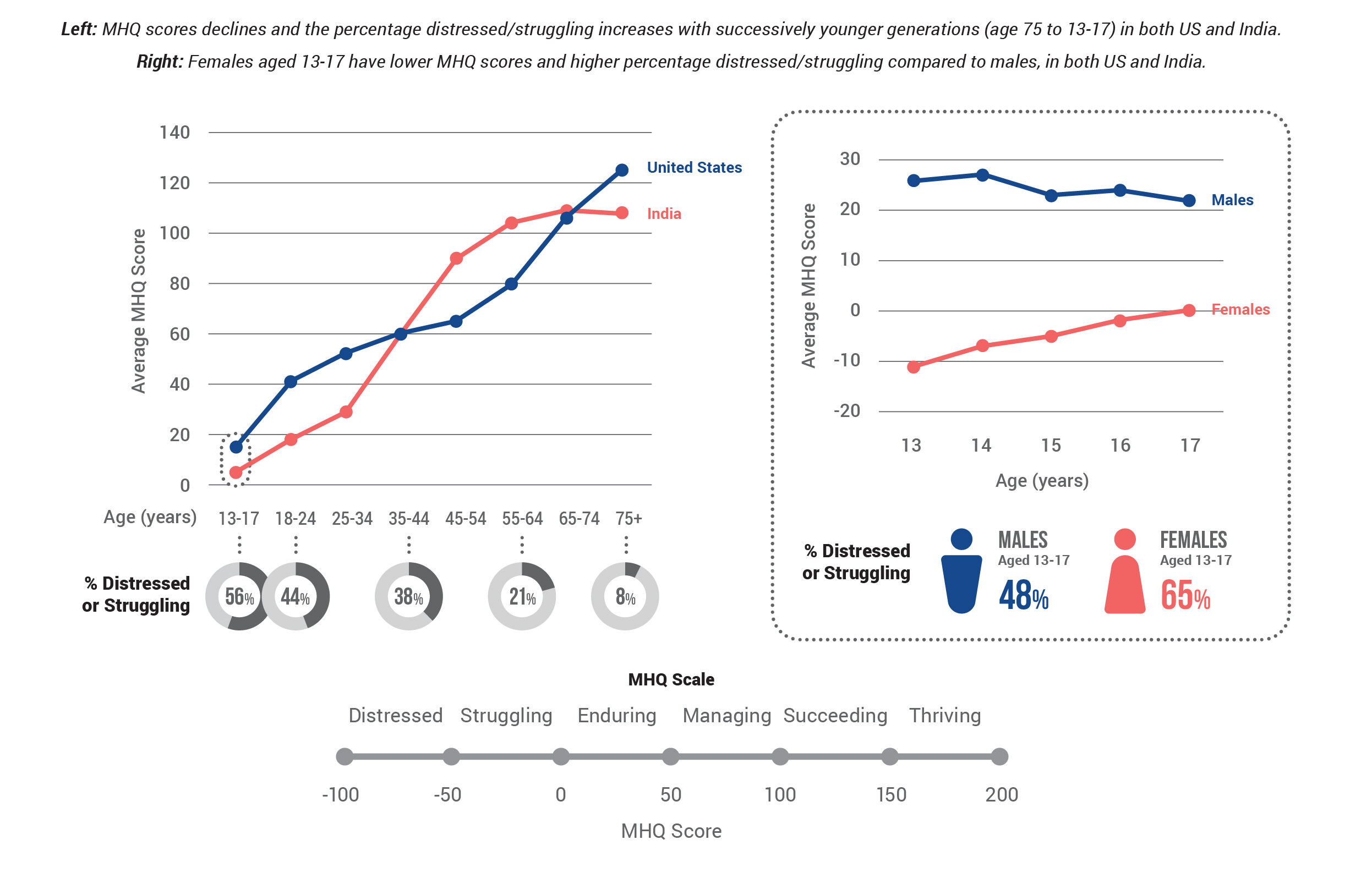
MHQ score declines and the percentage of distressed struggling increases with successively younger generations in both the US and India
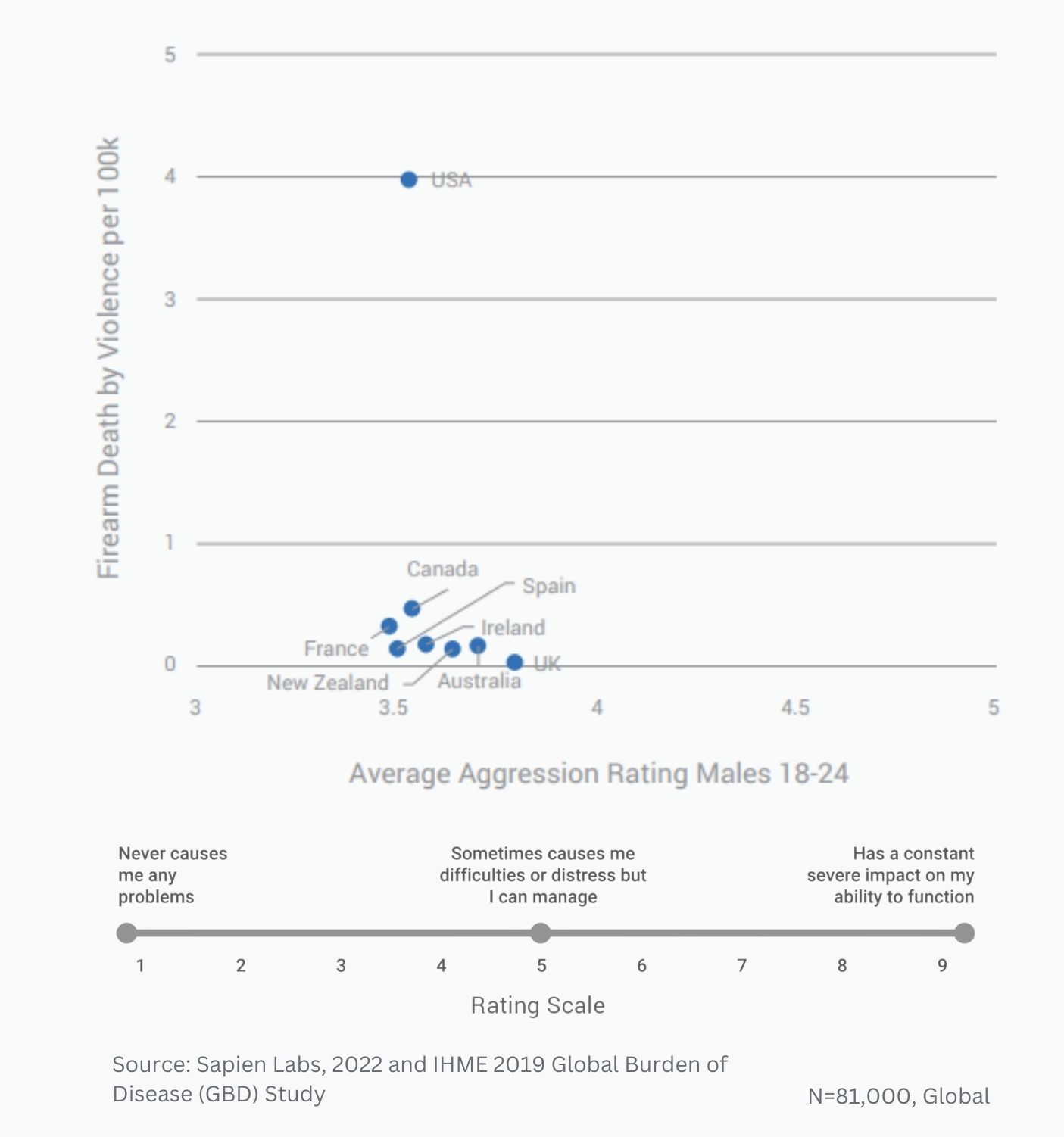
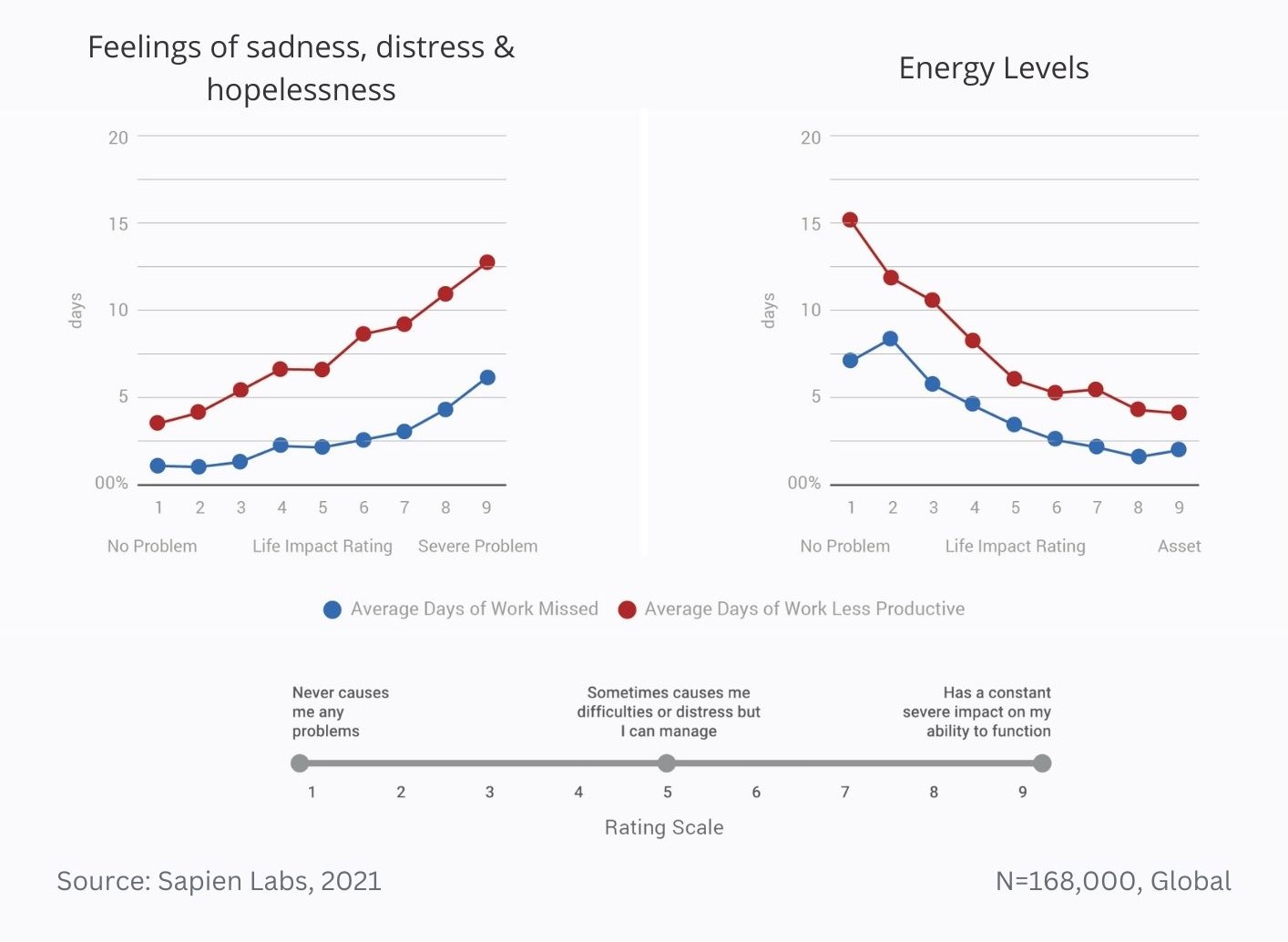
Percentage of 13-17 year olds who report problems with aggression, anger & irritability, and hallucinations in comparison to age of first smartphone

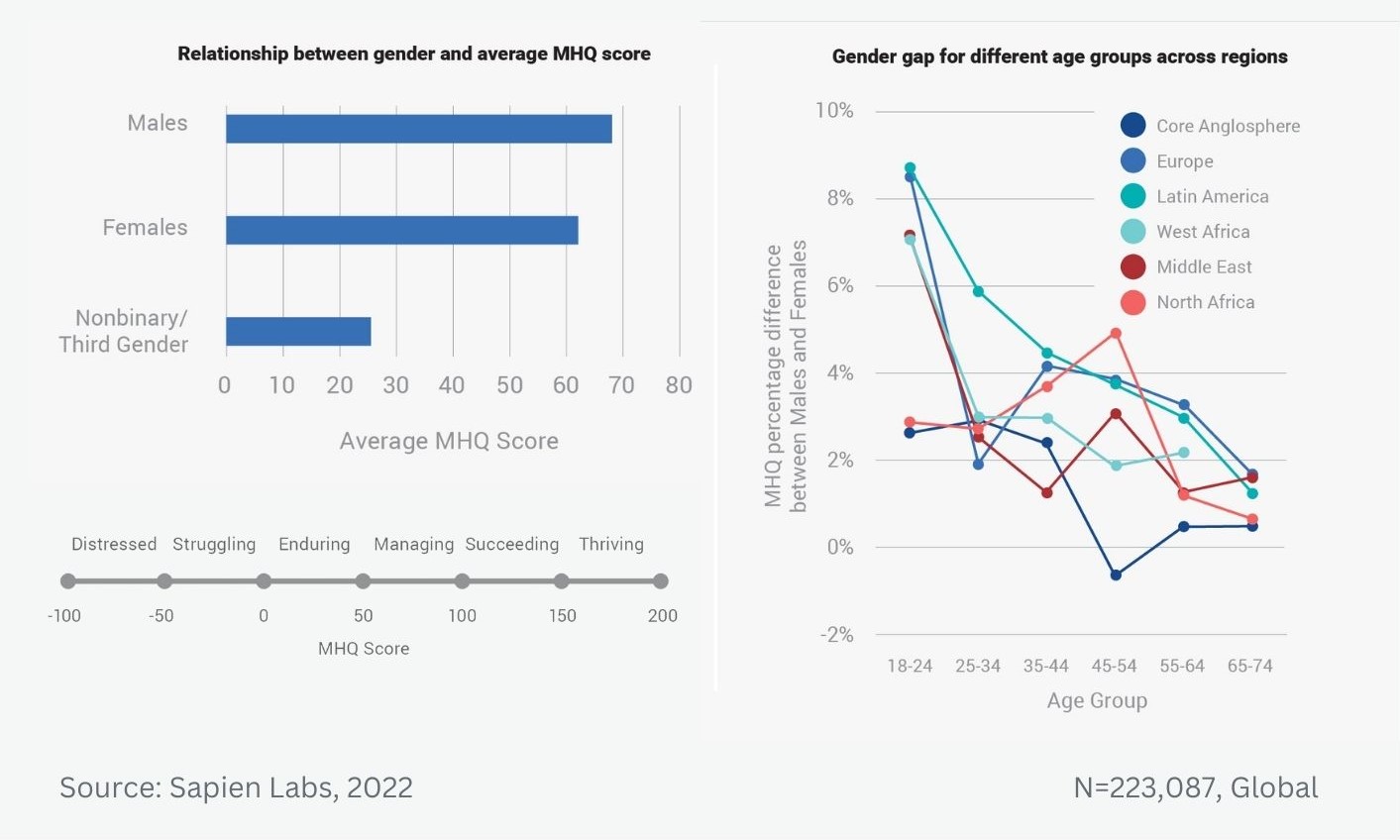
Age trend for males and females in India and the US for the 3 items shown to have the biggest difference between 13 and 17 year olds

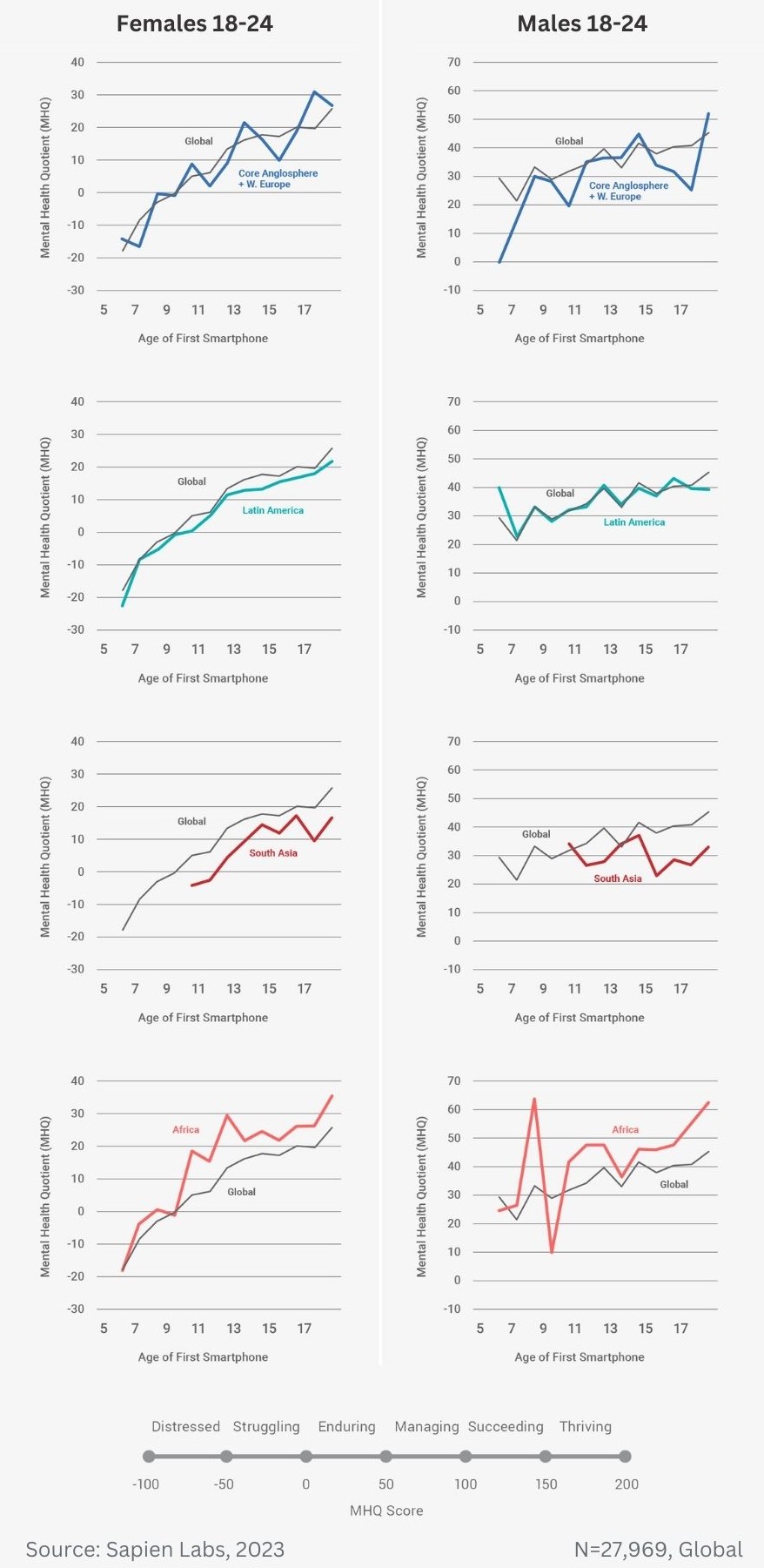
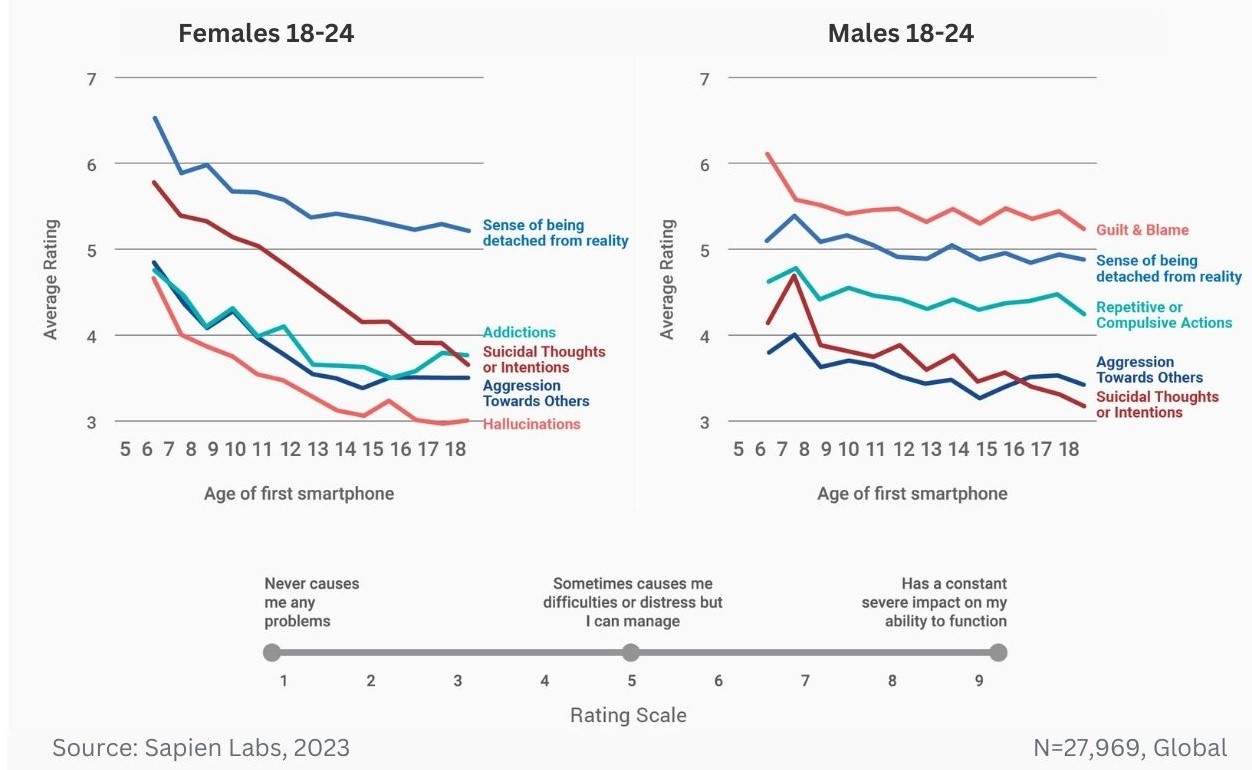
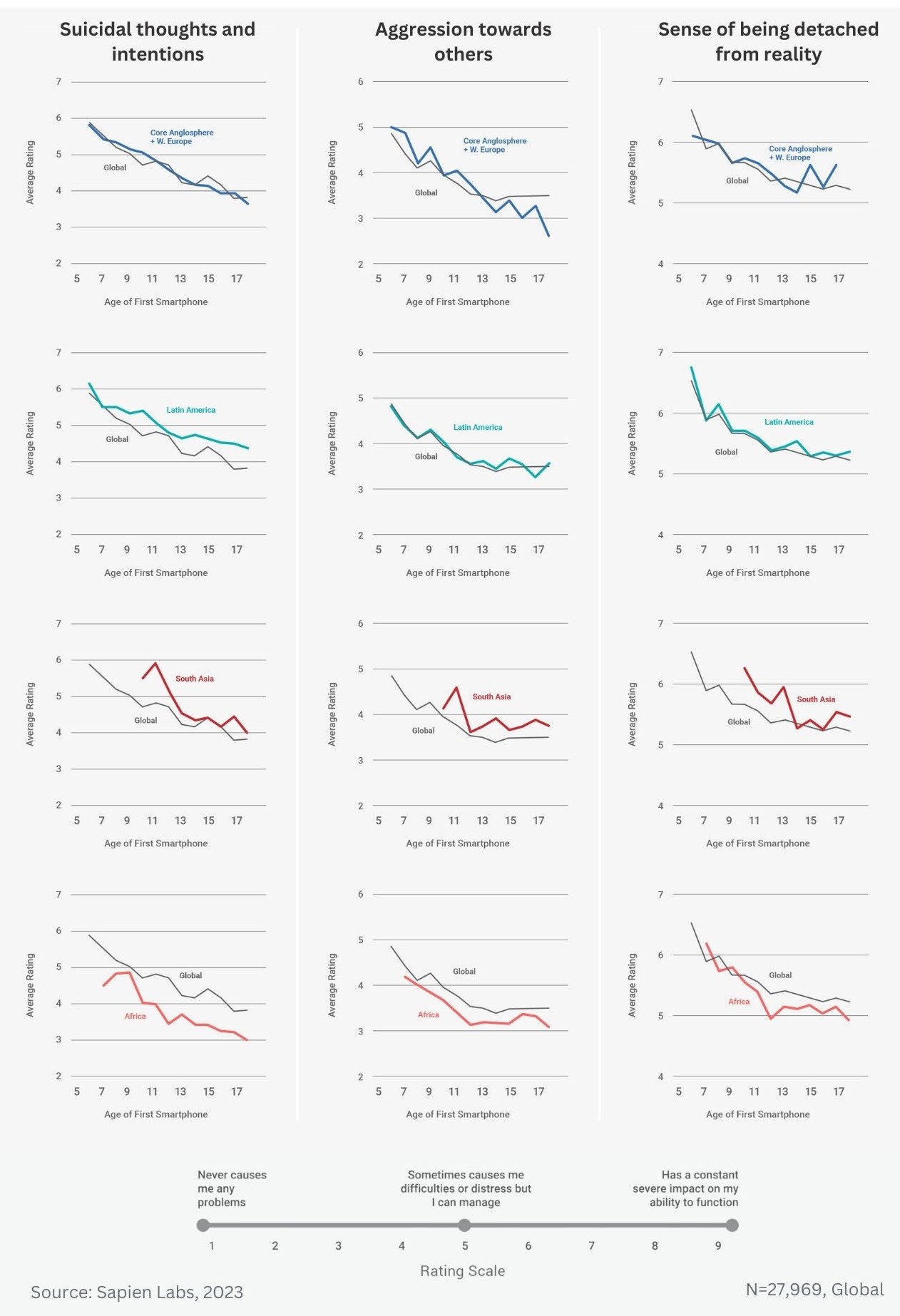
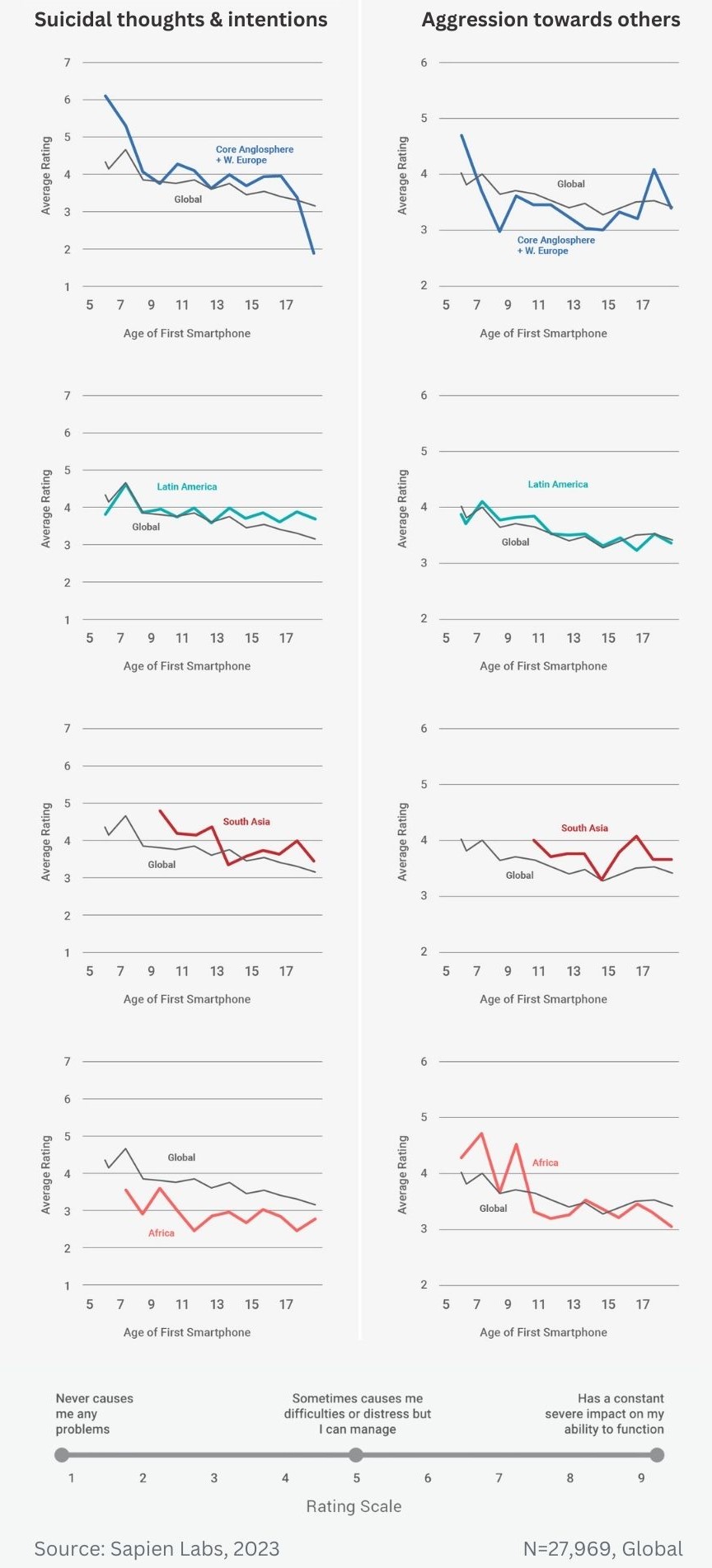
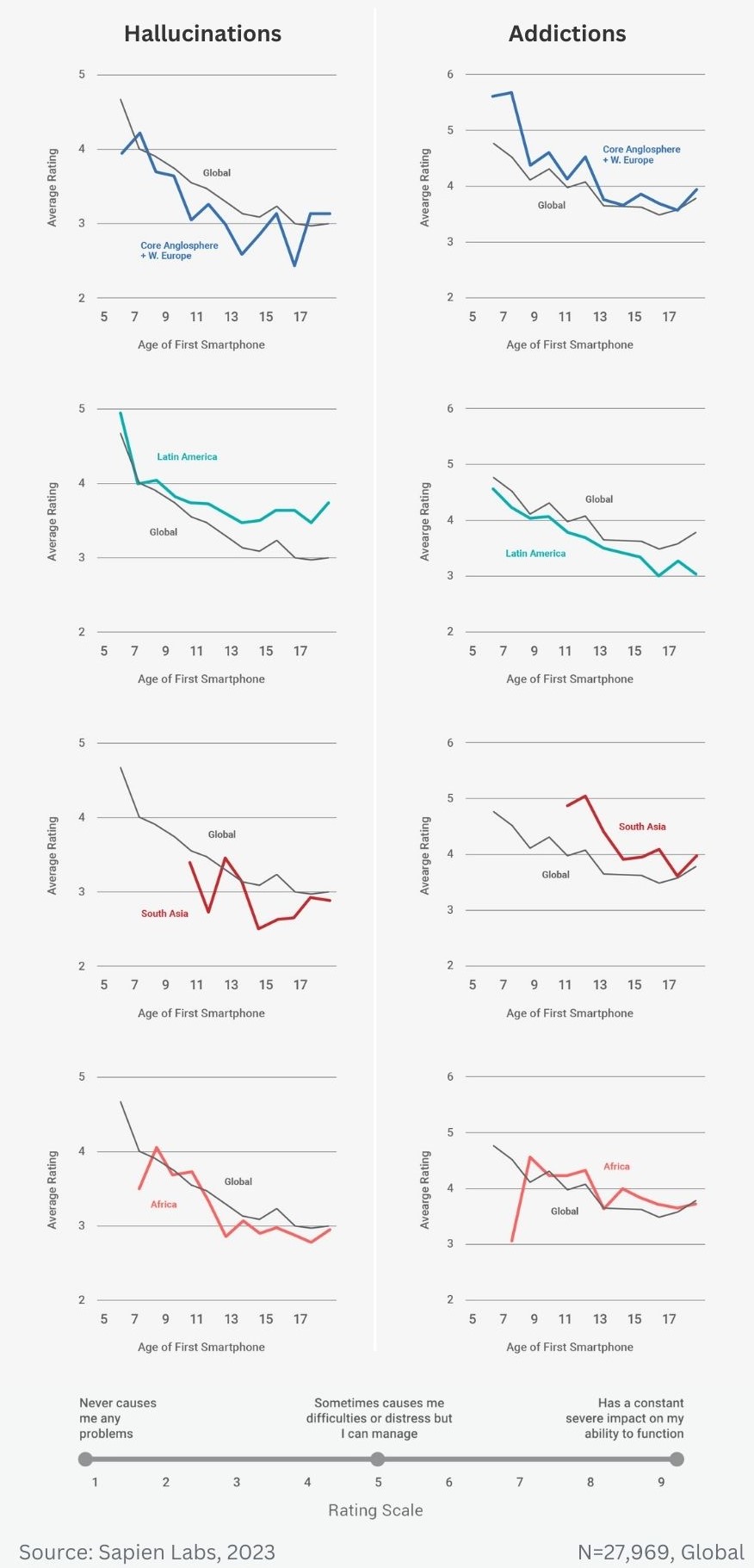
Regional ratings of mental health problems by age of first smartphone ownership in females aged 18-24
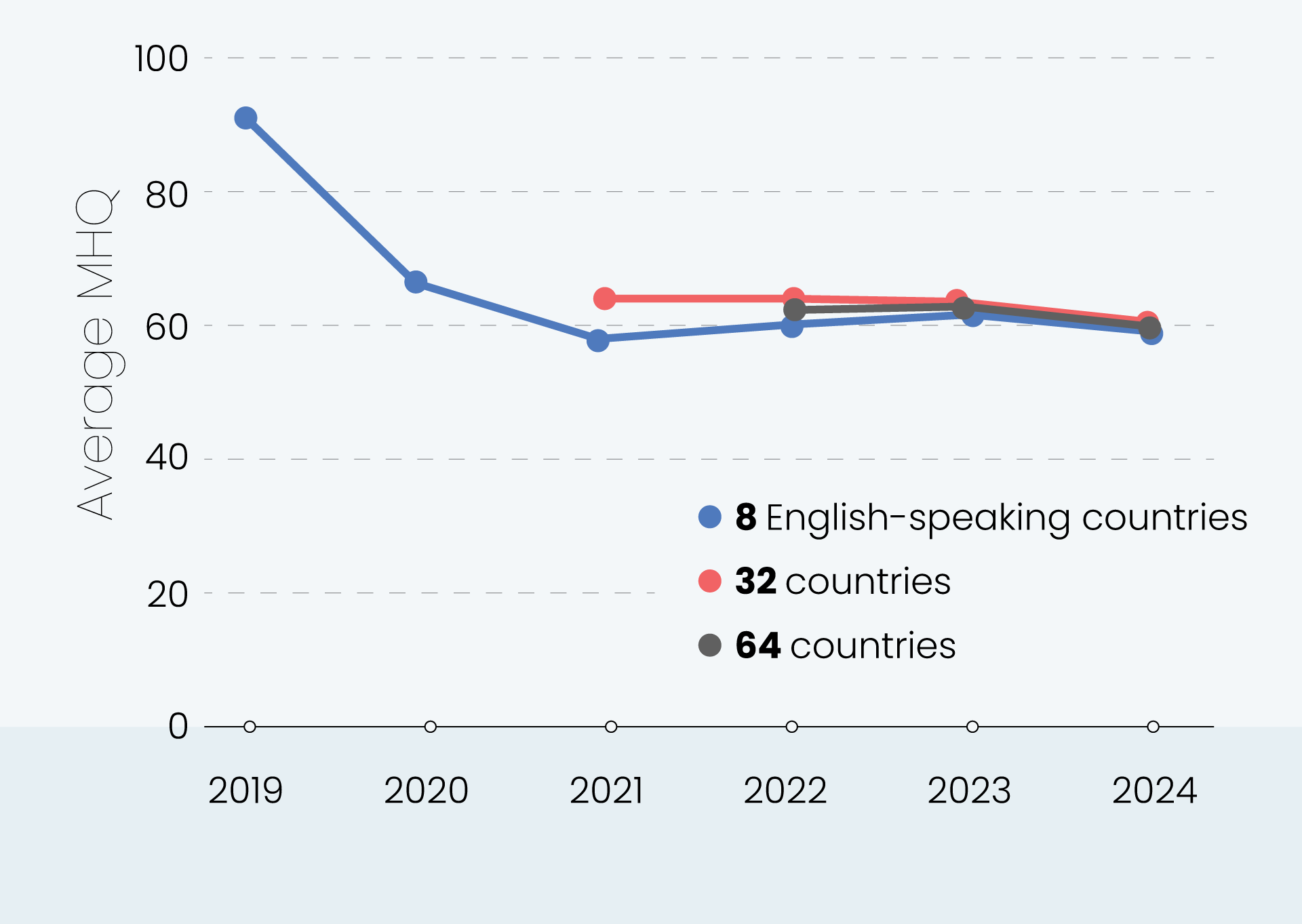
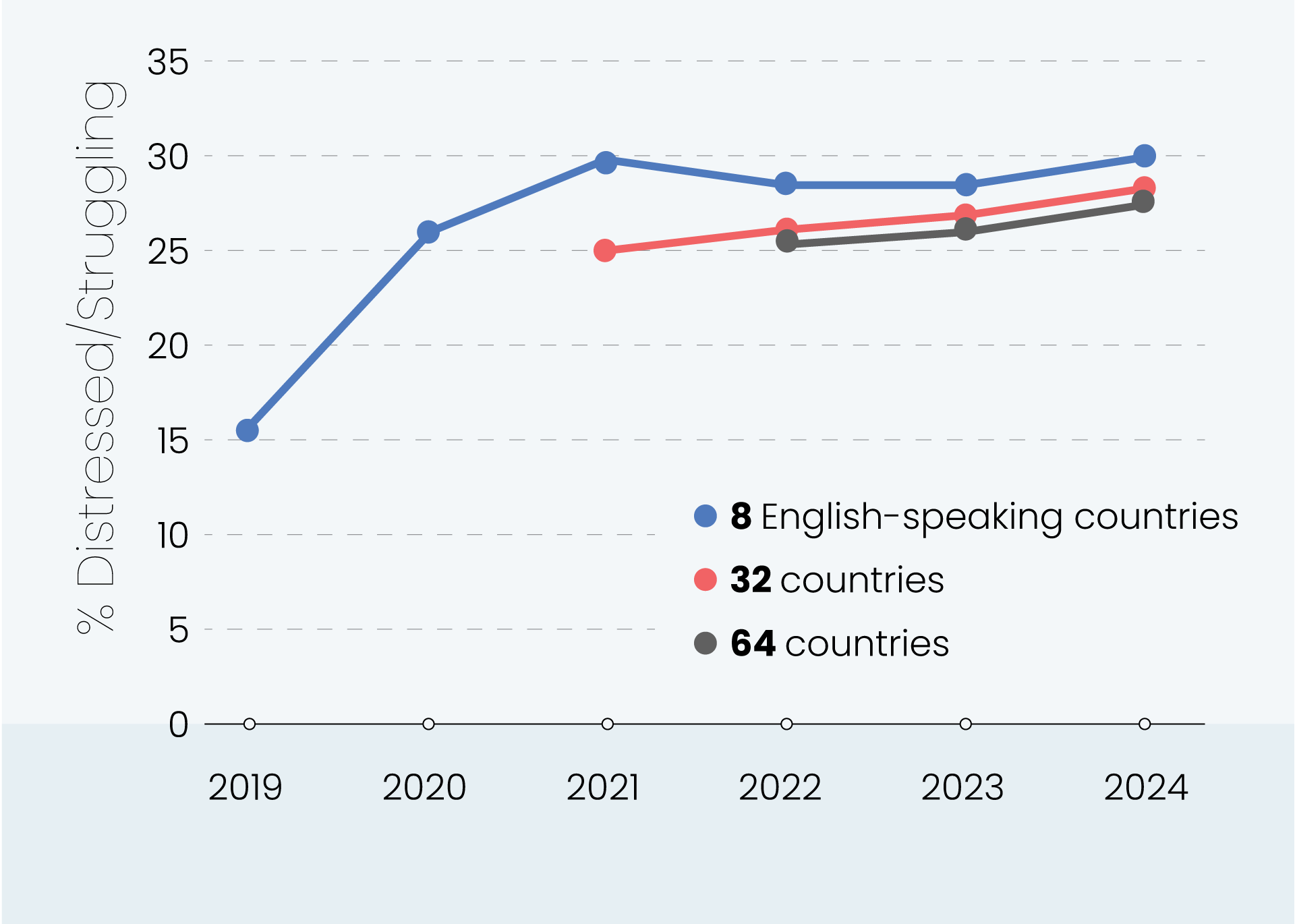
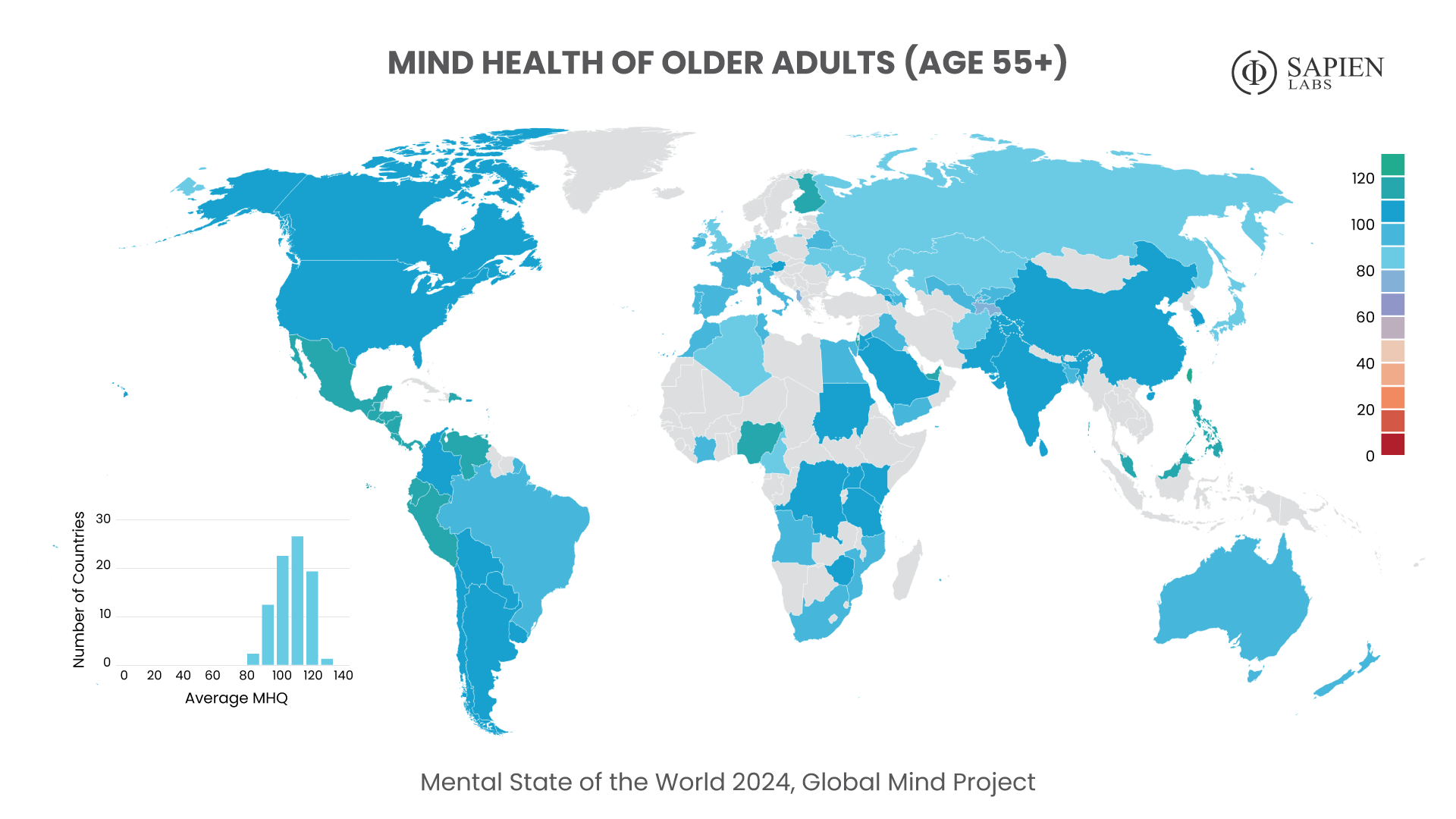
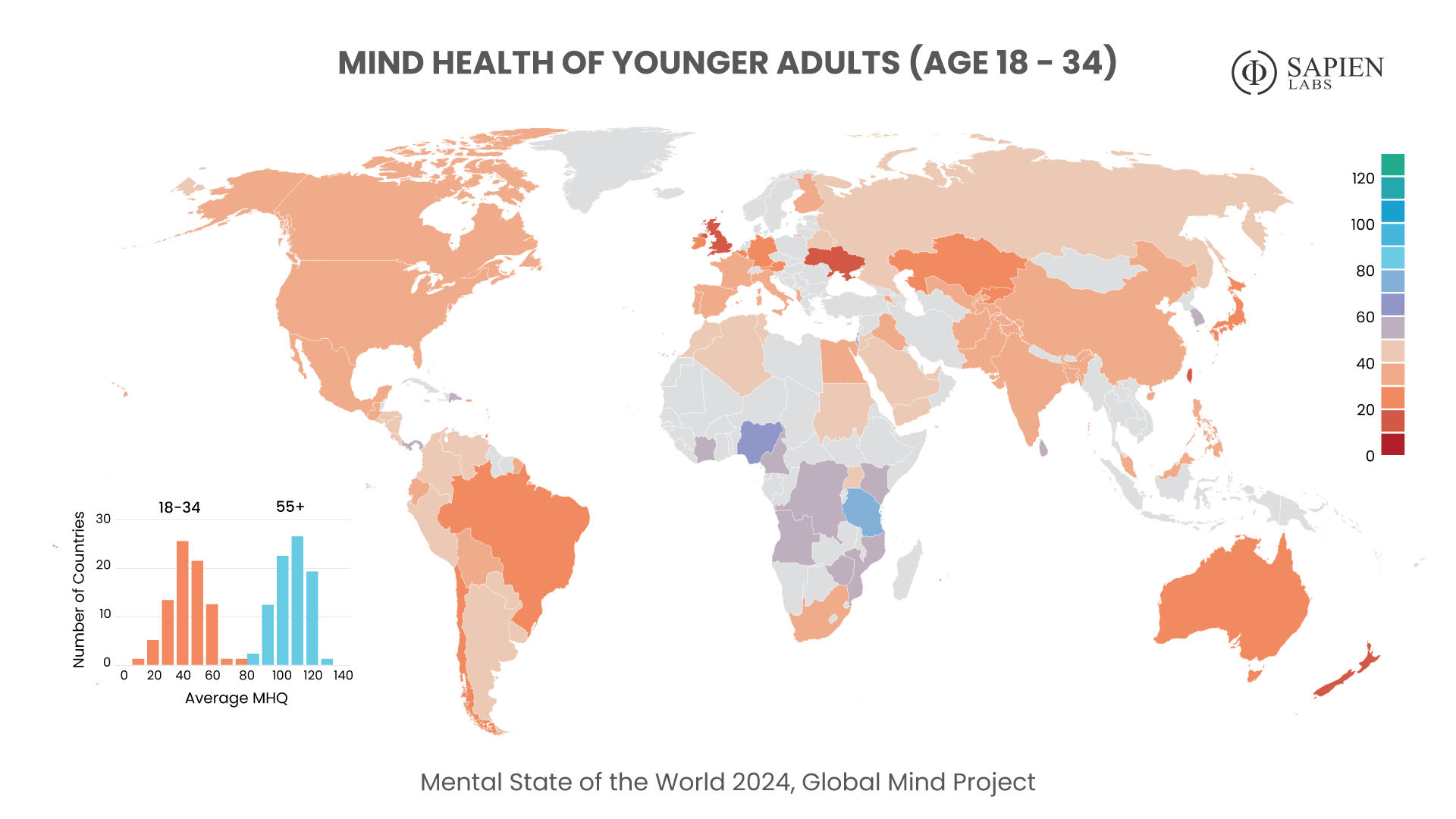
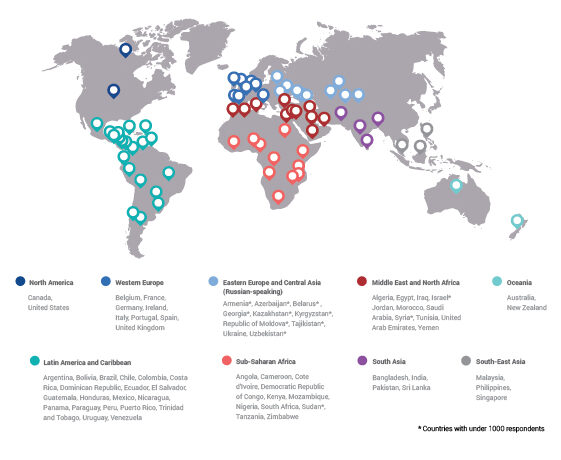
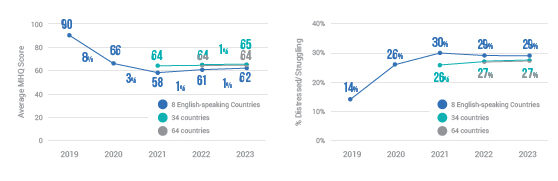
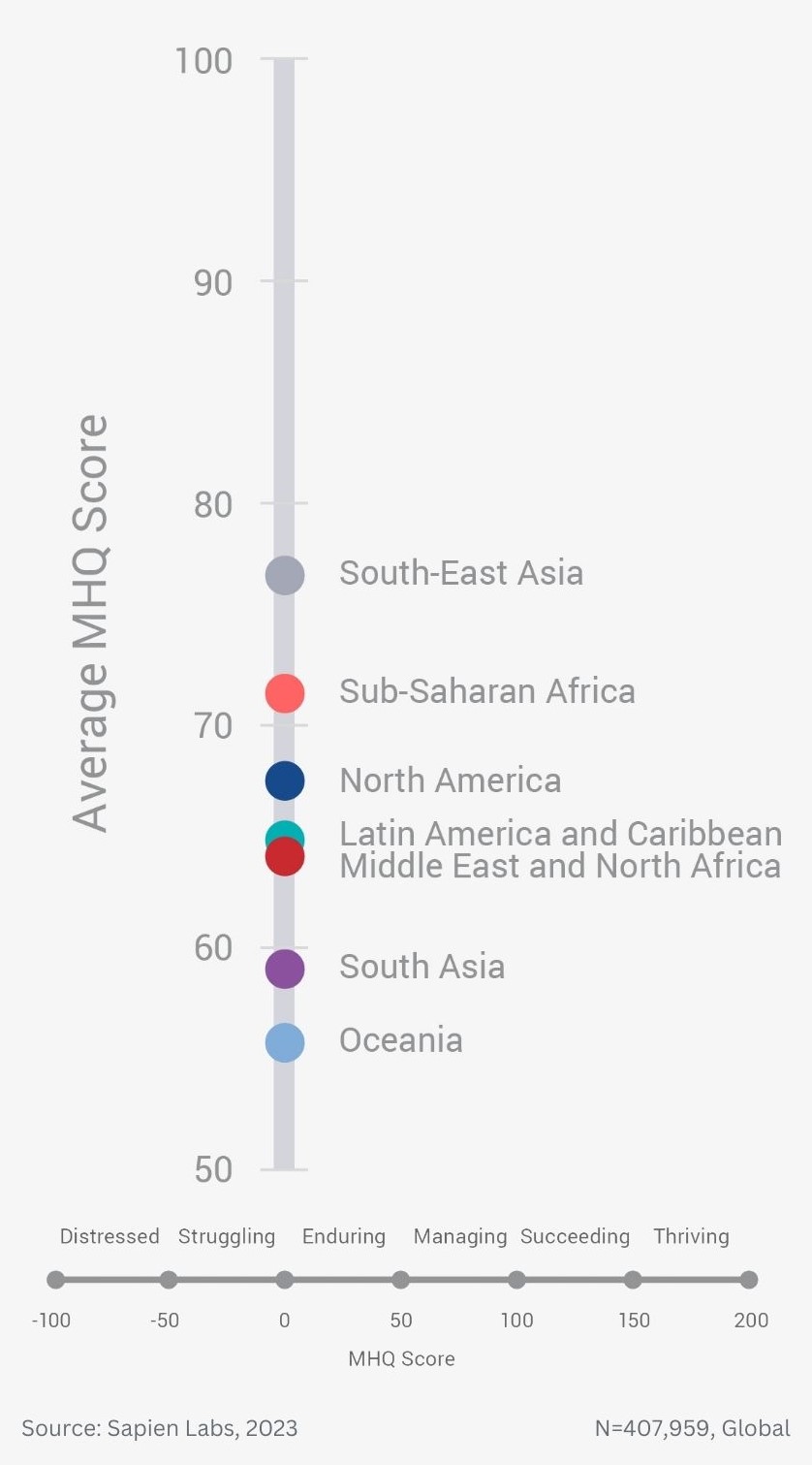
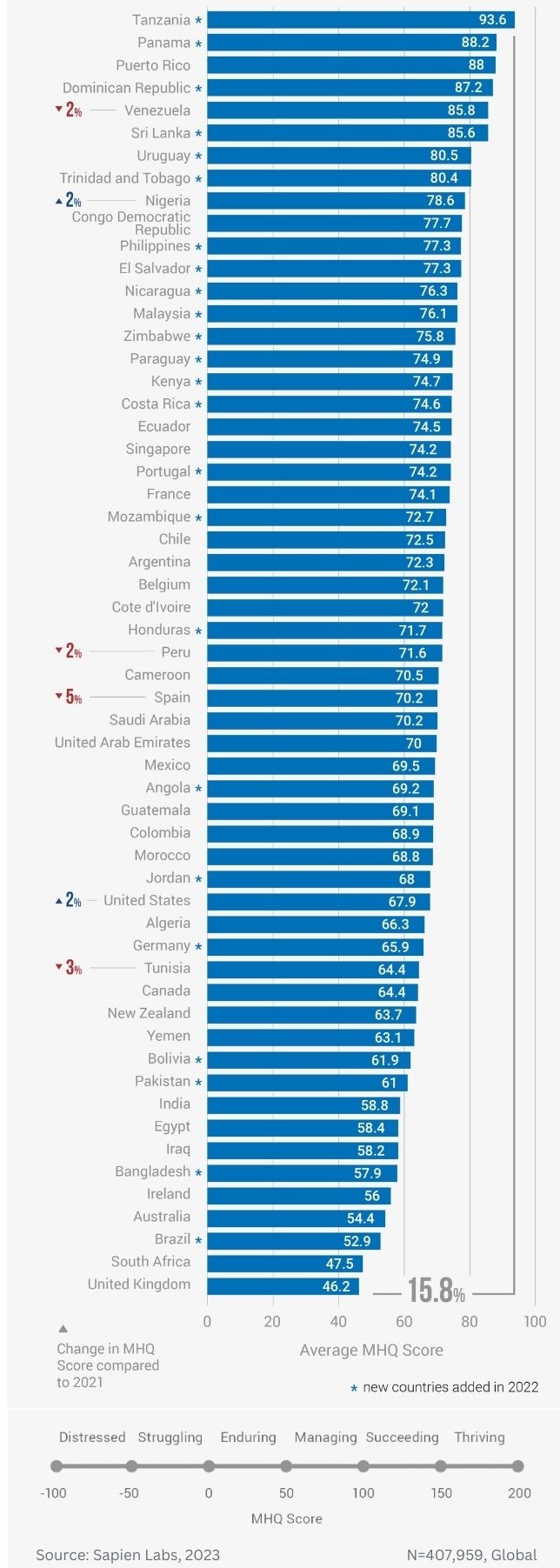
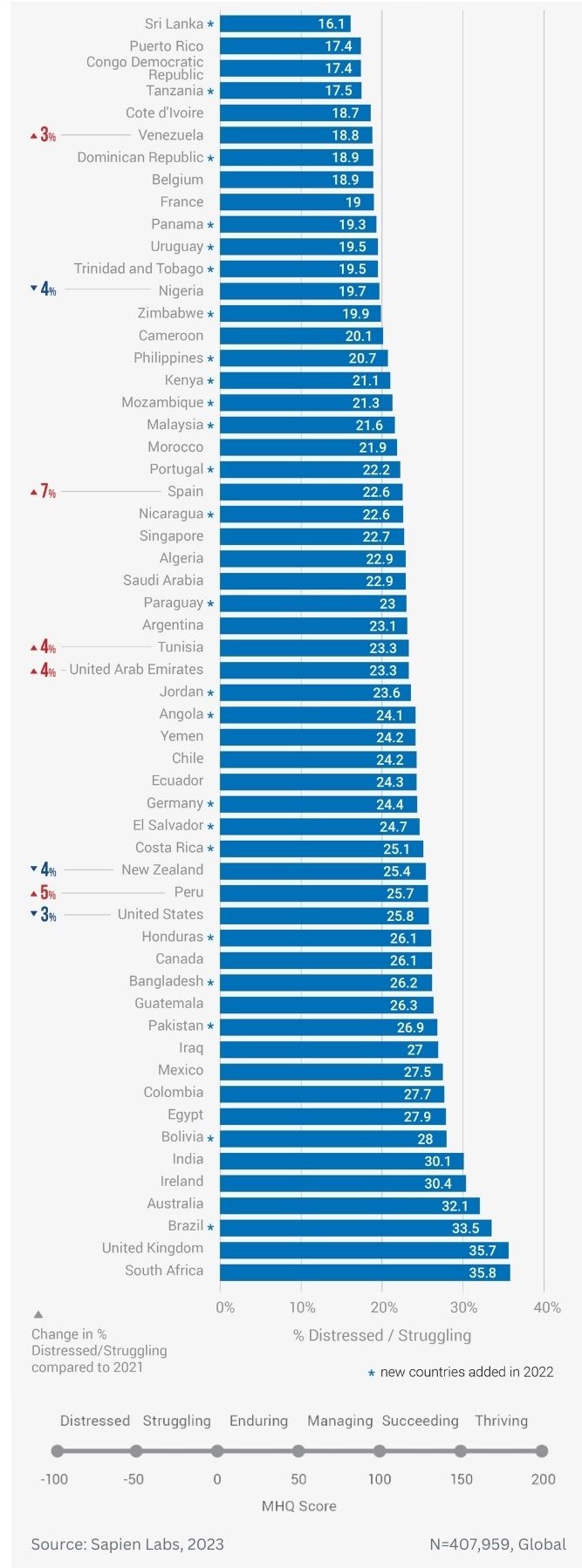
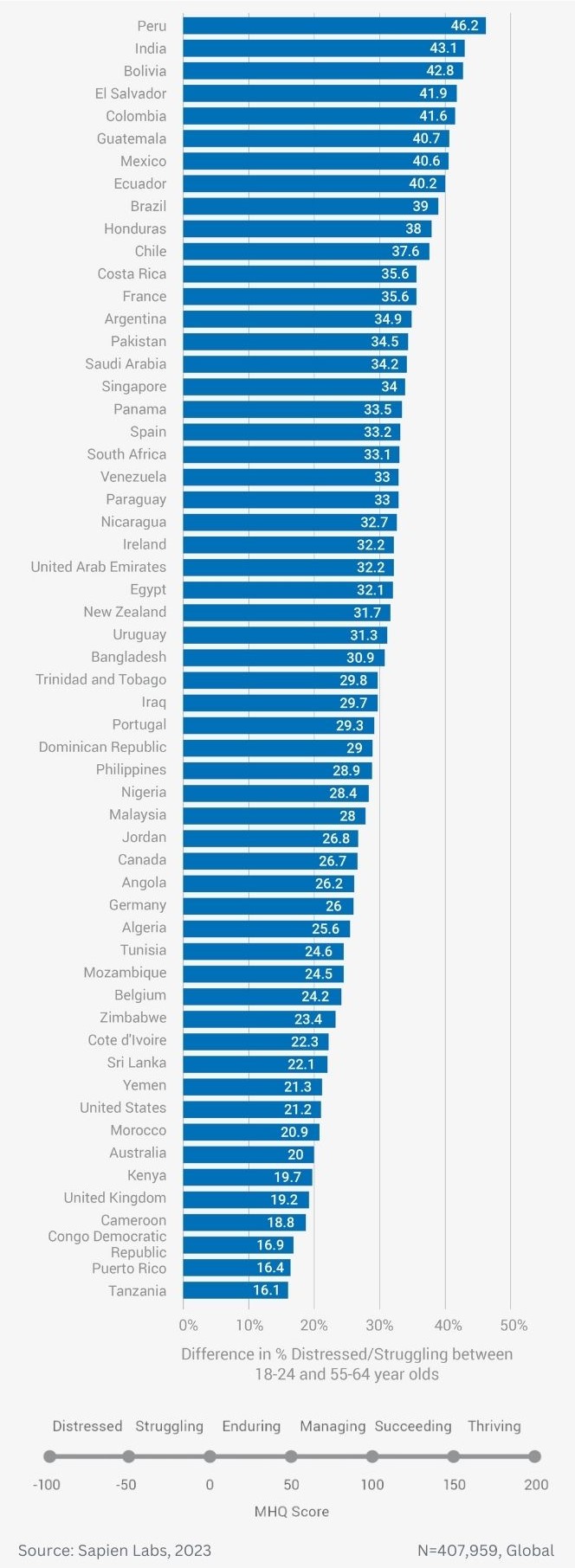
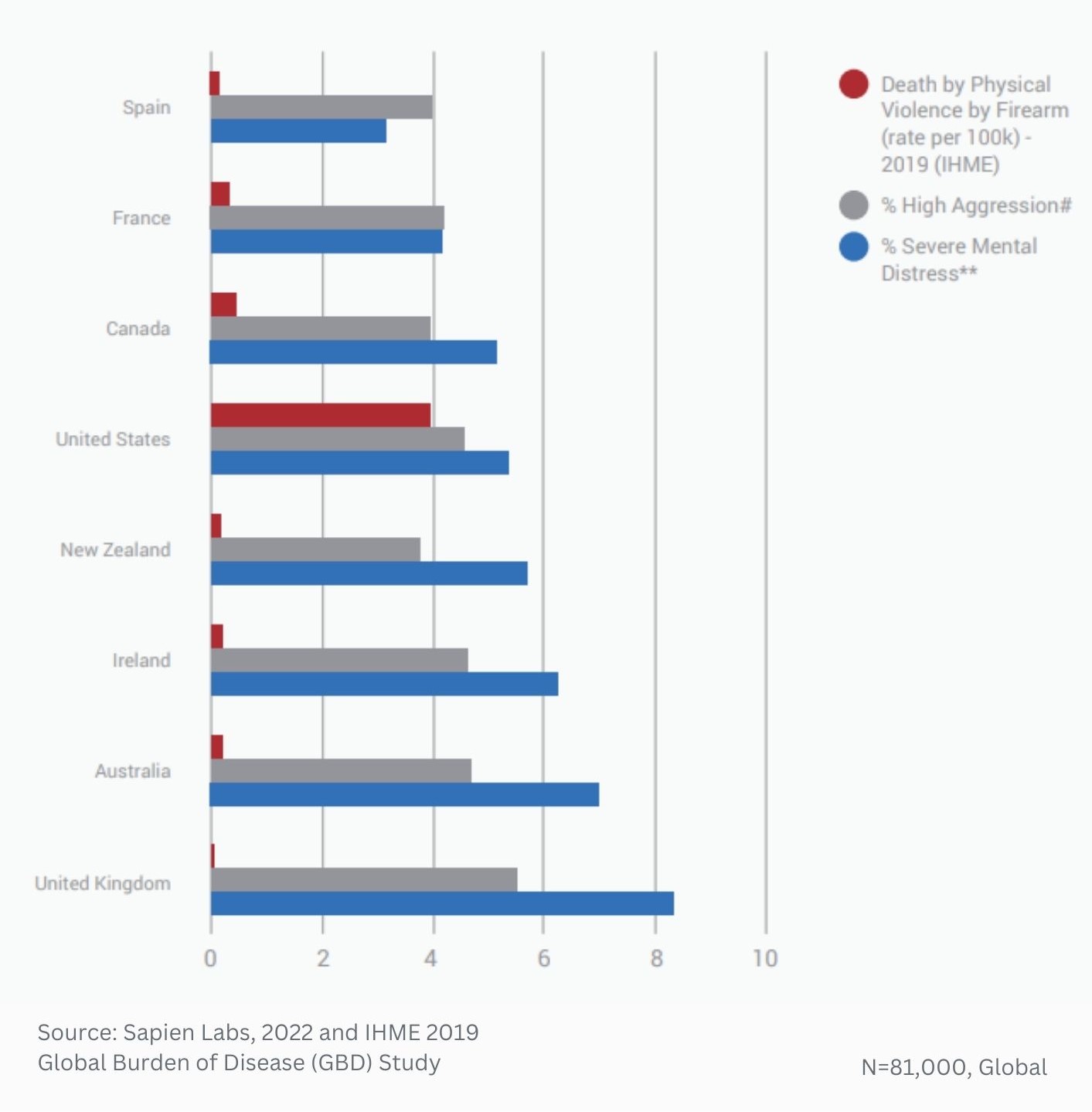
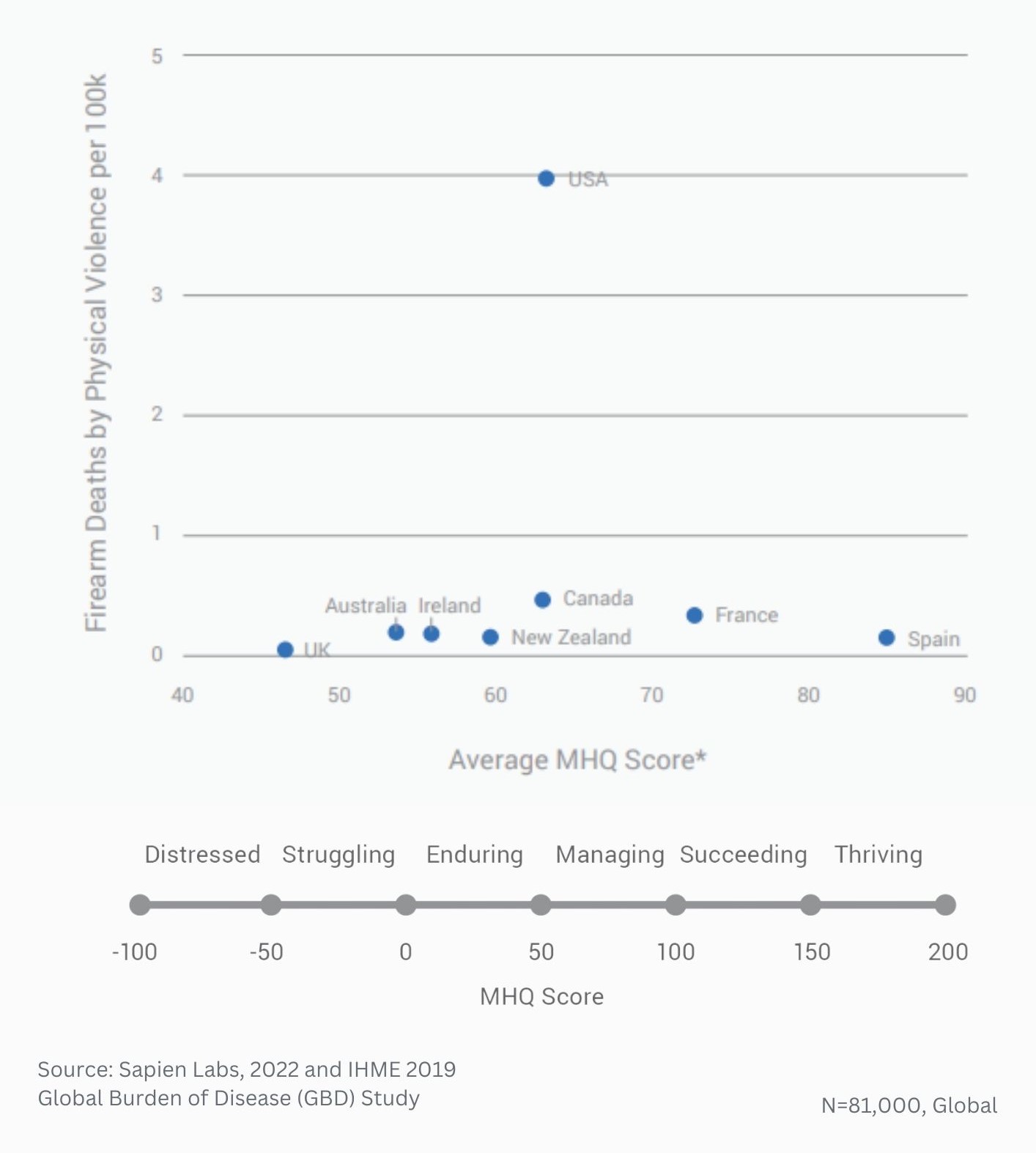
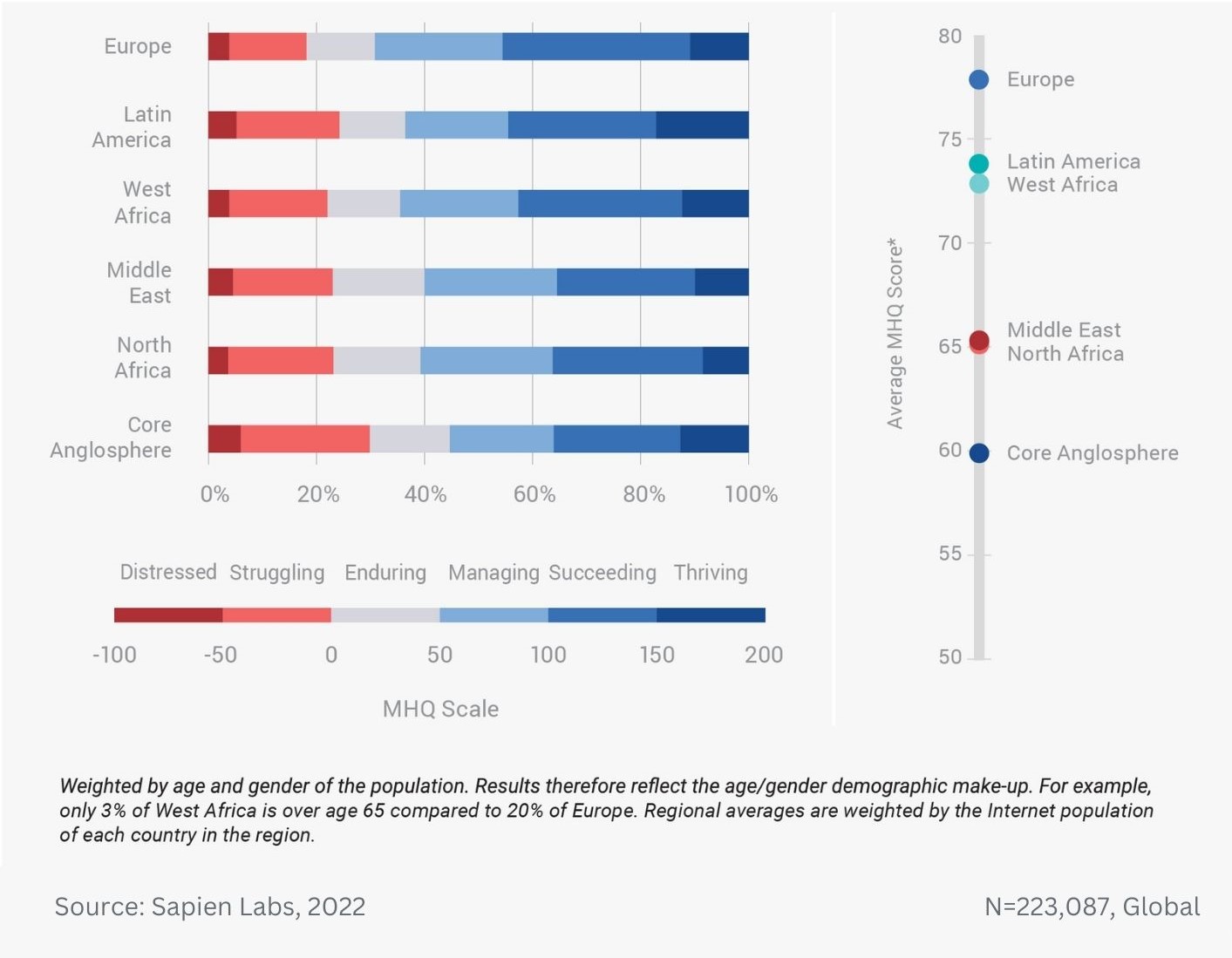
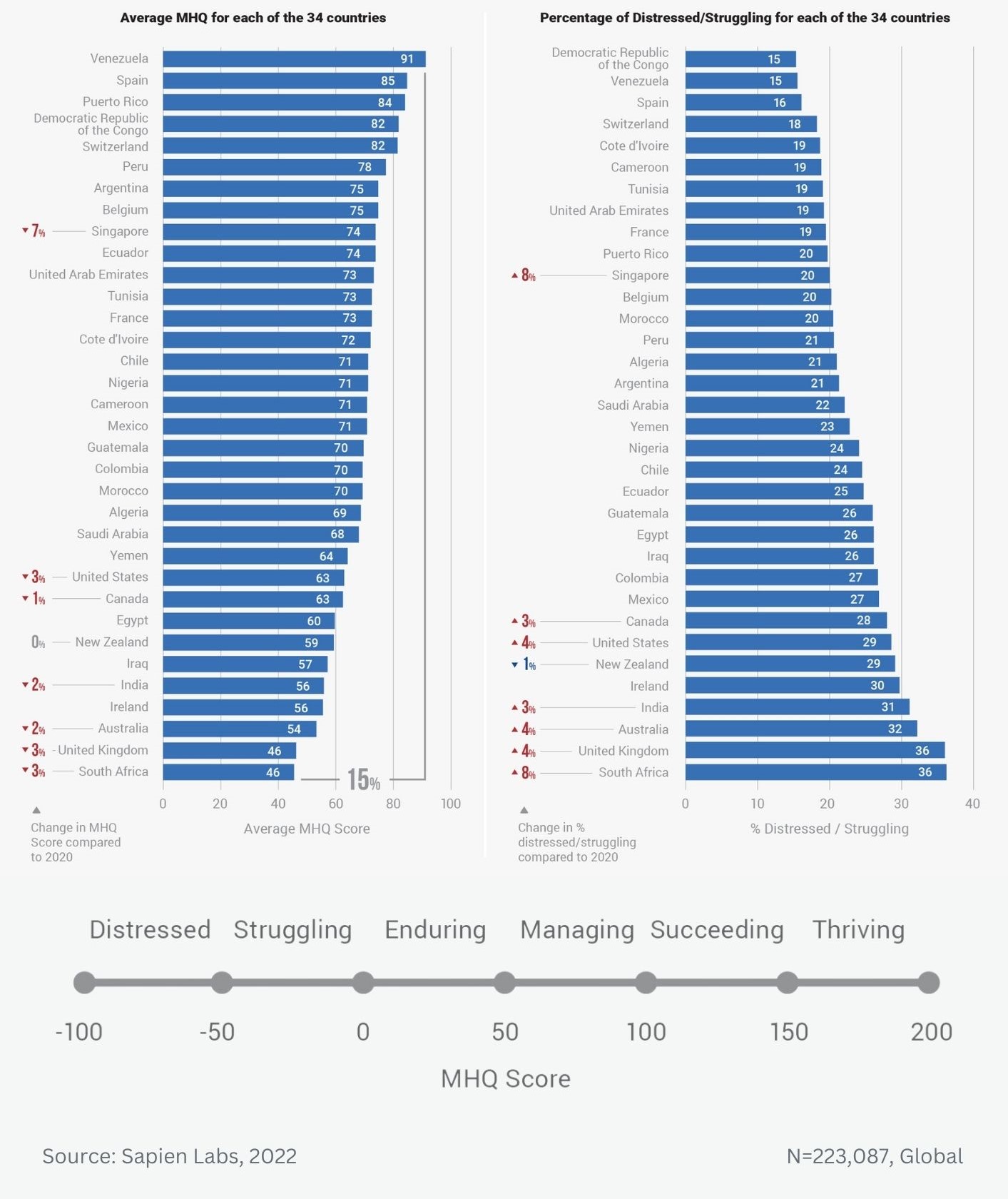
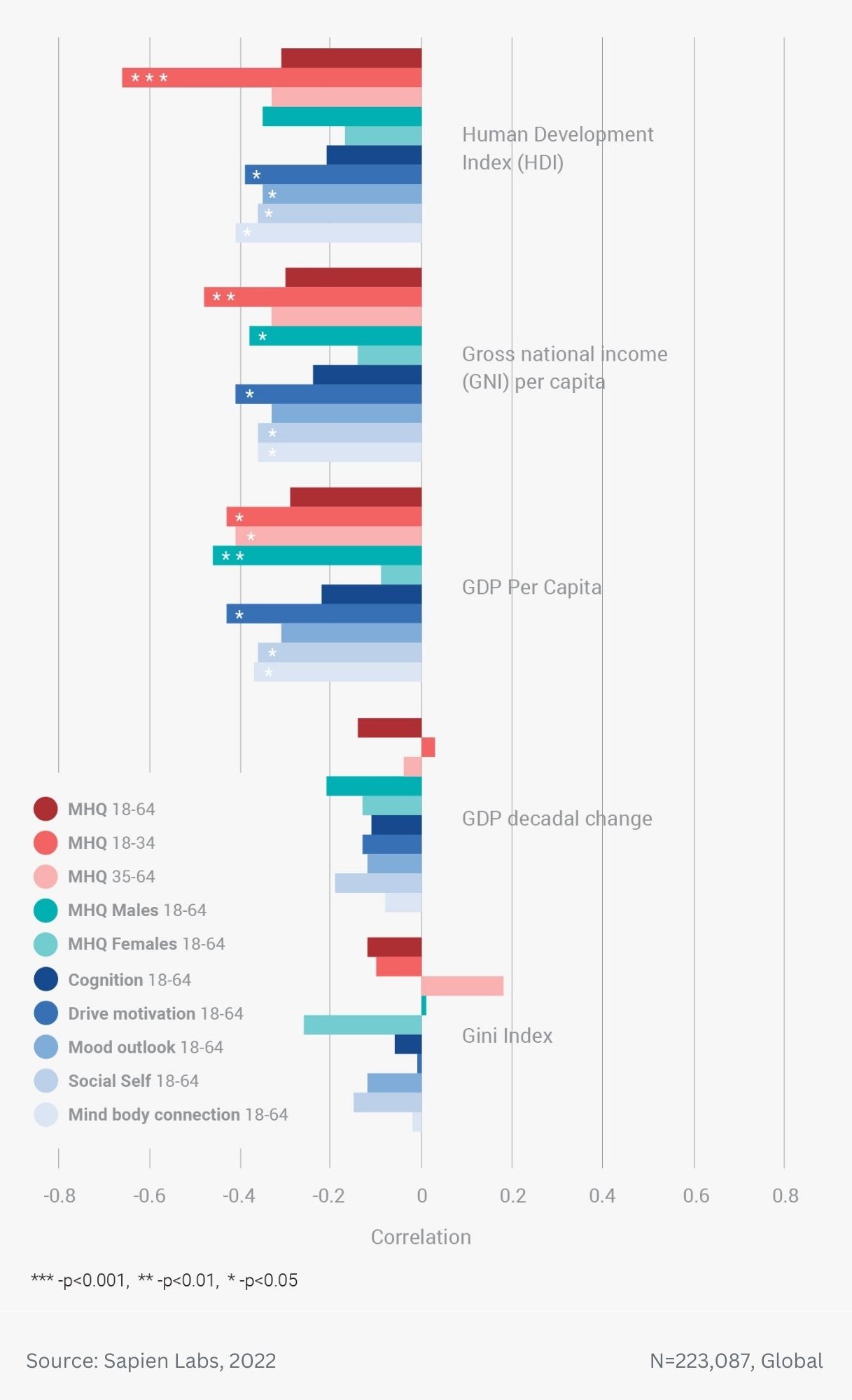
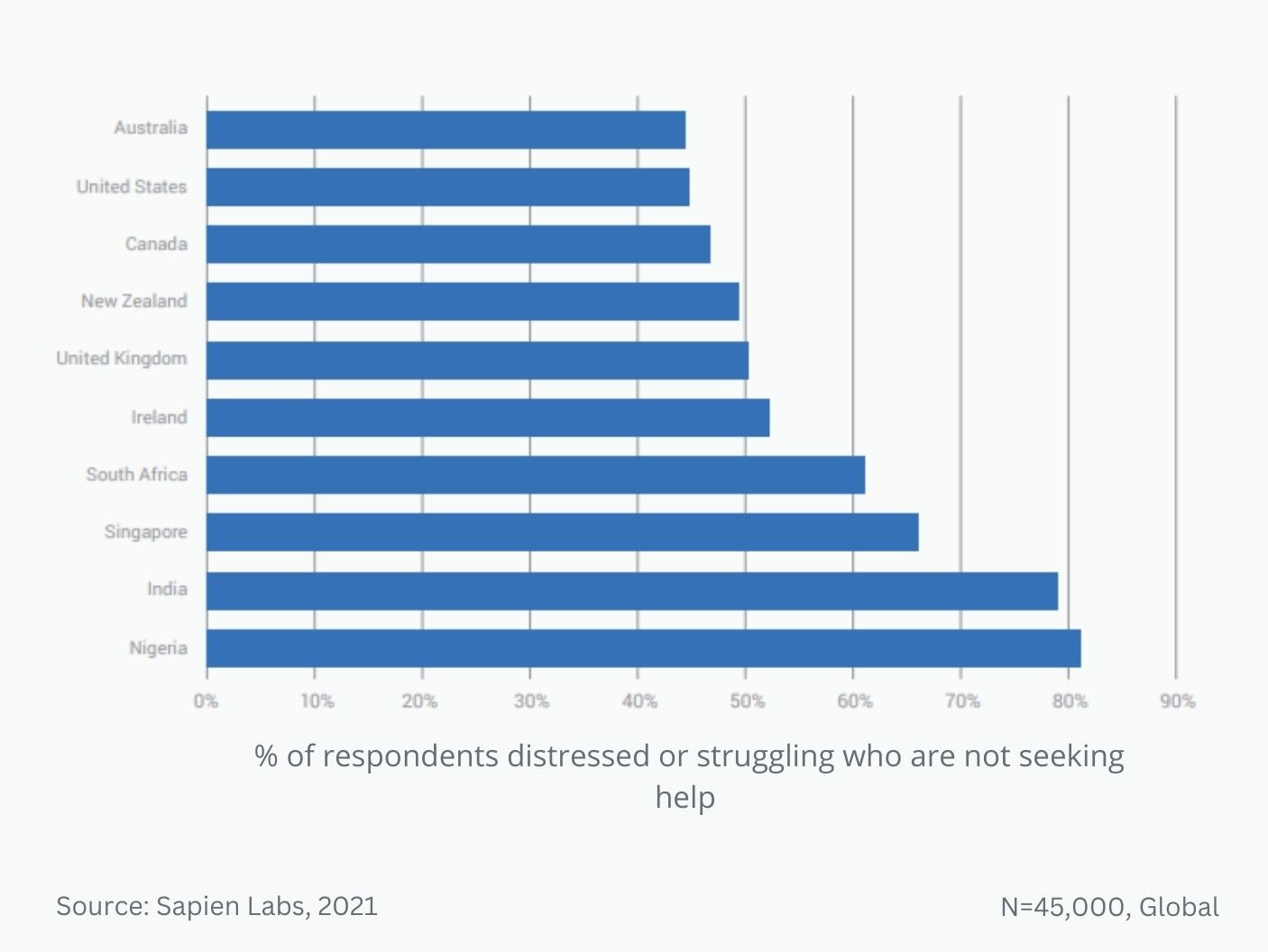
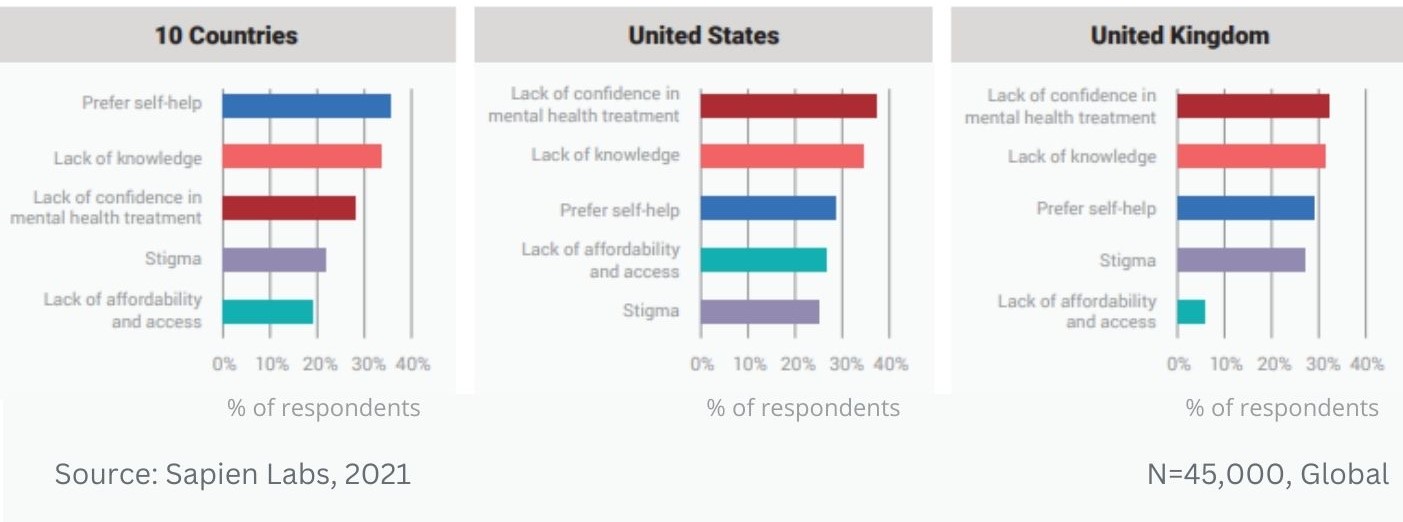
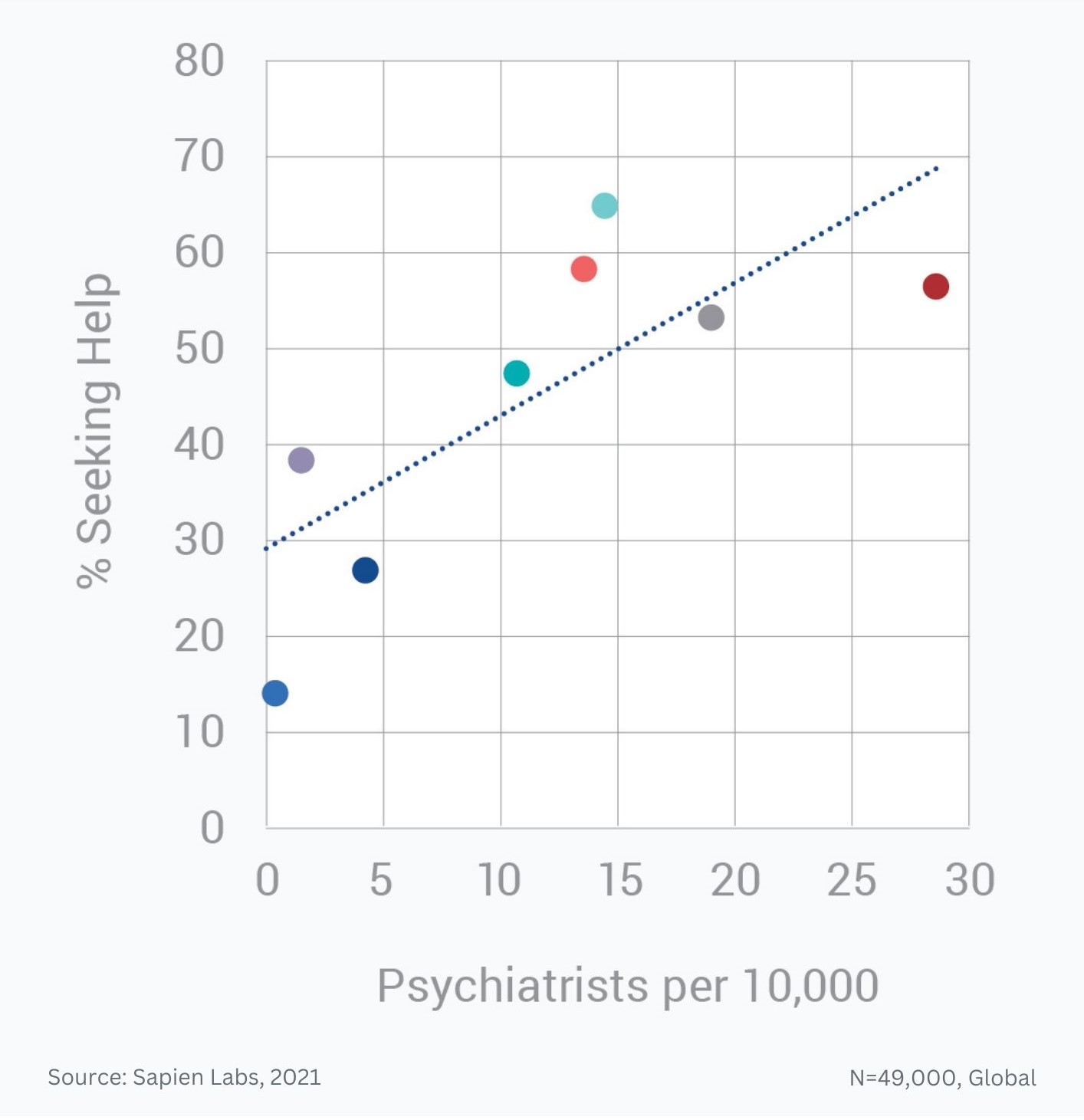
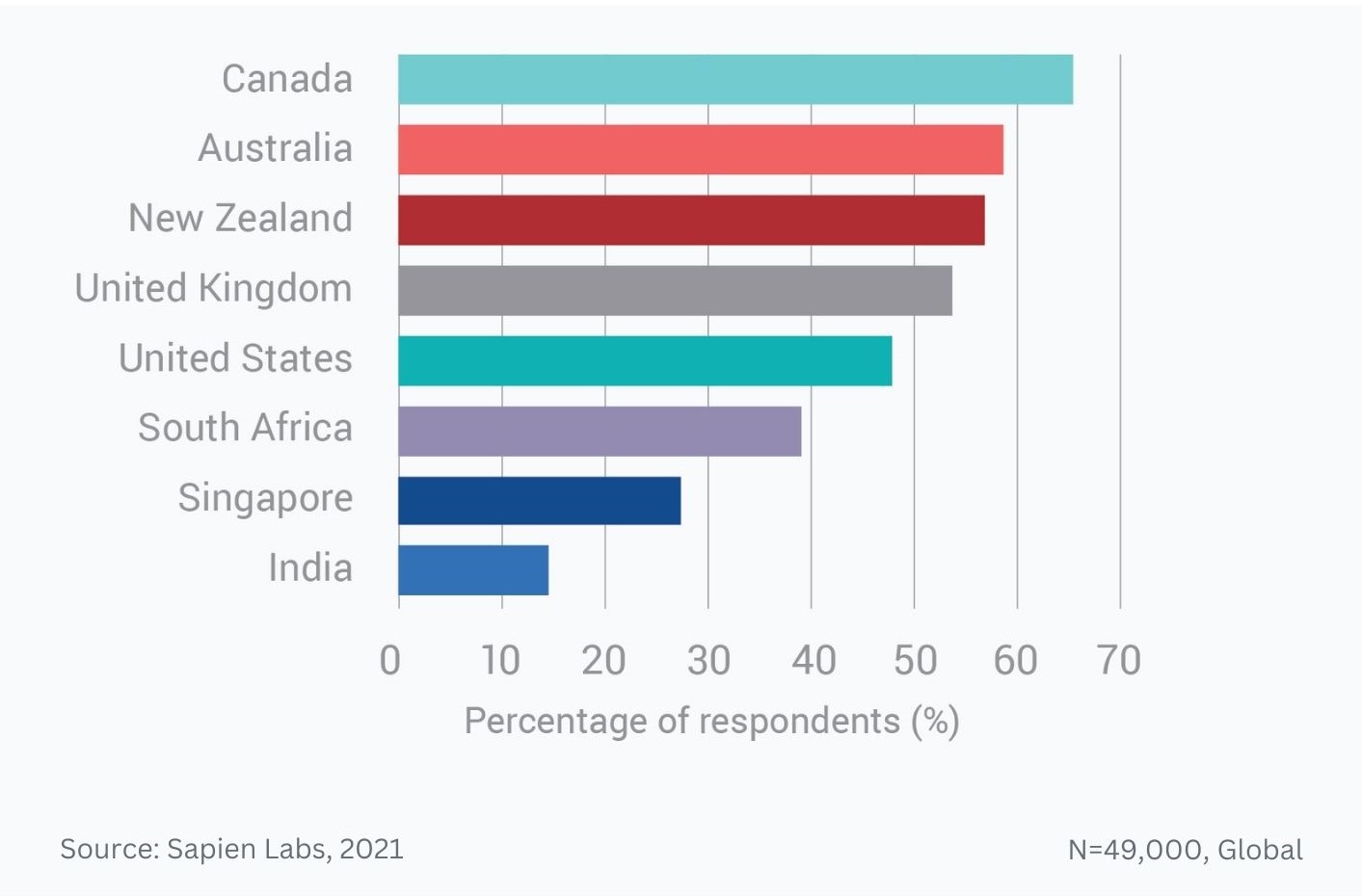
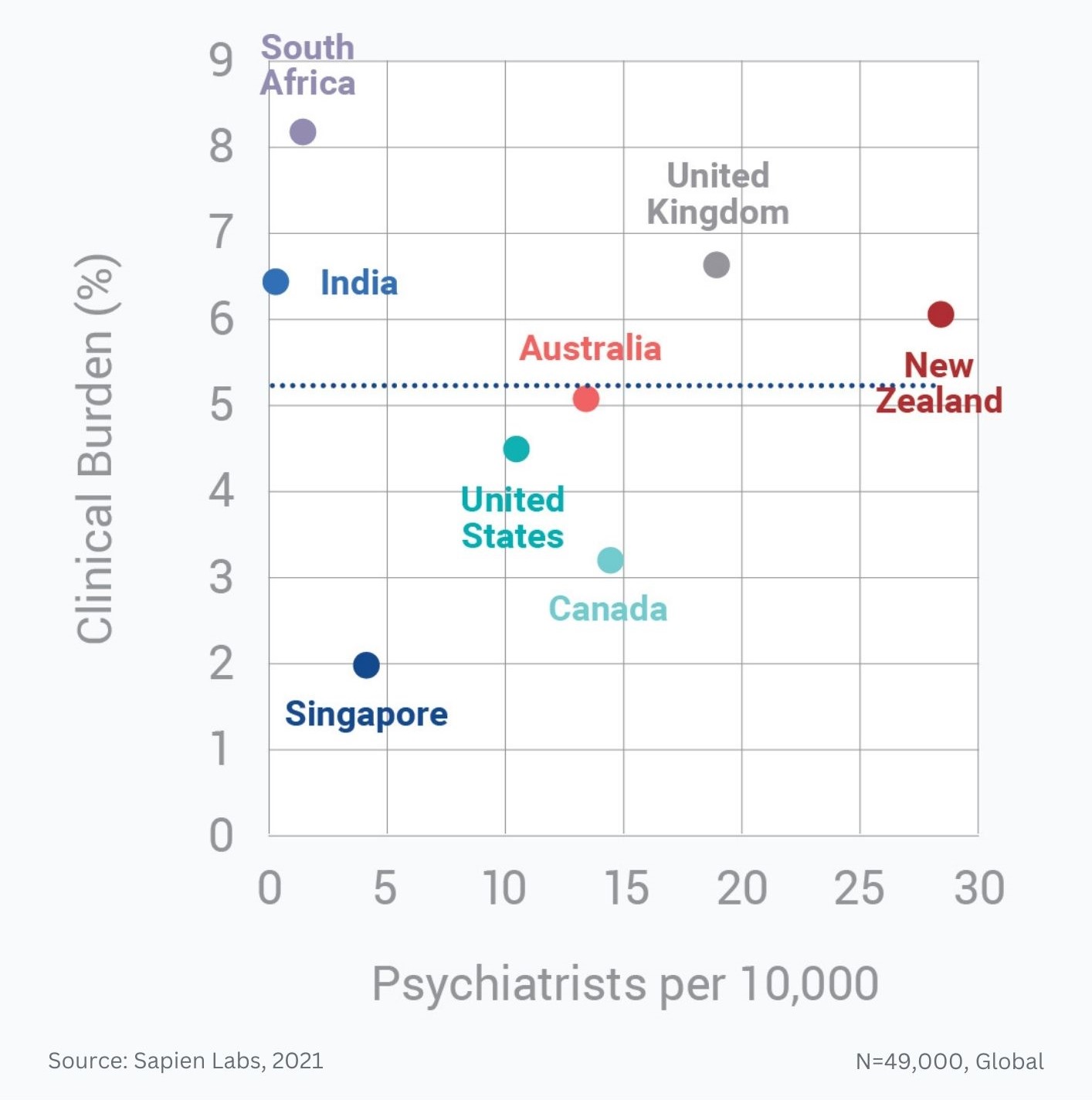
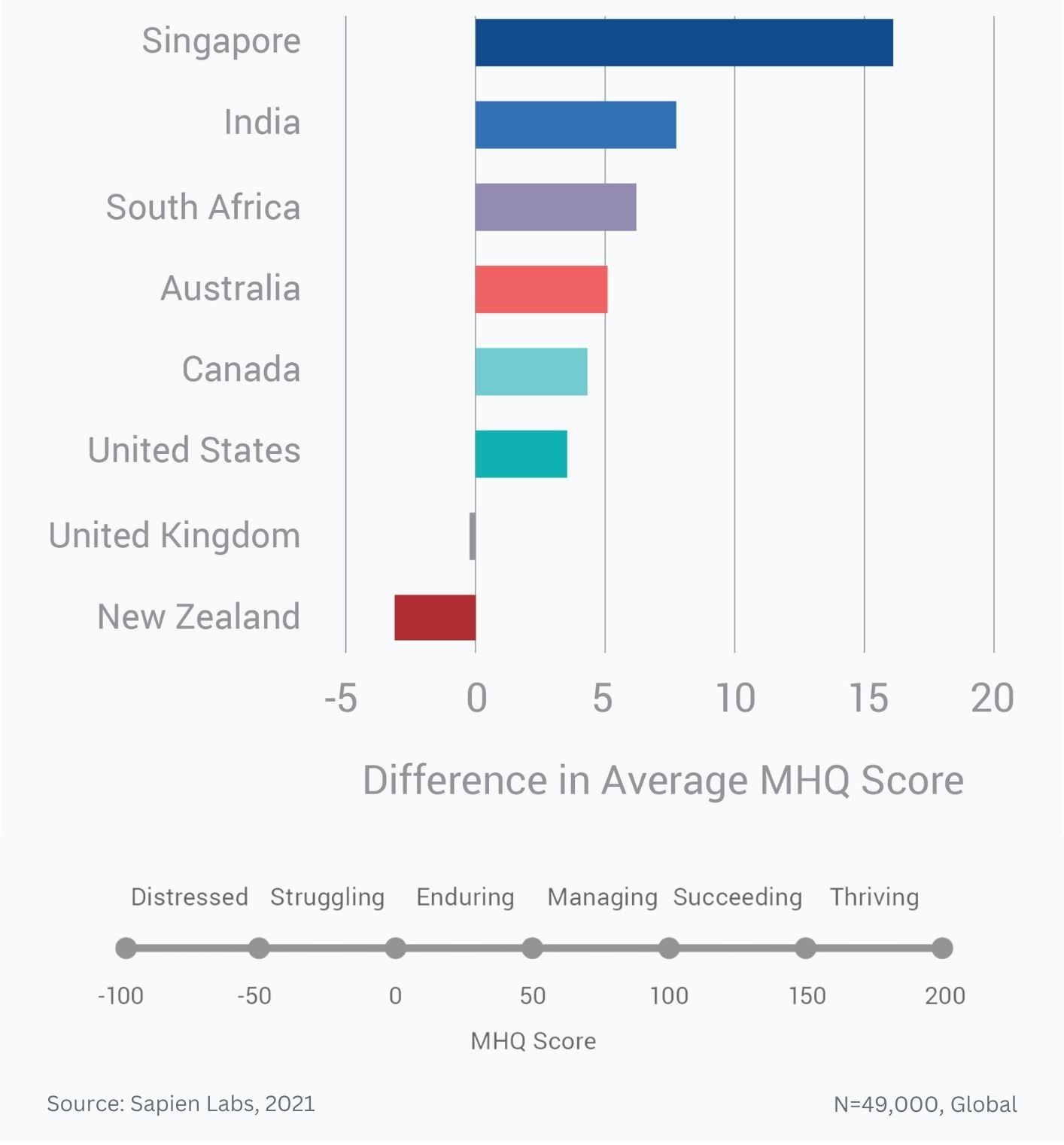
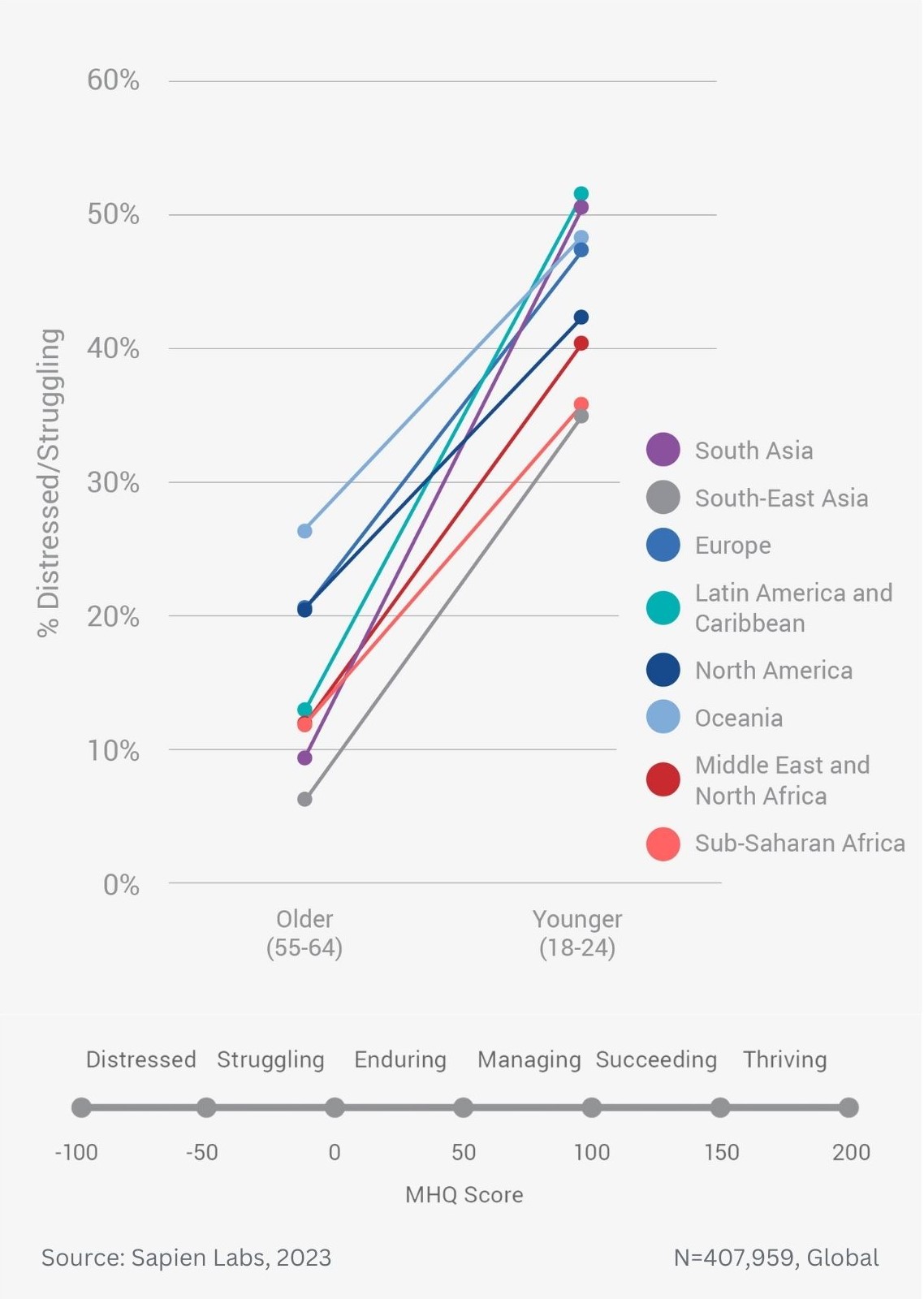
Globally, young adults are 3 to 4 times as likely to struggle with their mental health as their parents’ generation (Regions)
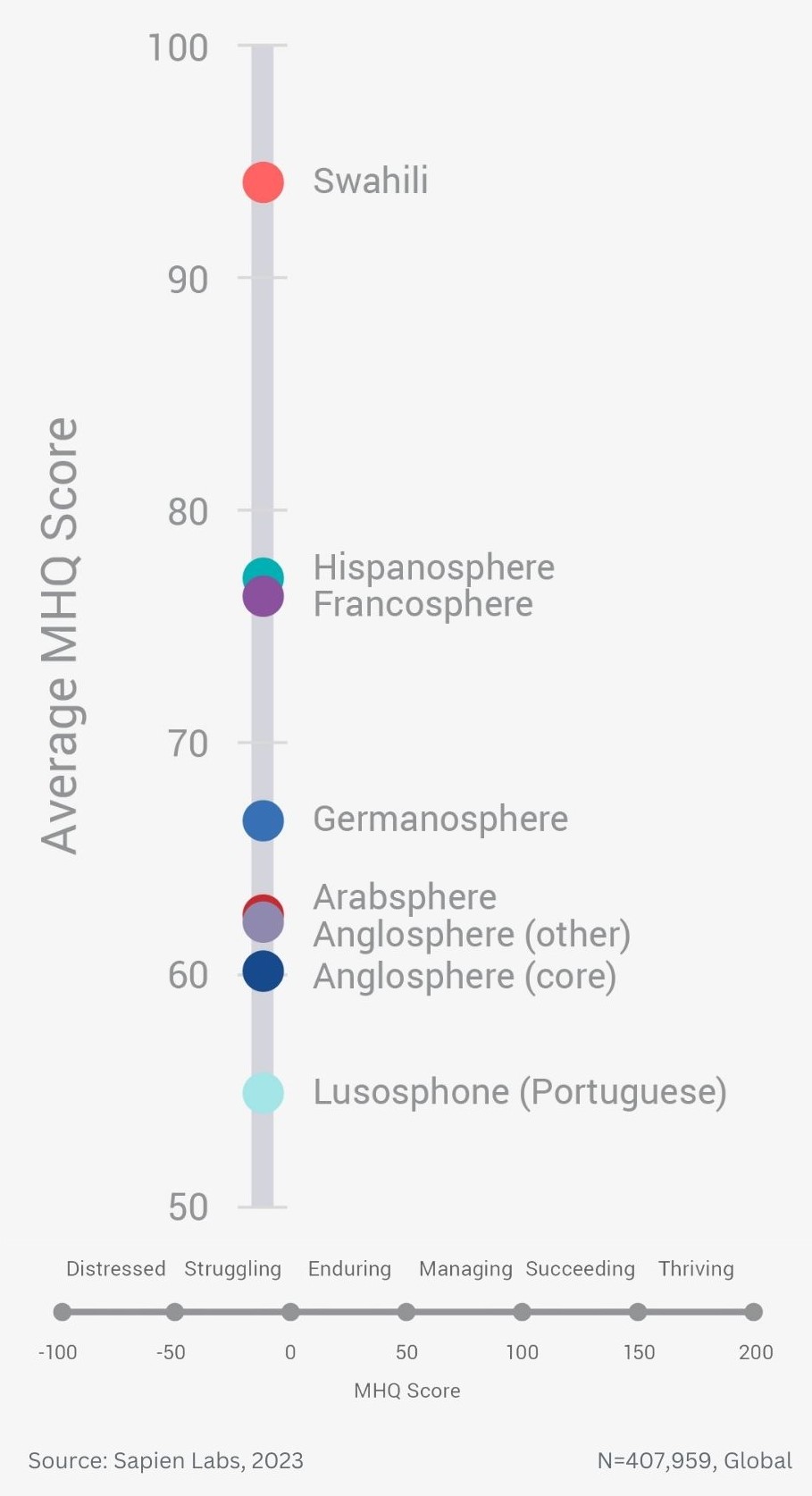
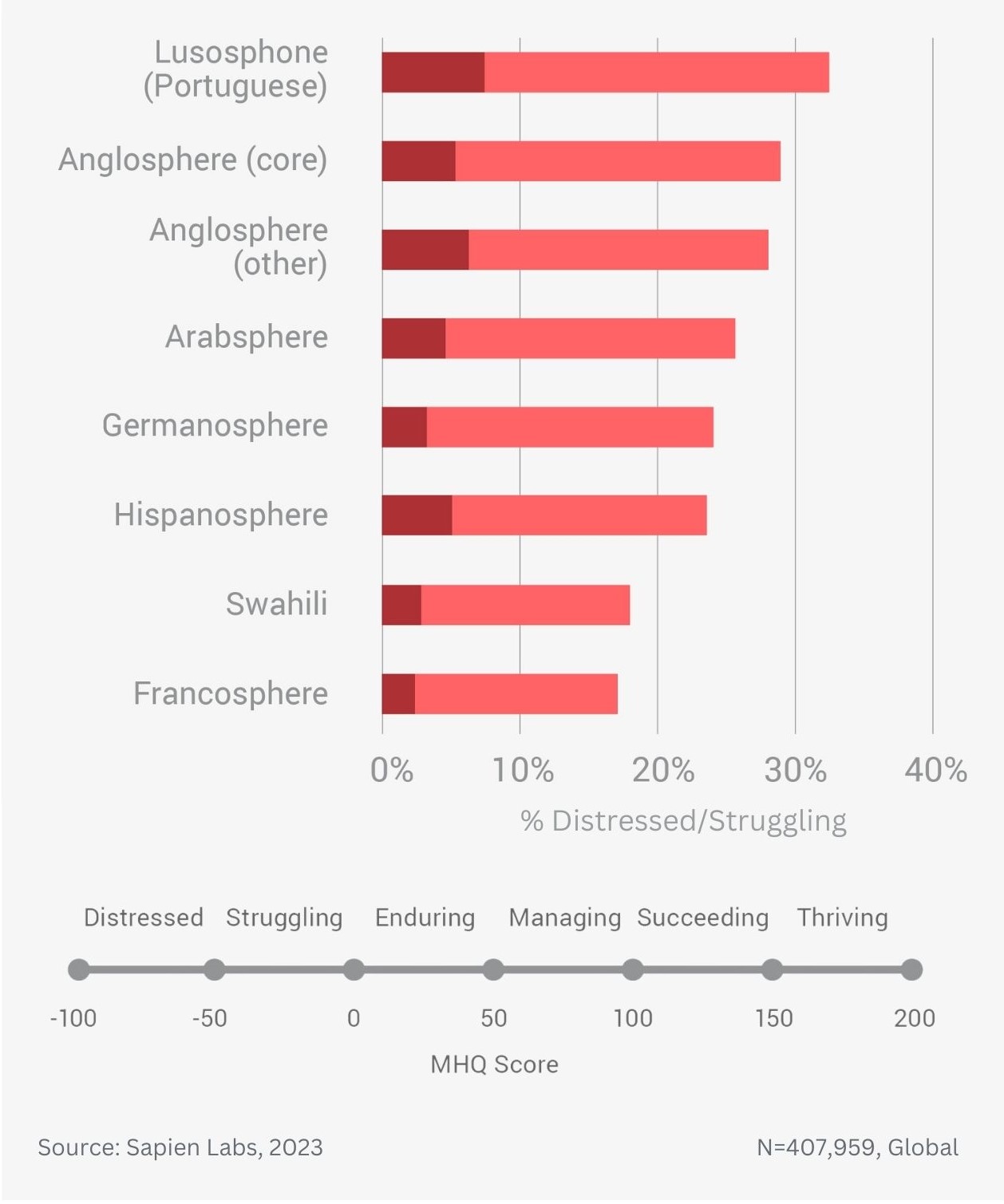
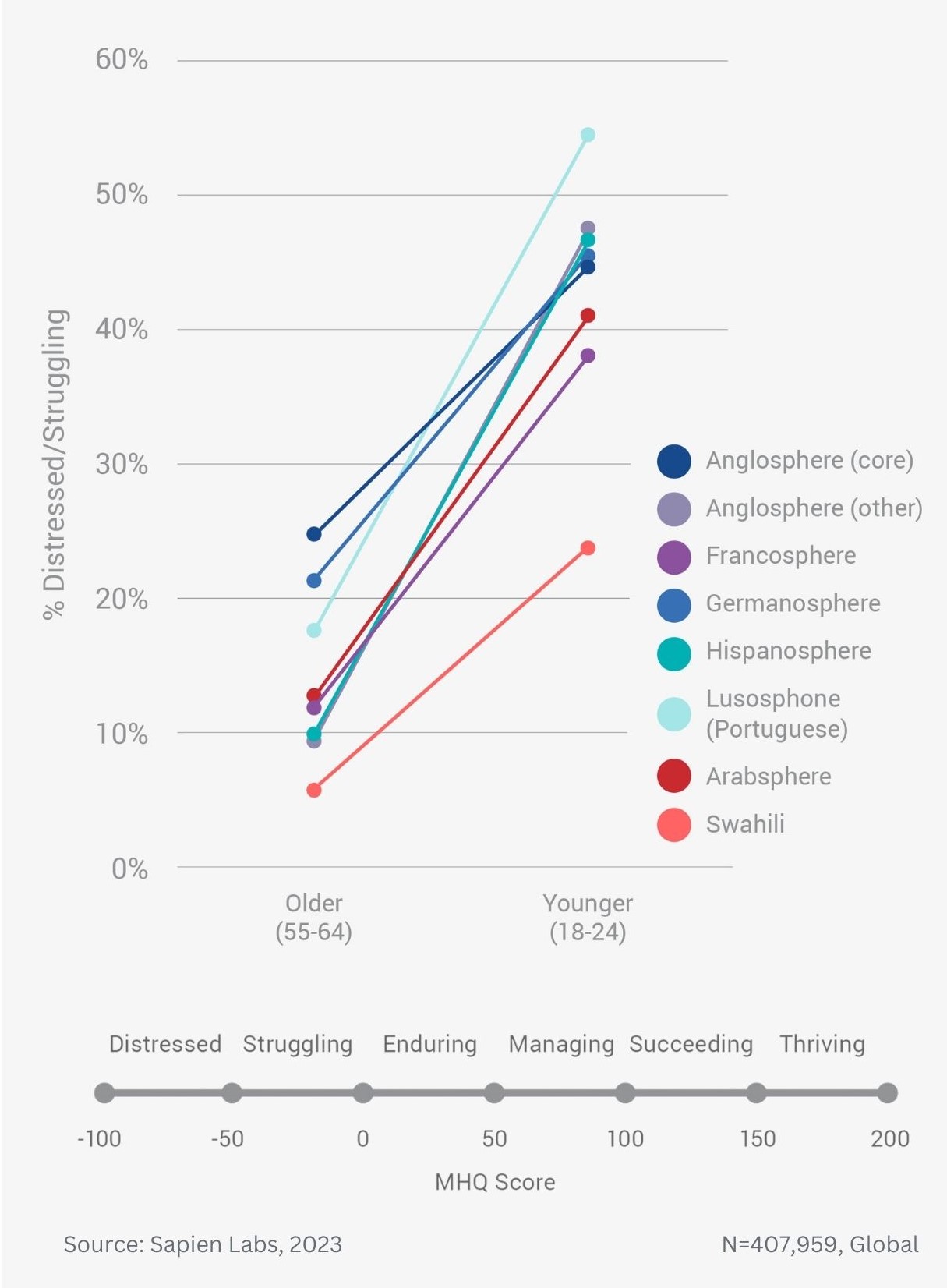
Globally, young adults are 3 to 4 times as likely to struggle with their mental health as their parents’ generation (Language groups)
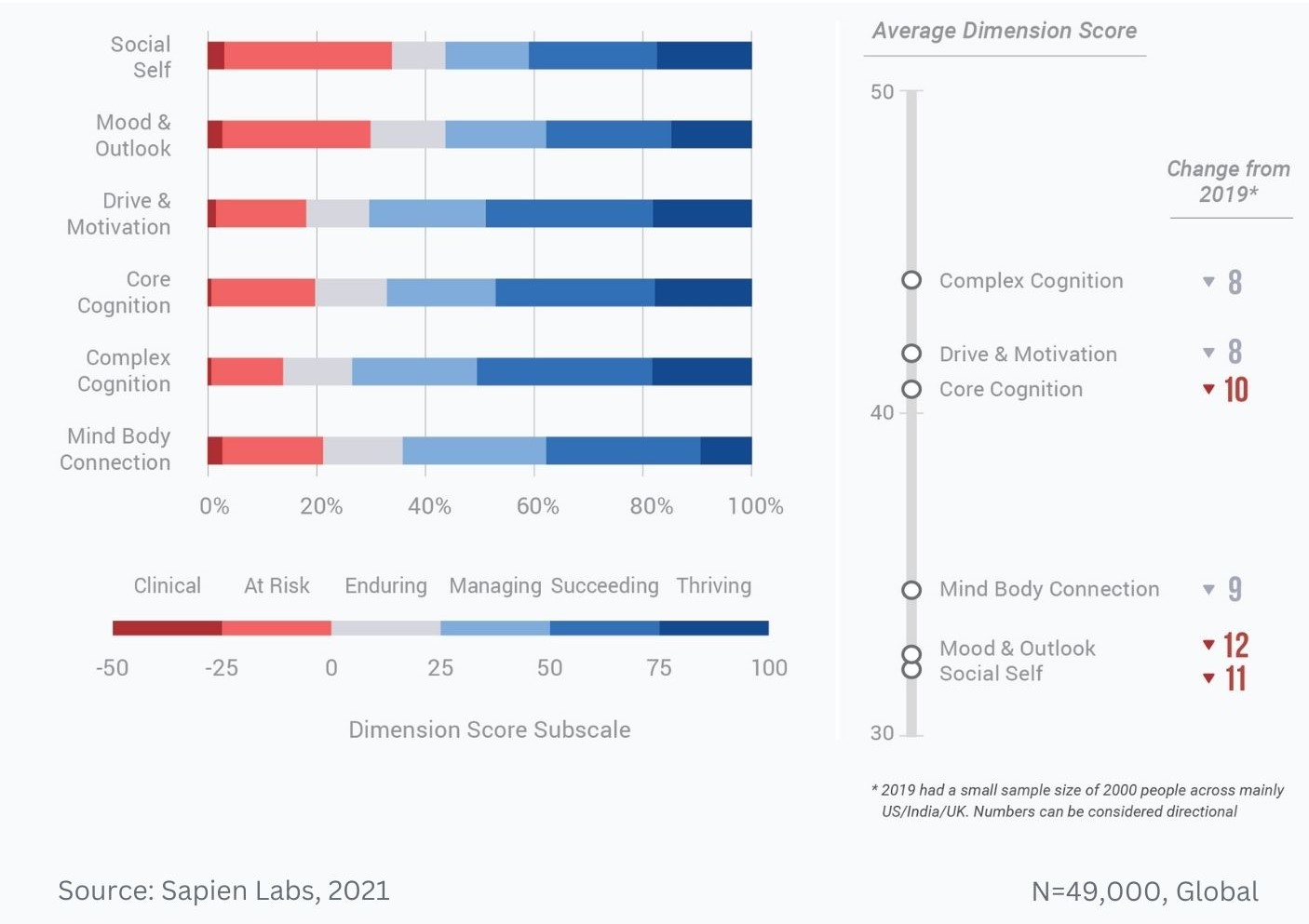
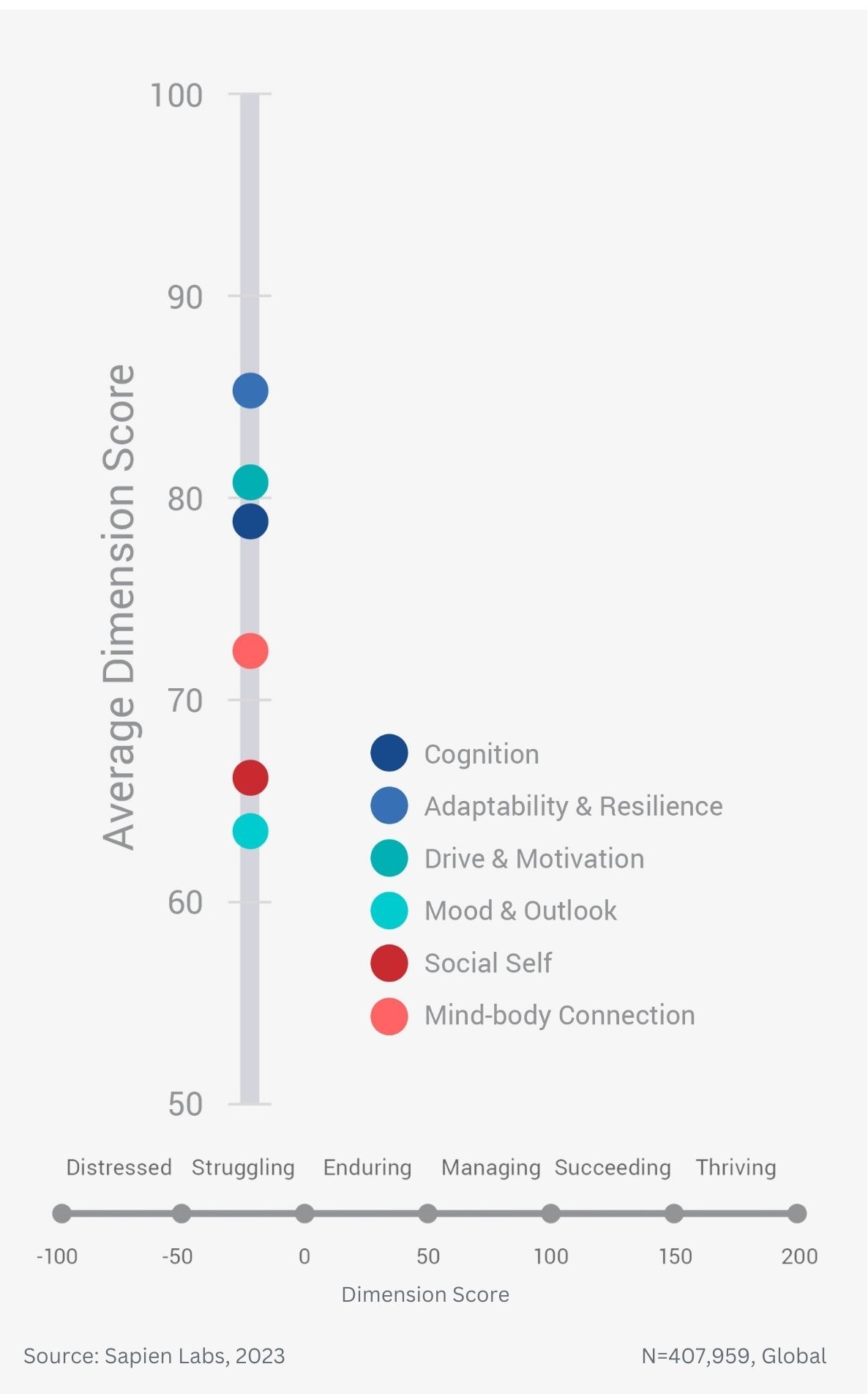
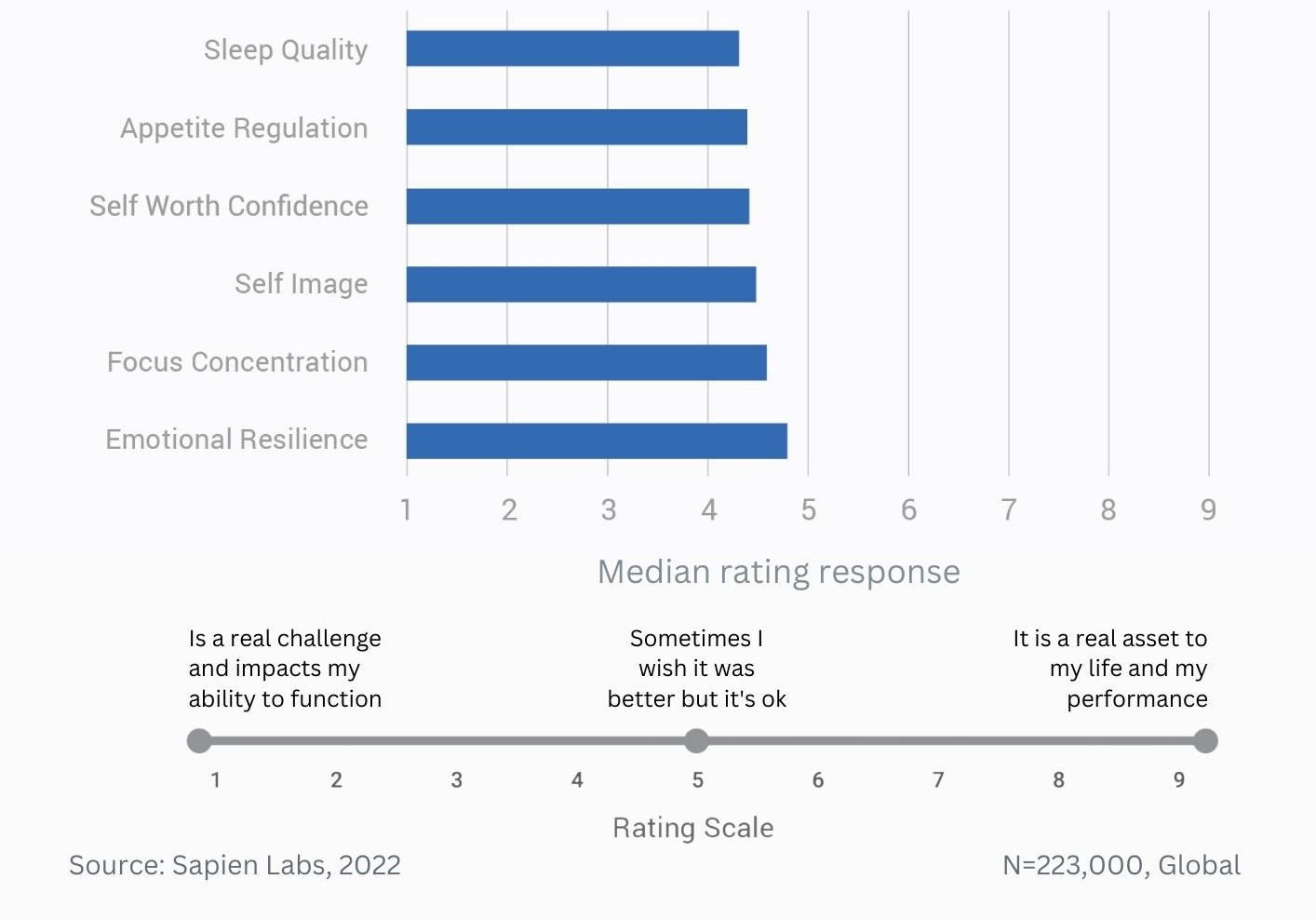
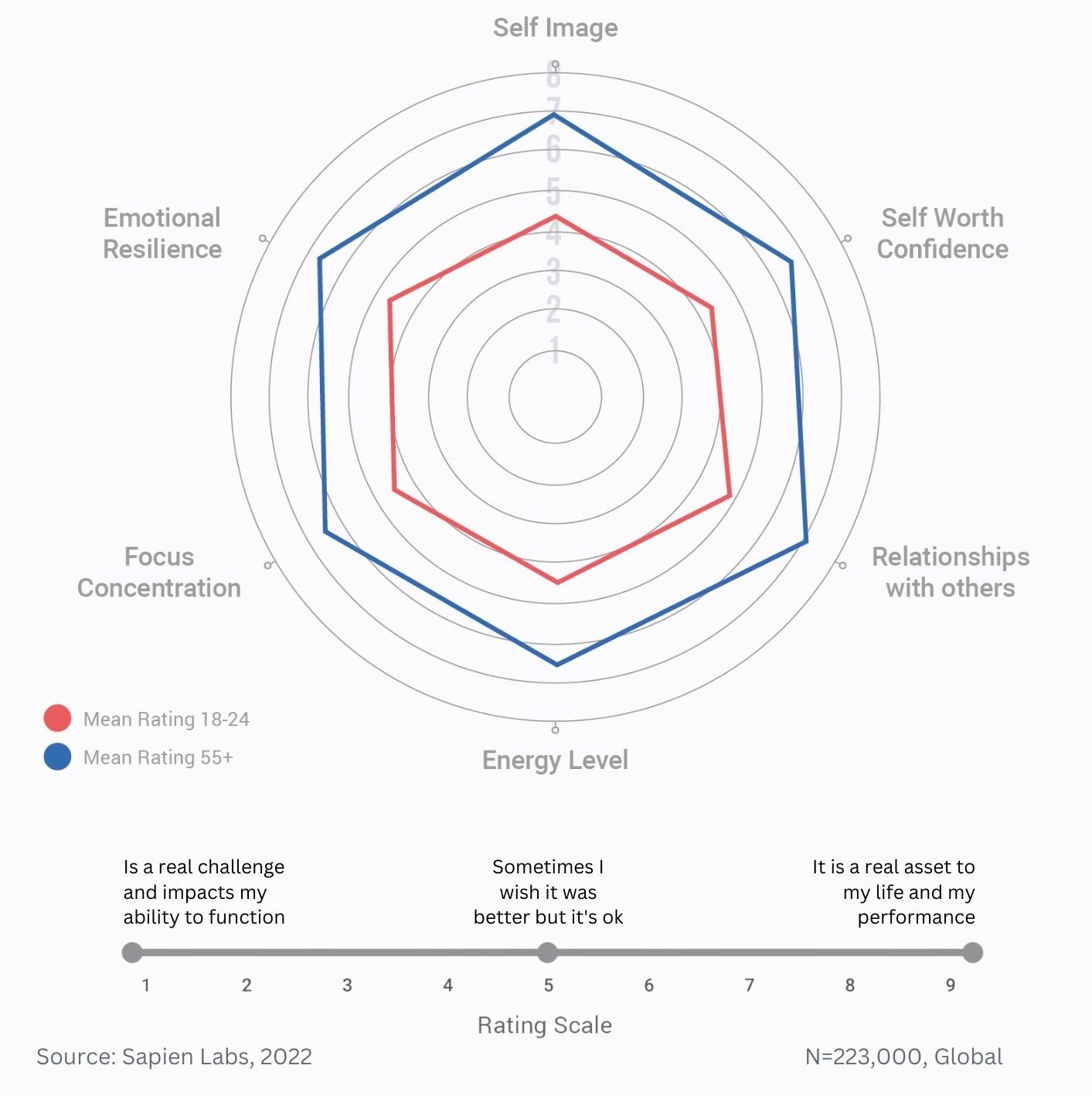
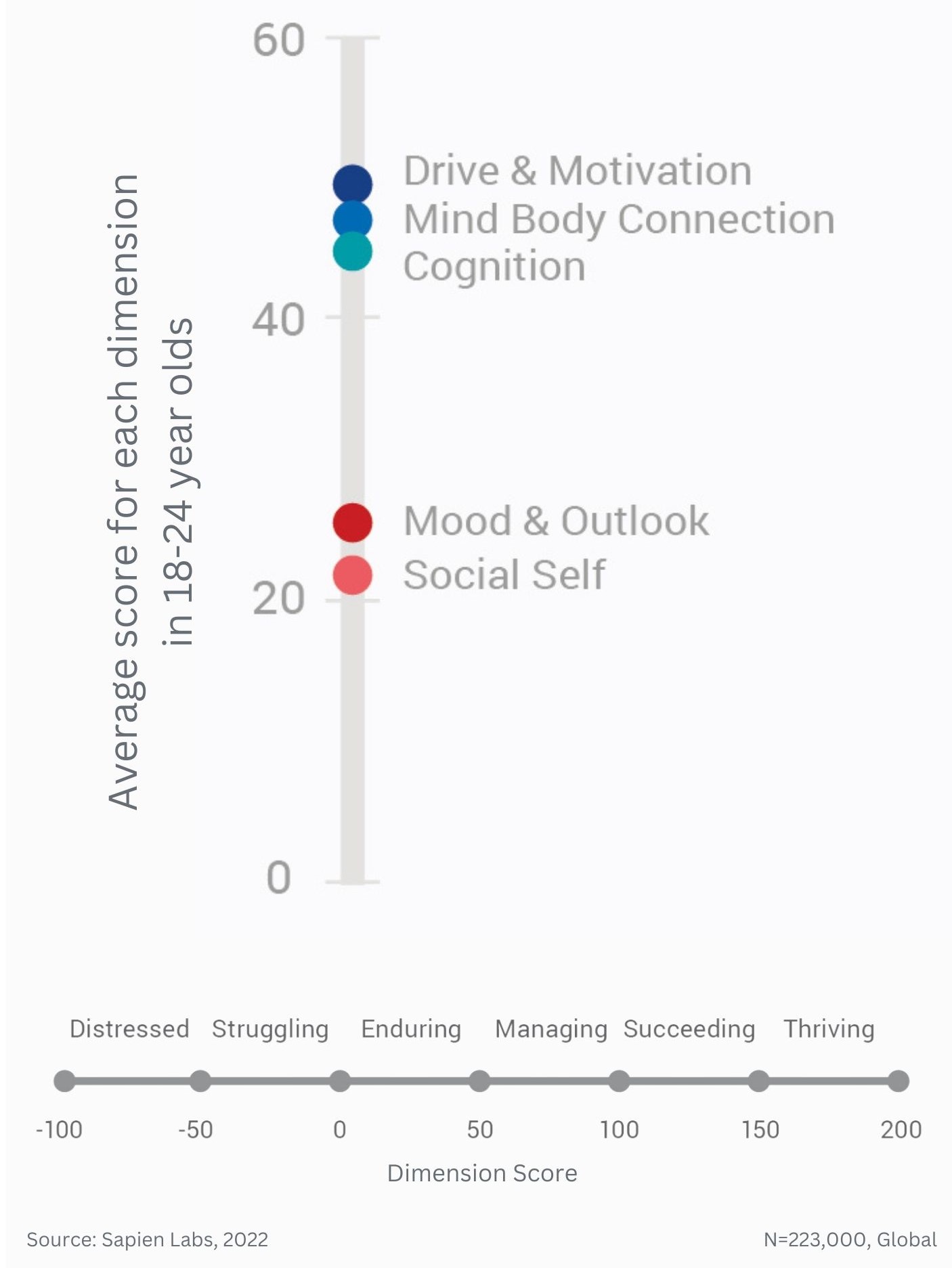
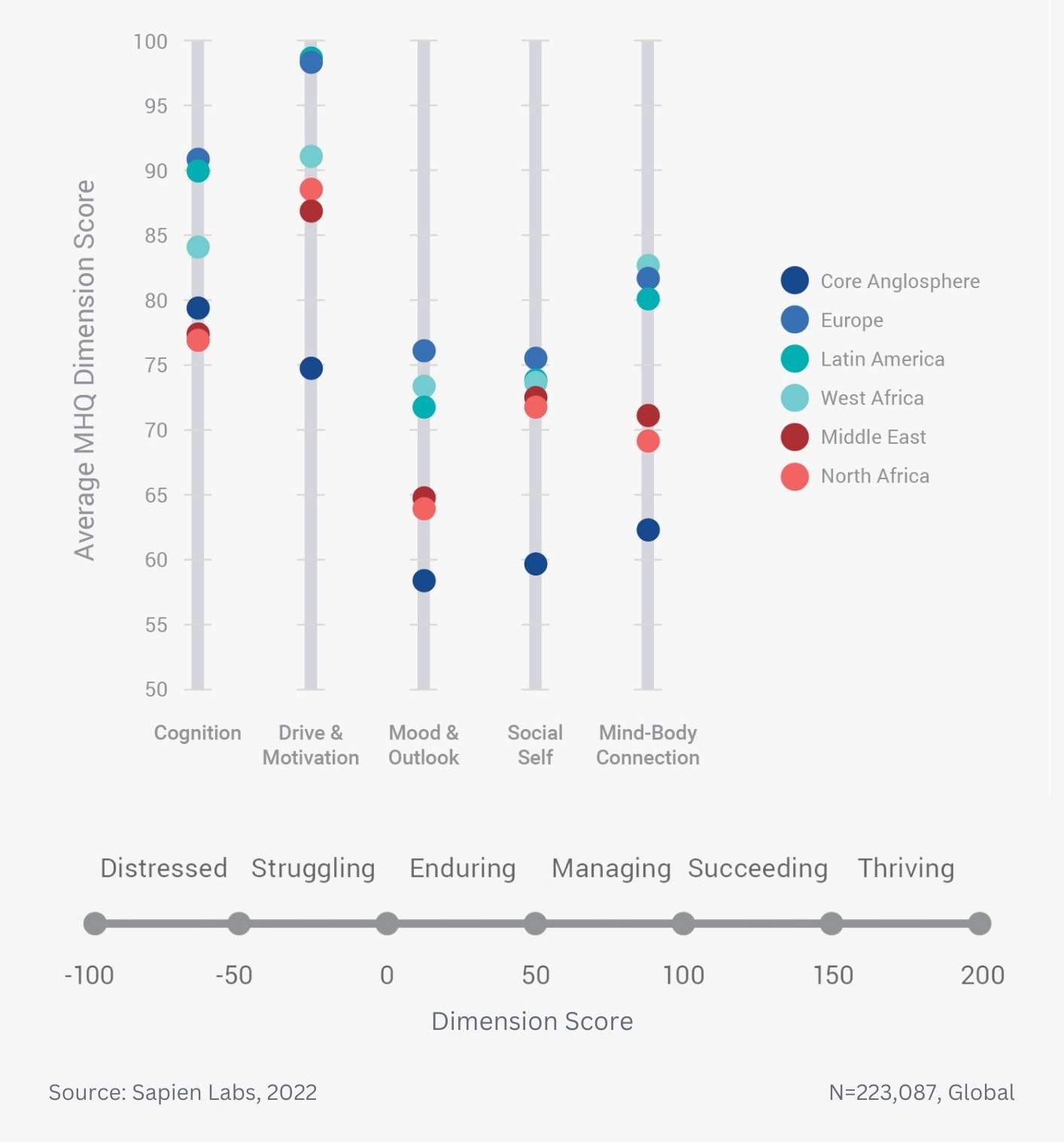
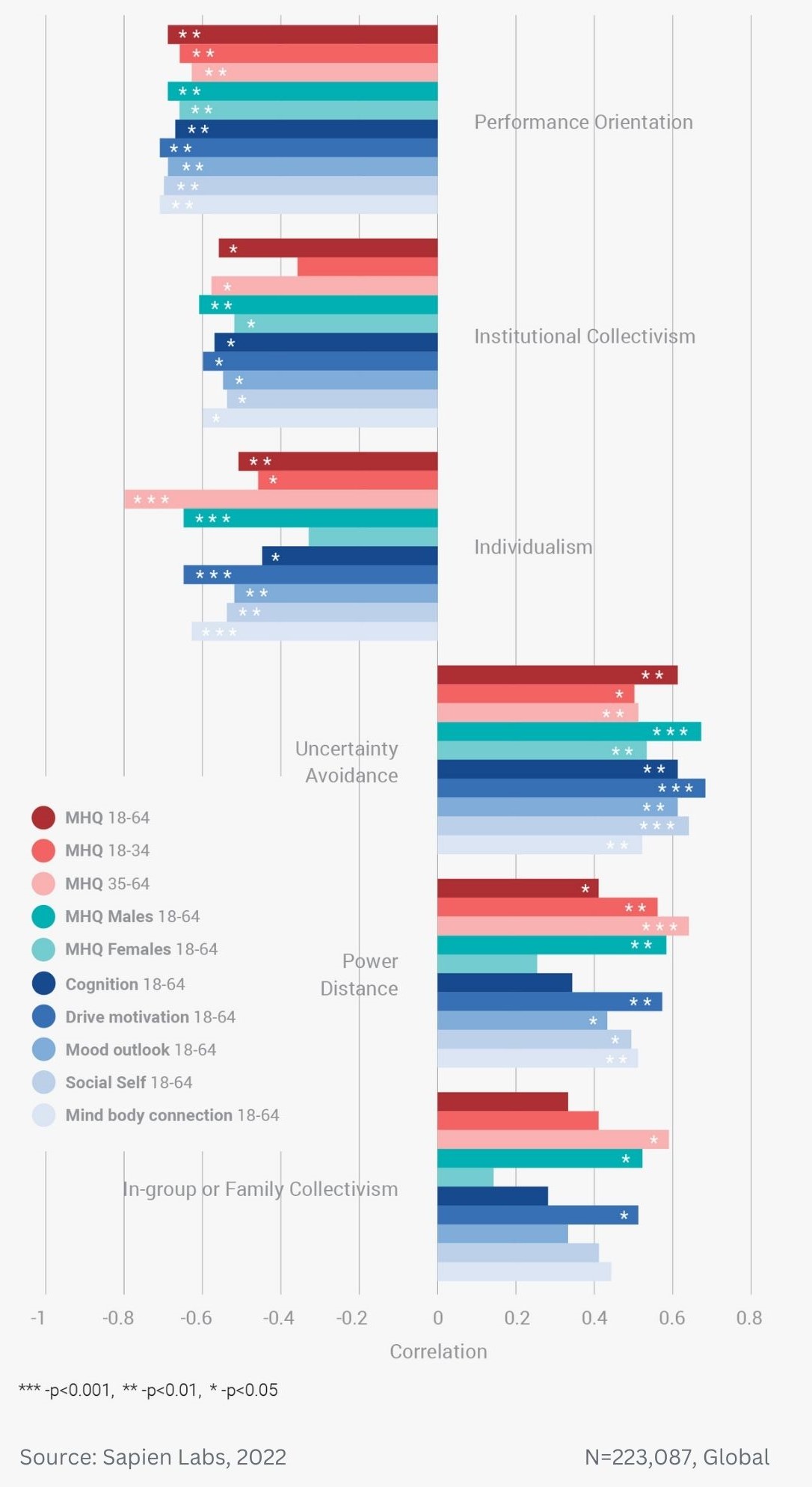
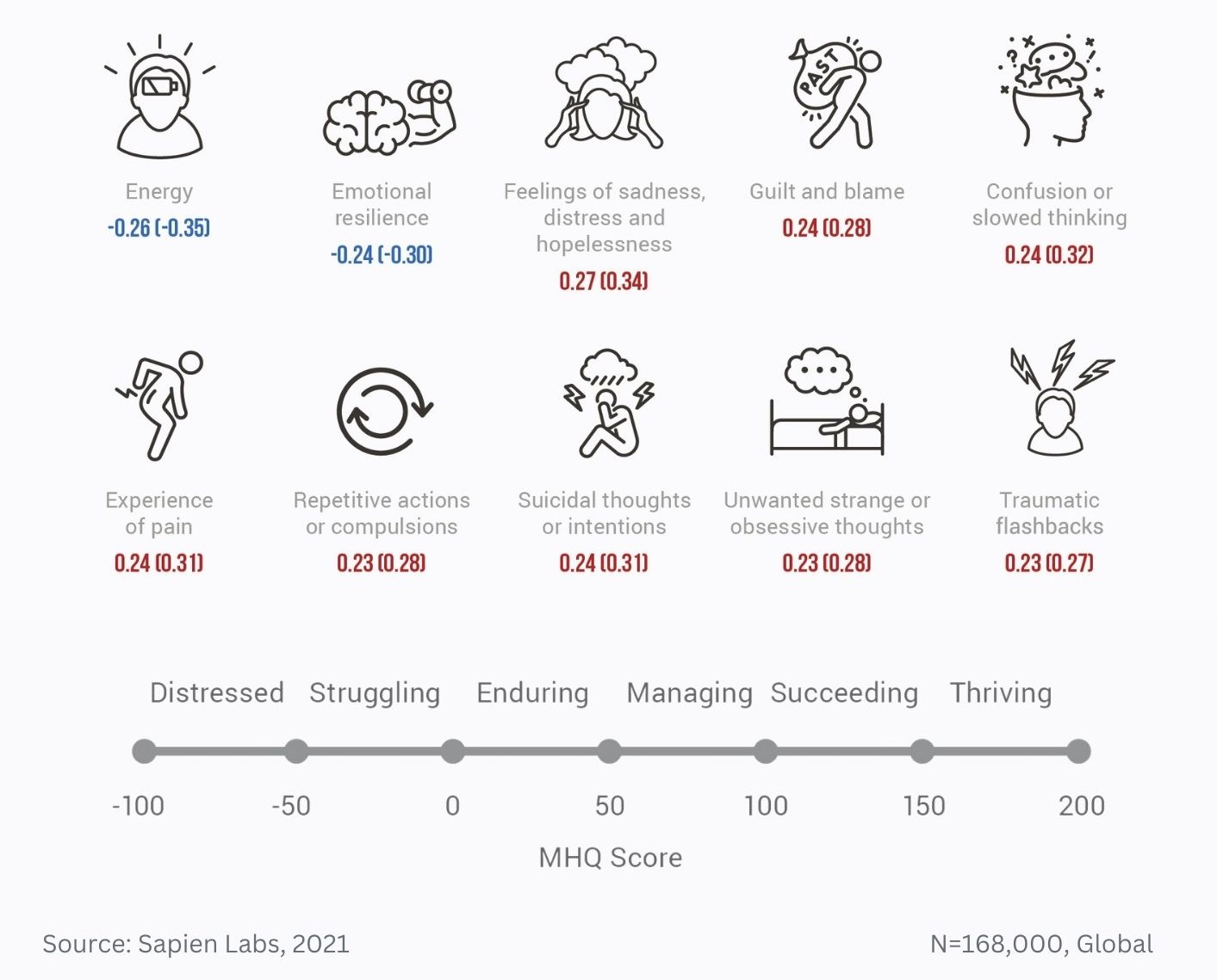
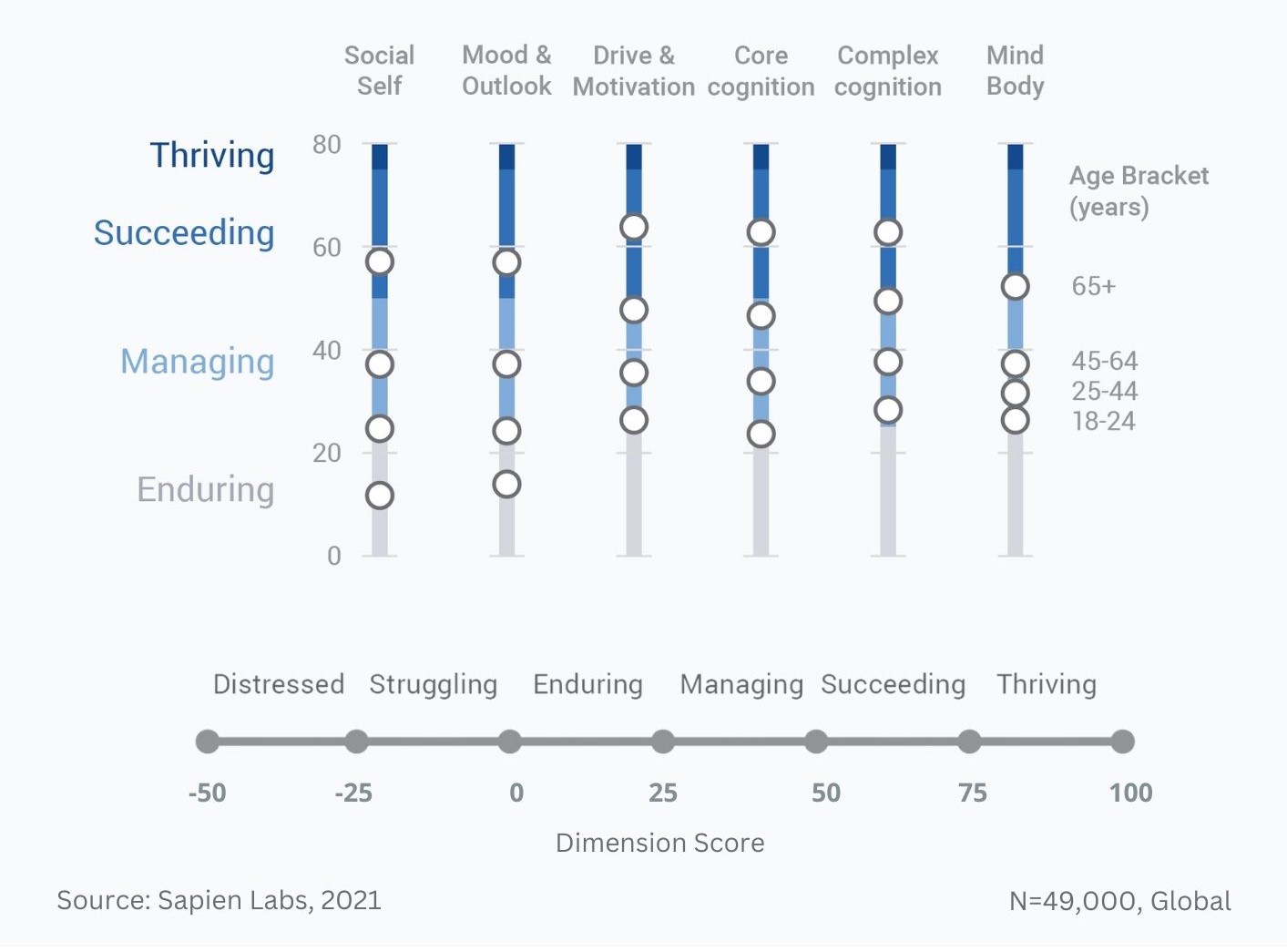
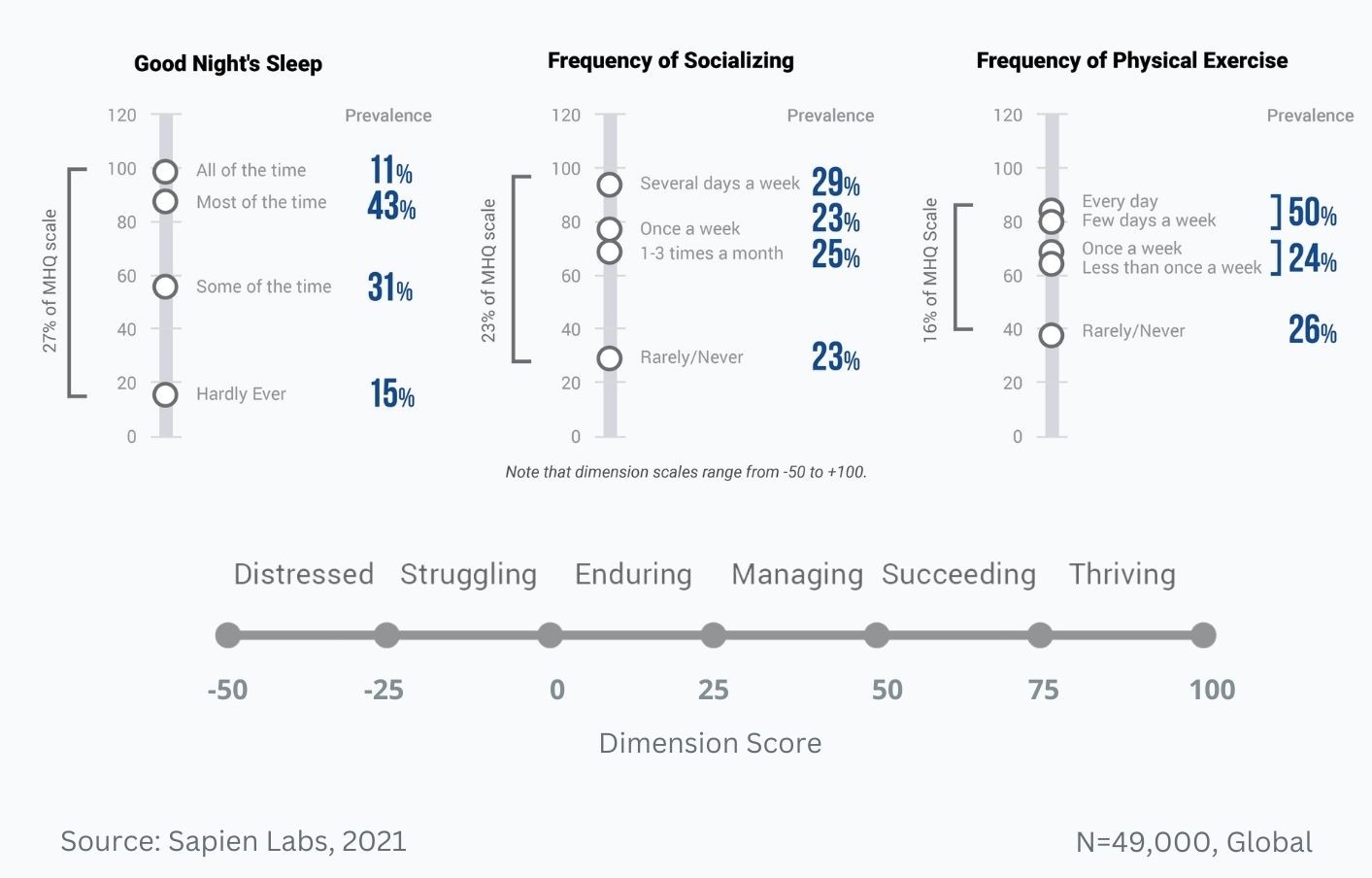
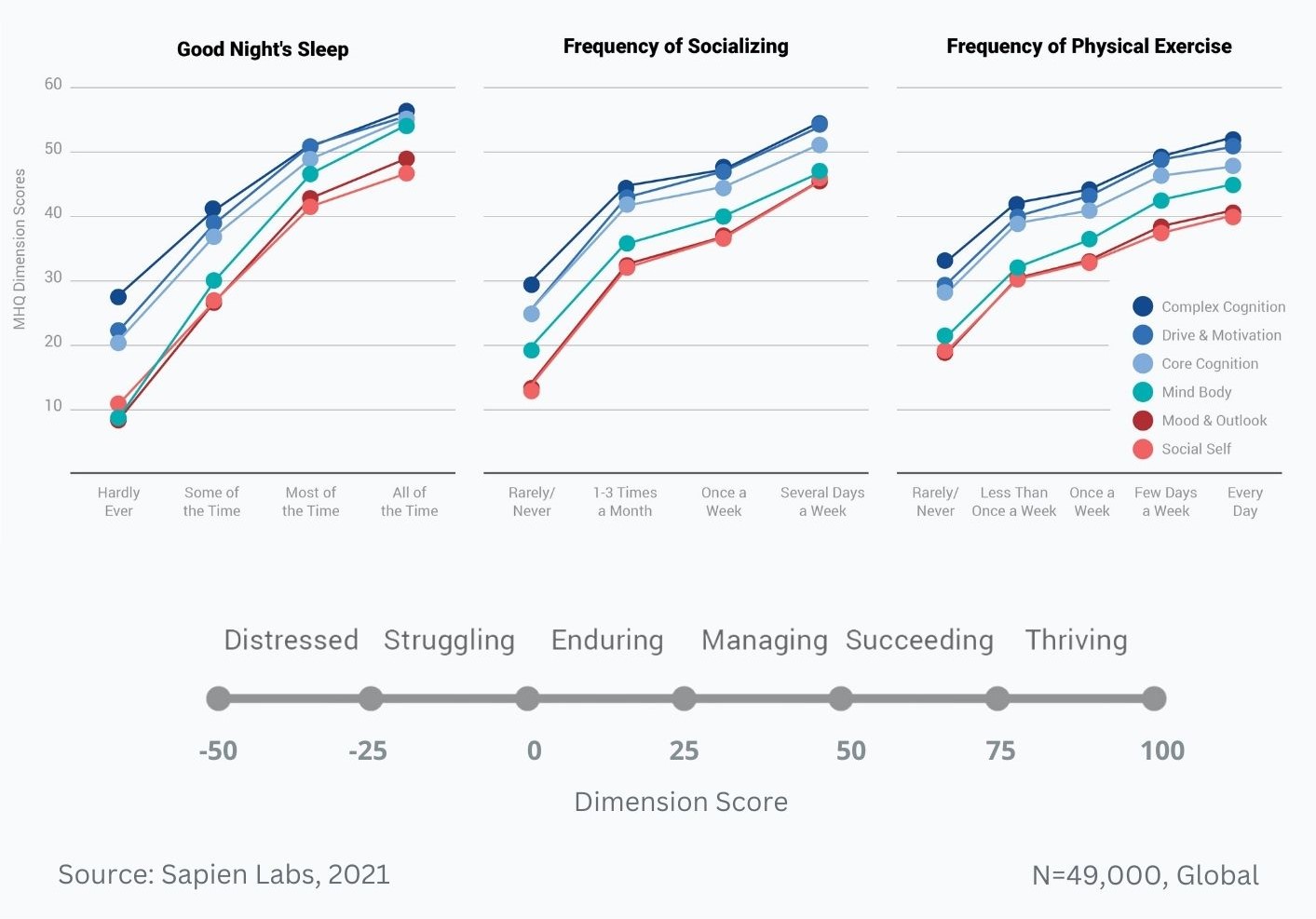
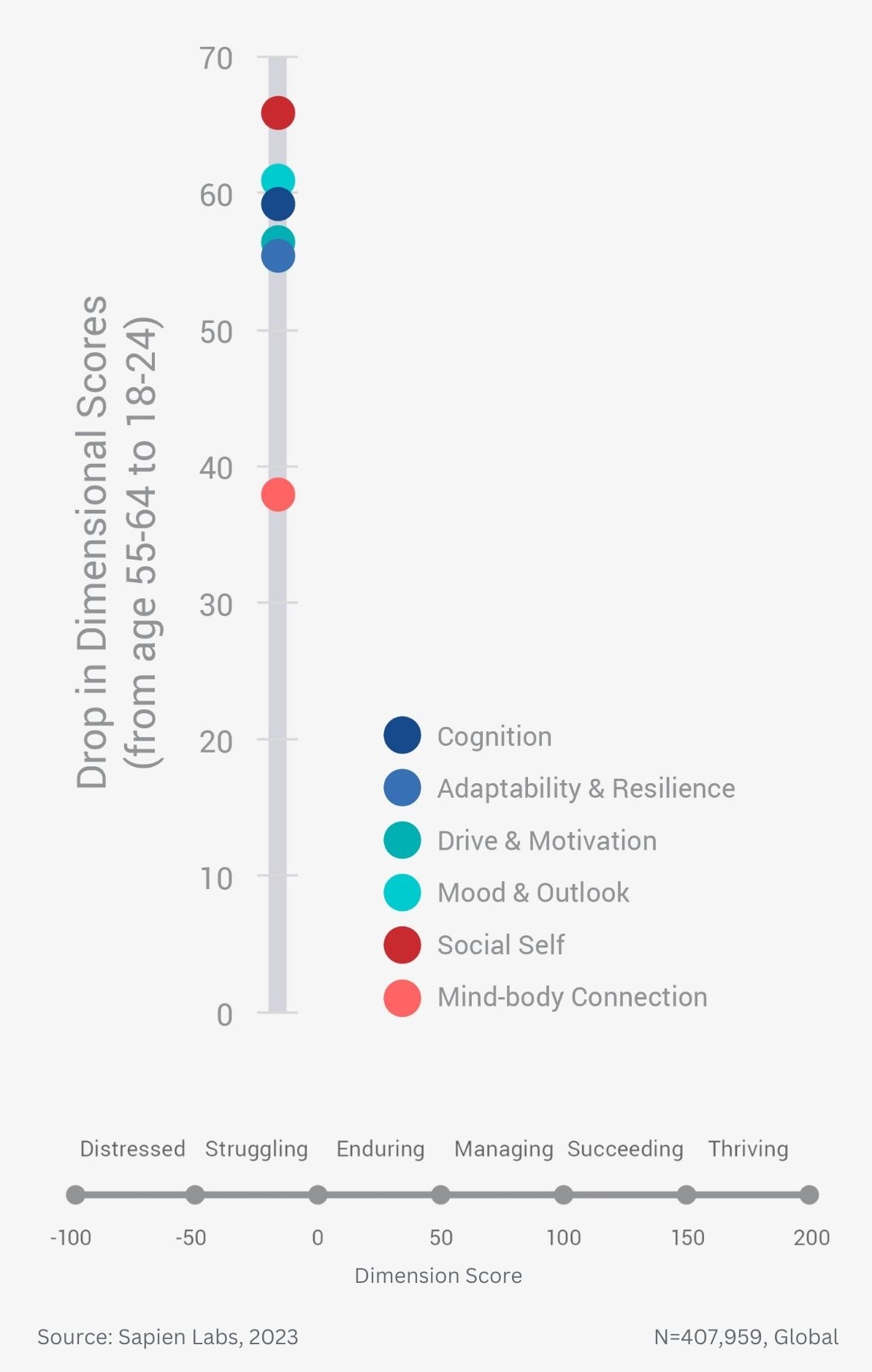
Difference in mental wellbeing between older and younger adults across the 6 dimensions – Average score
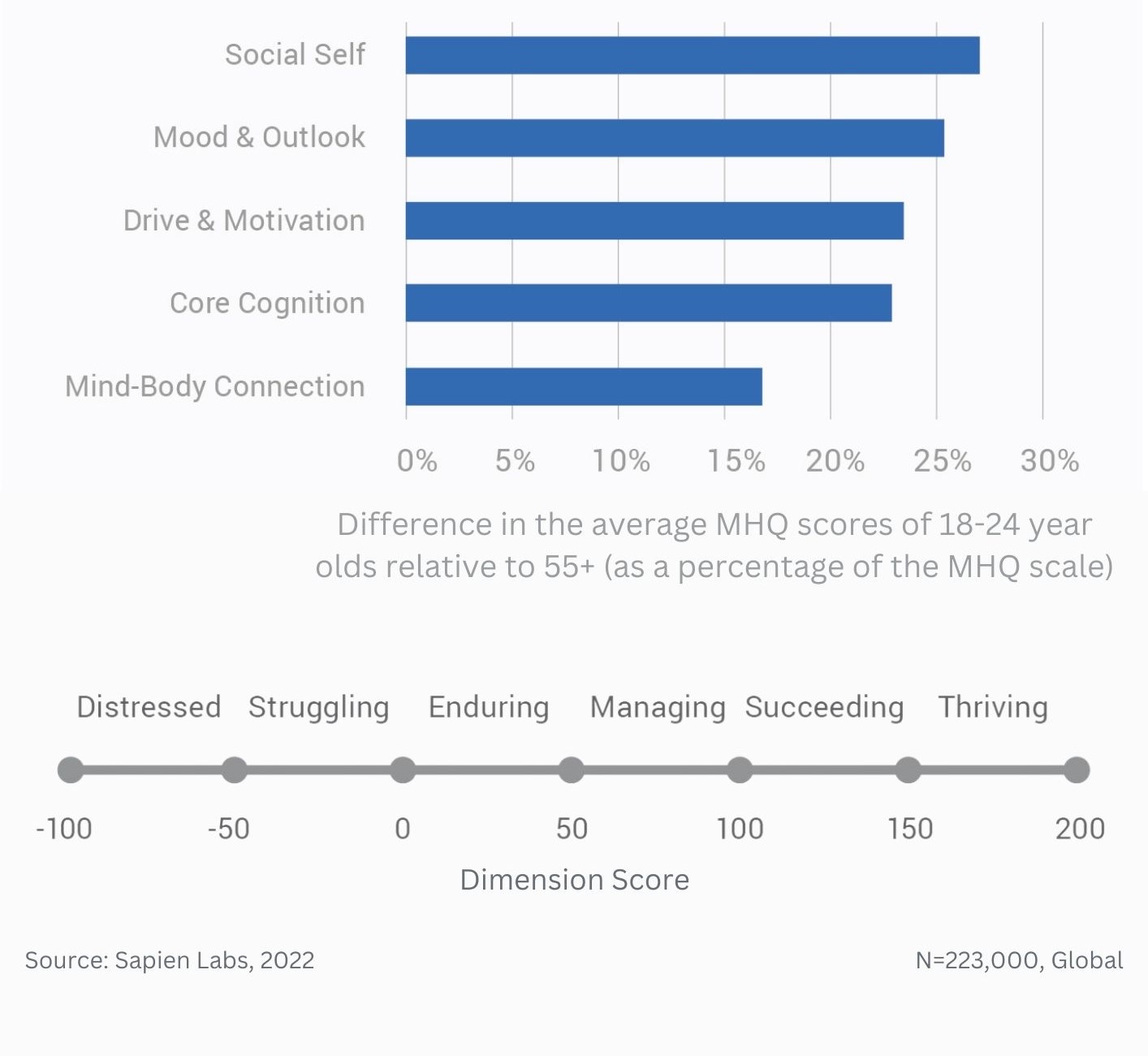
Difference in mental wellbeing between older and younger adults across the 6 dimensions – % Distressed or Struggling
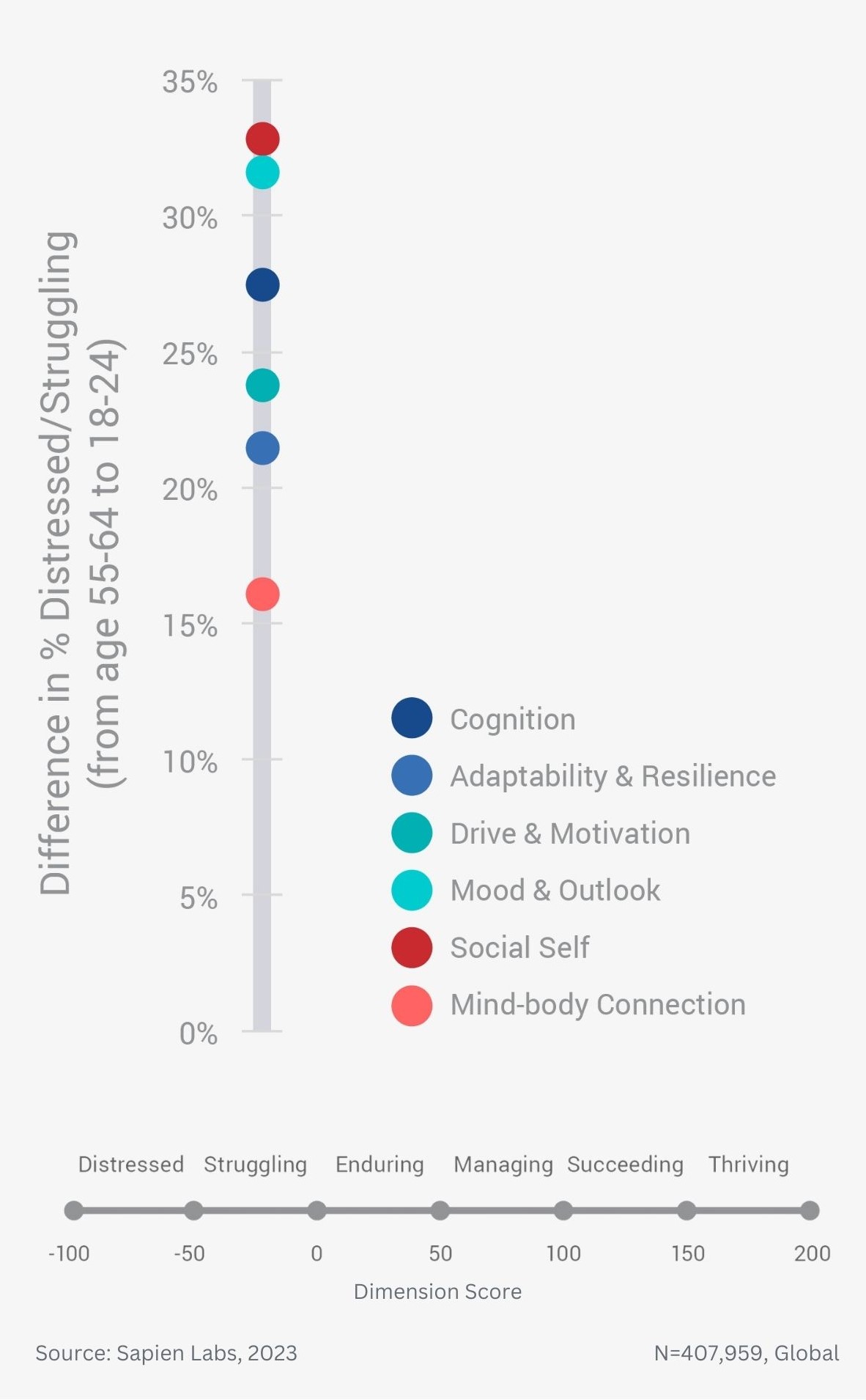
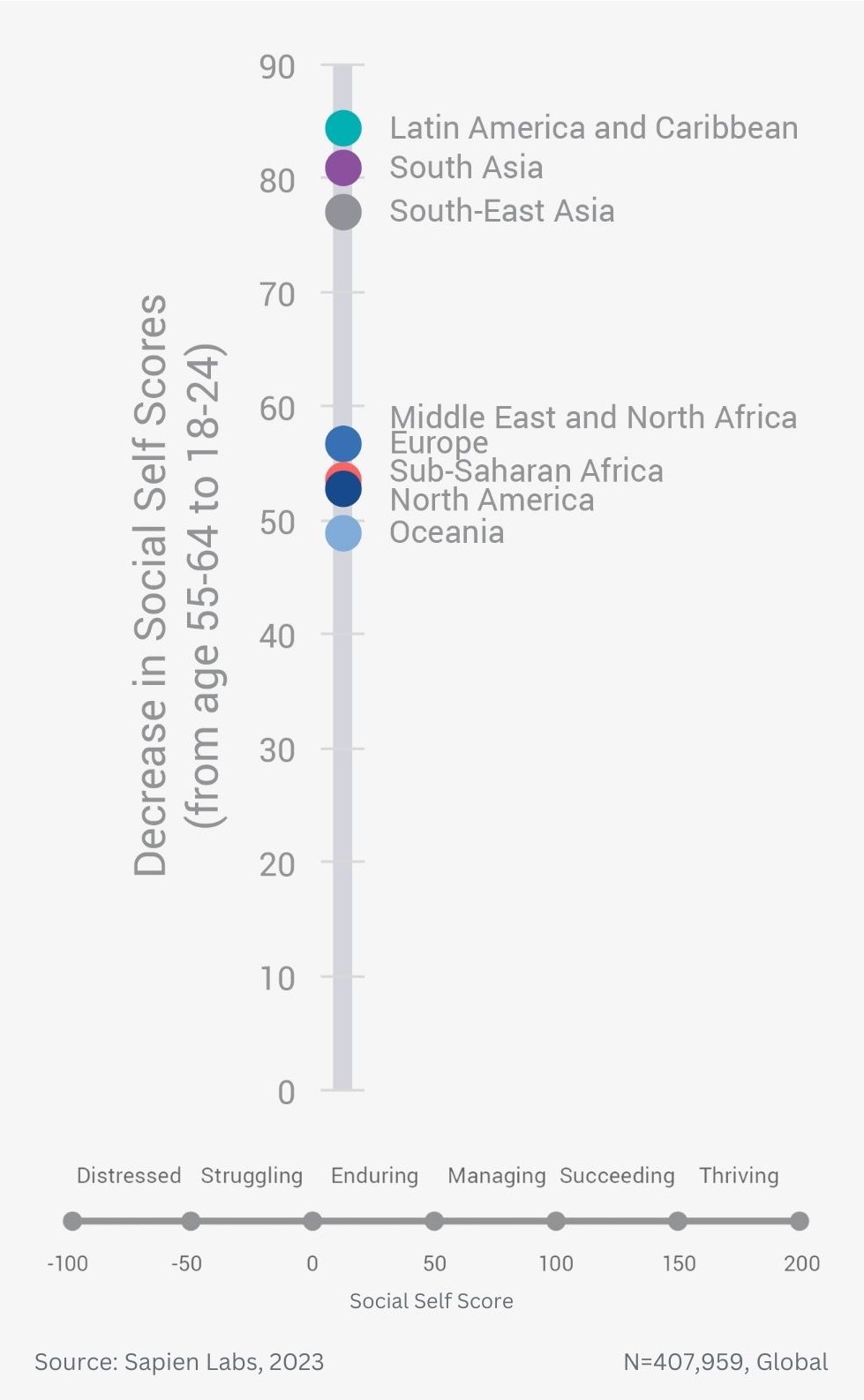
Difference in % Distressed or Struggling between older and younger adults across for Social Self – geographic regions
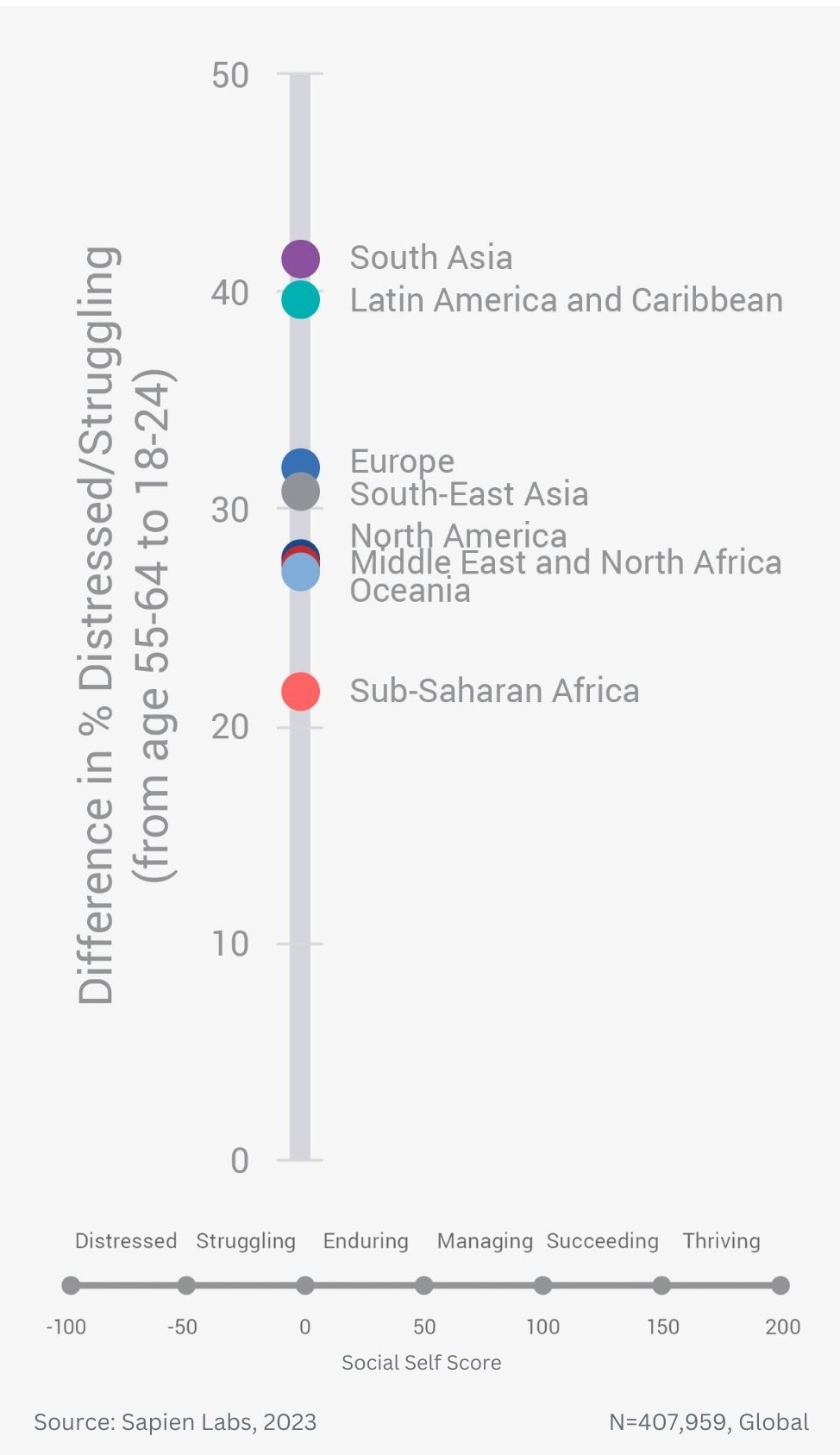
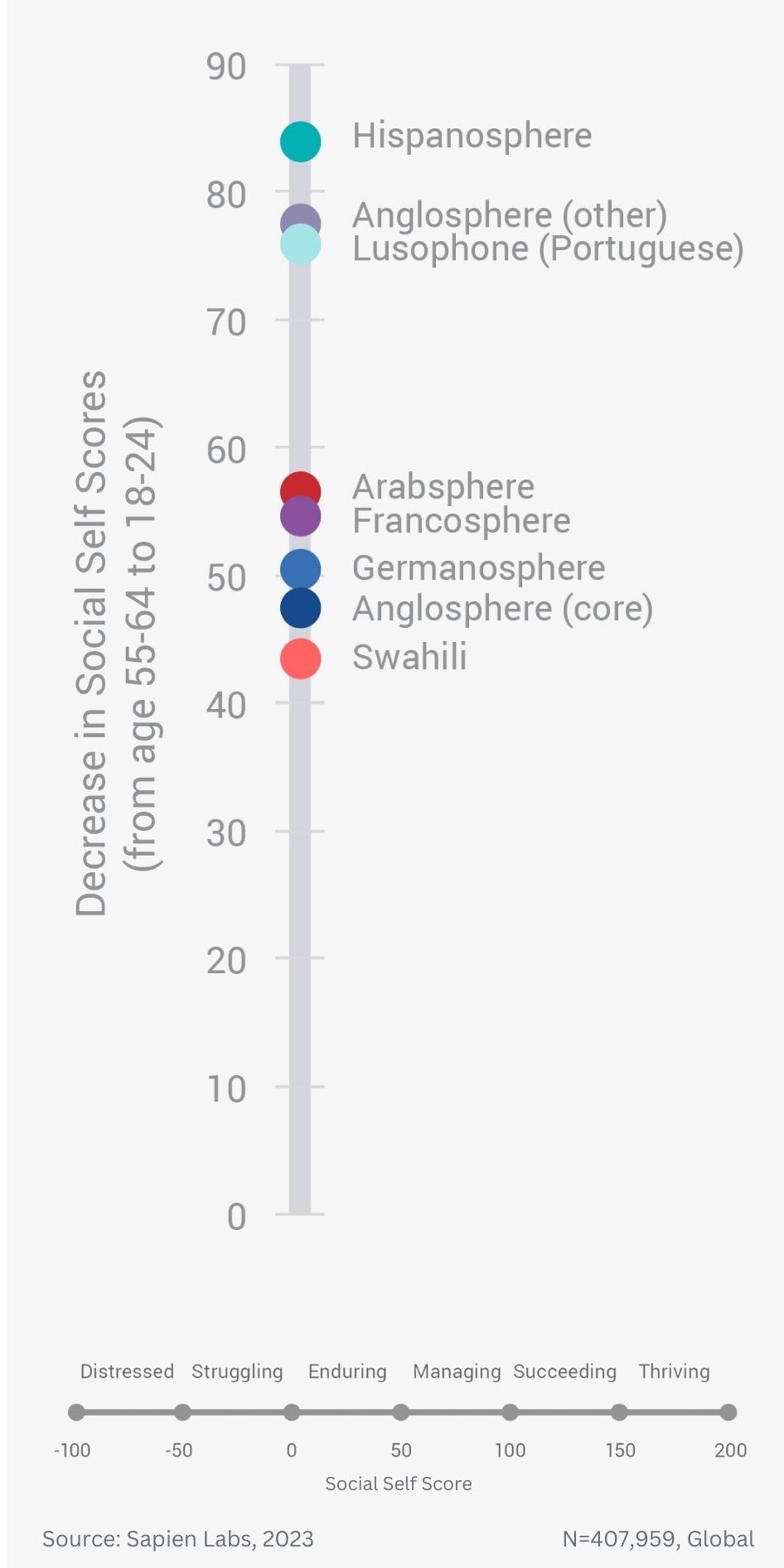
Difference in % Distressed or Struggling between older and younger adults across for Social Self – language groups
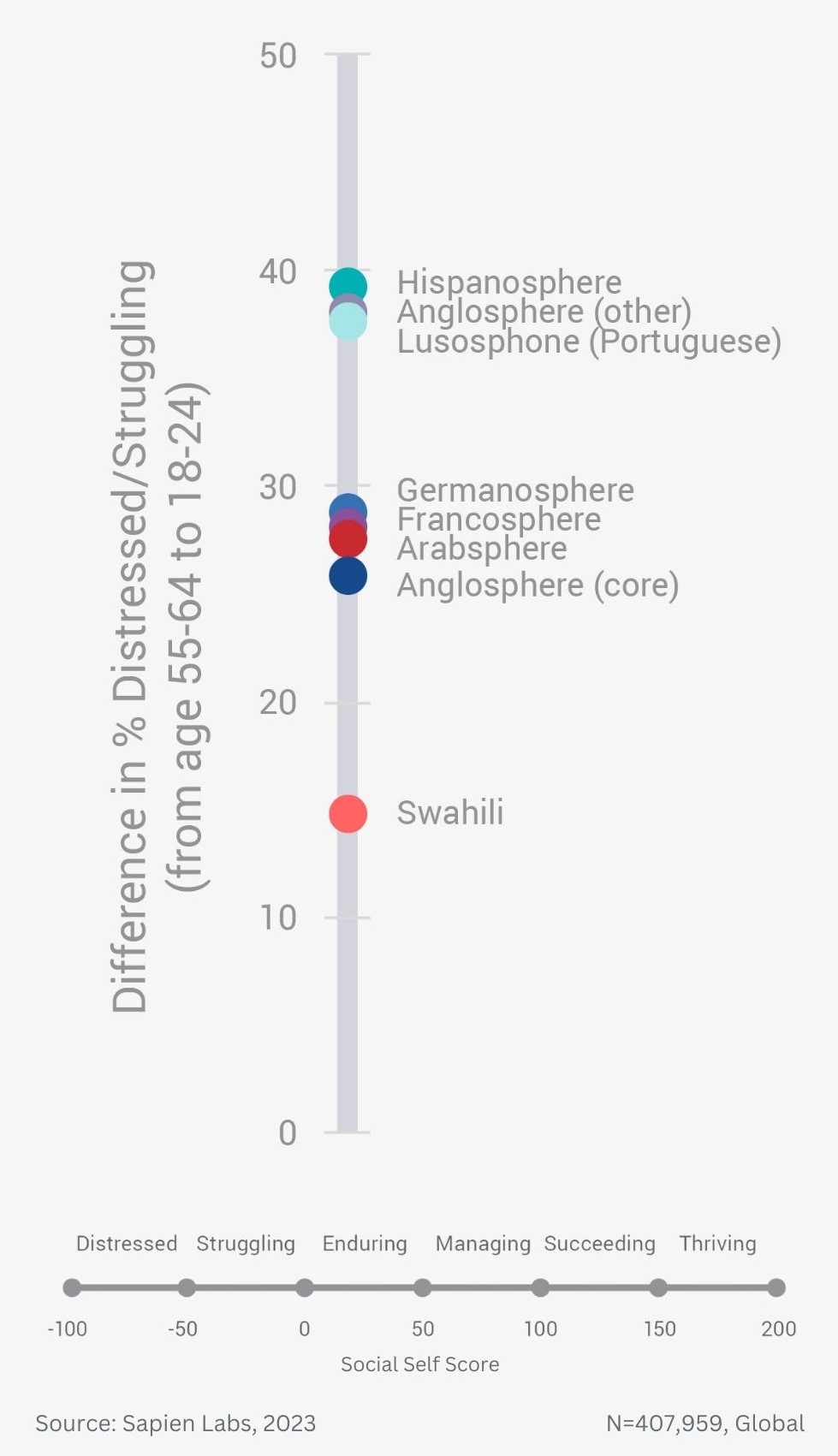
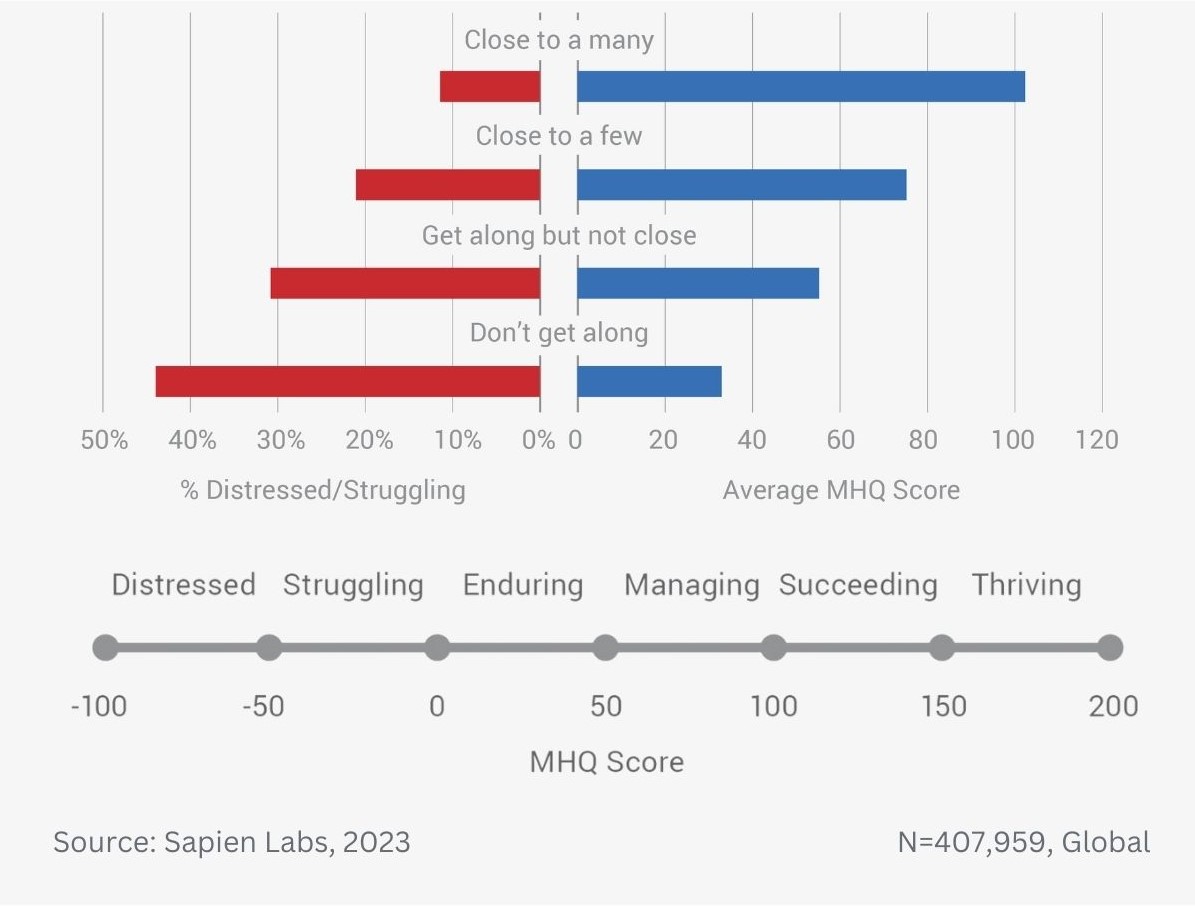
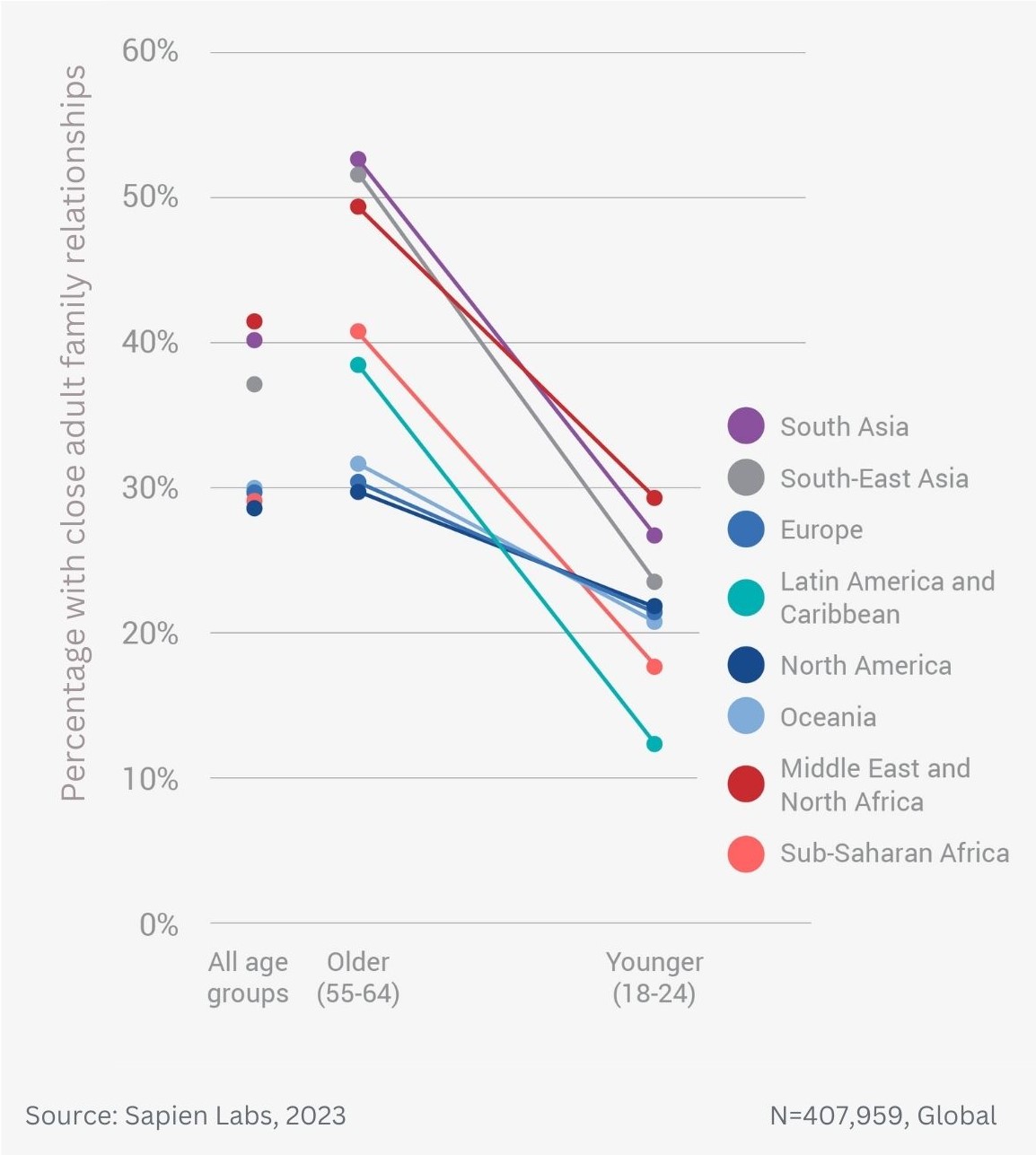
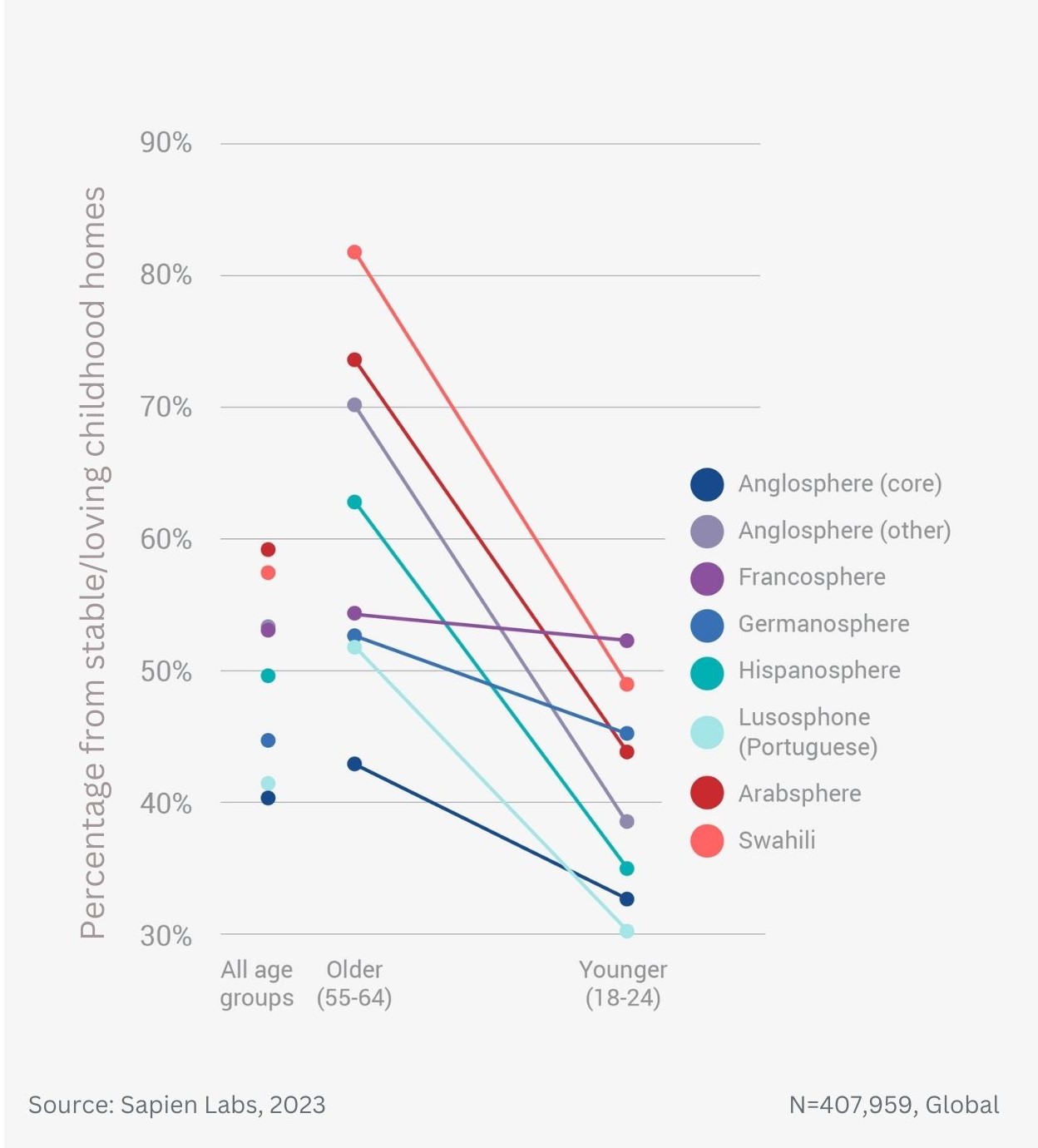
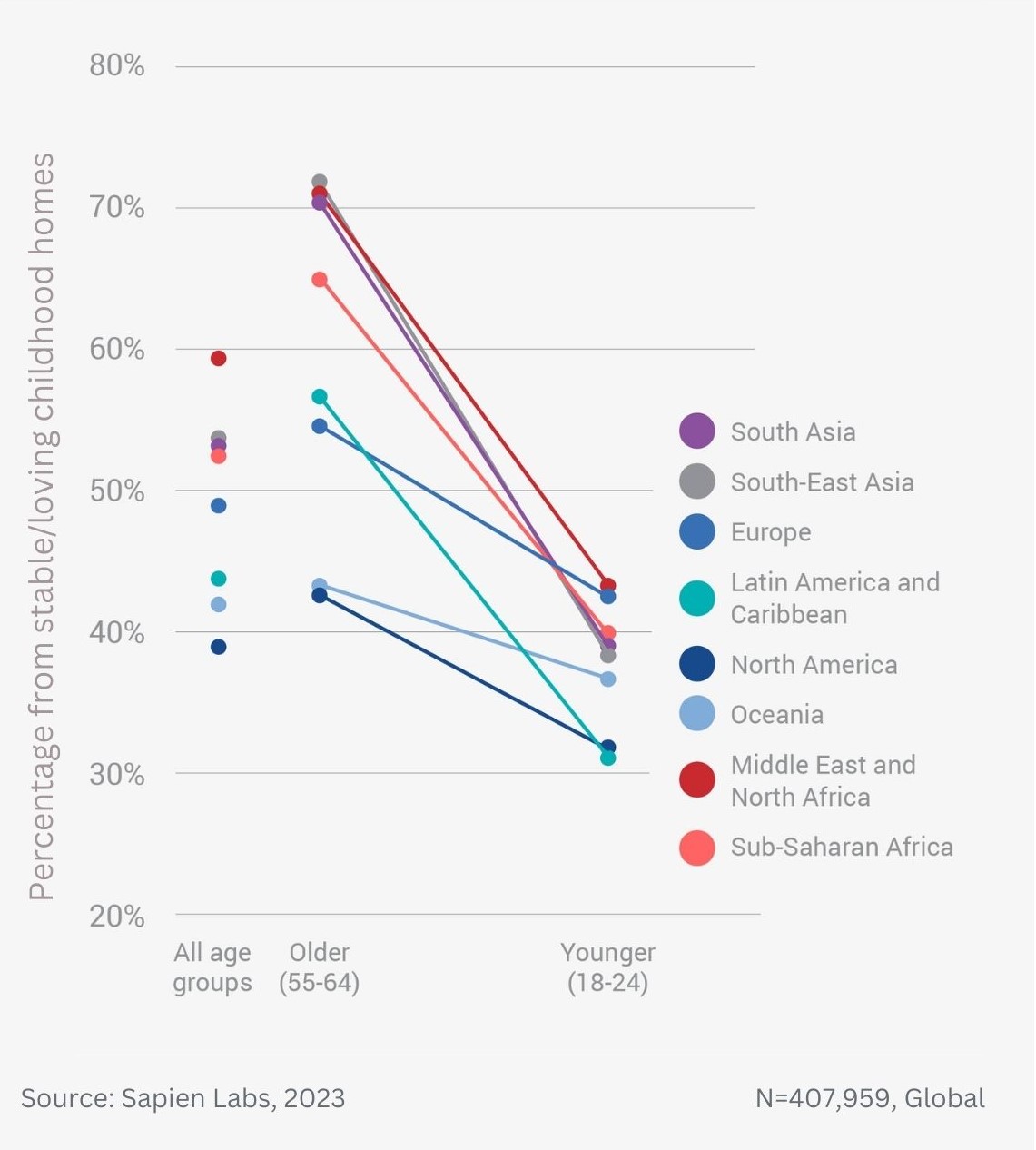
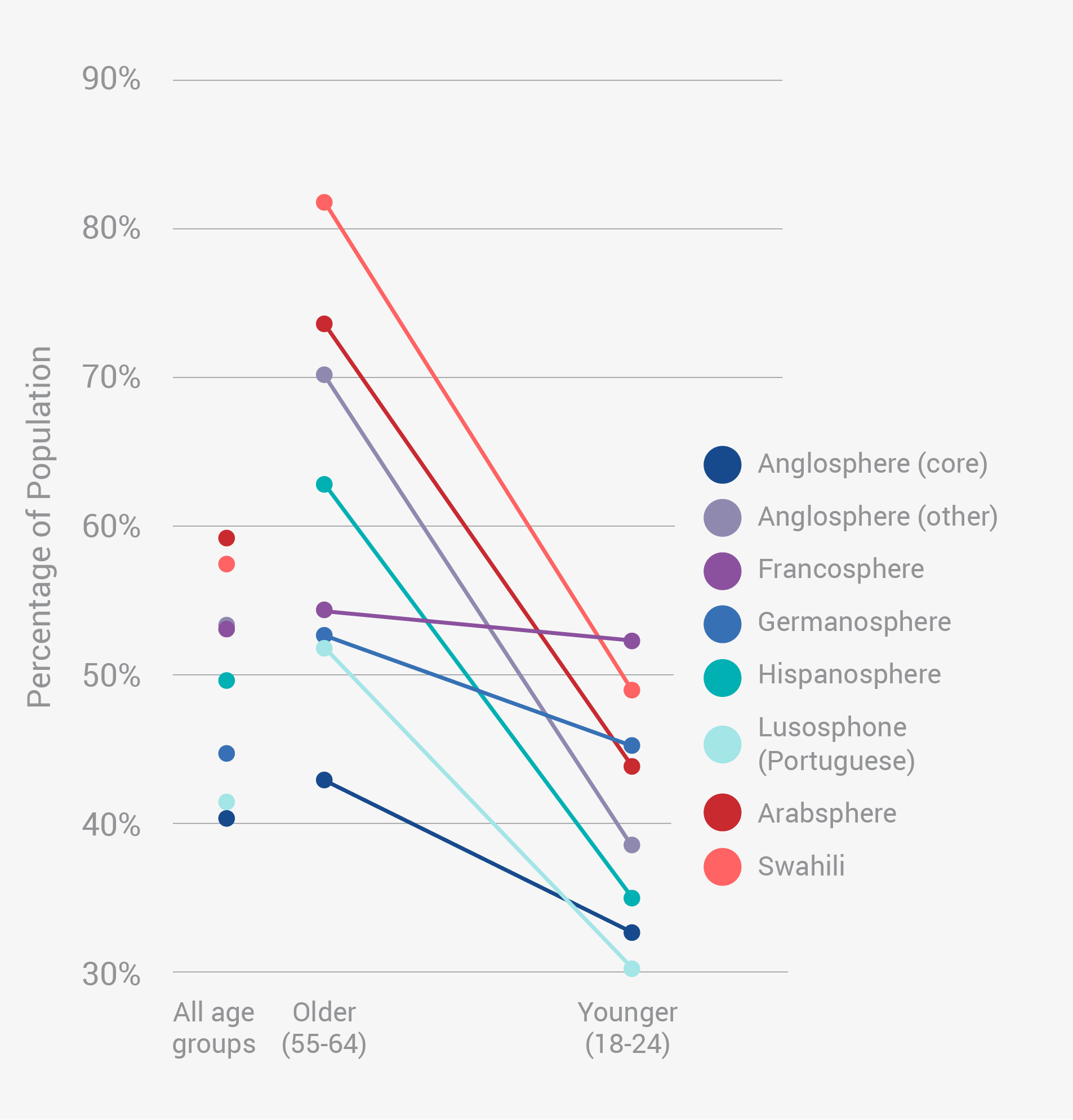
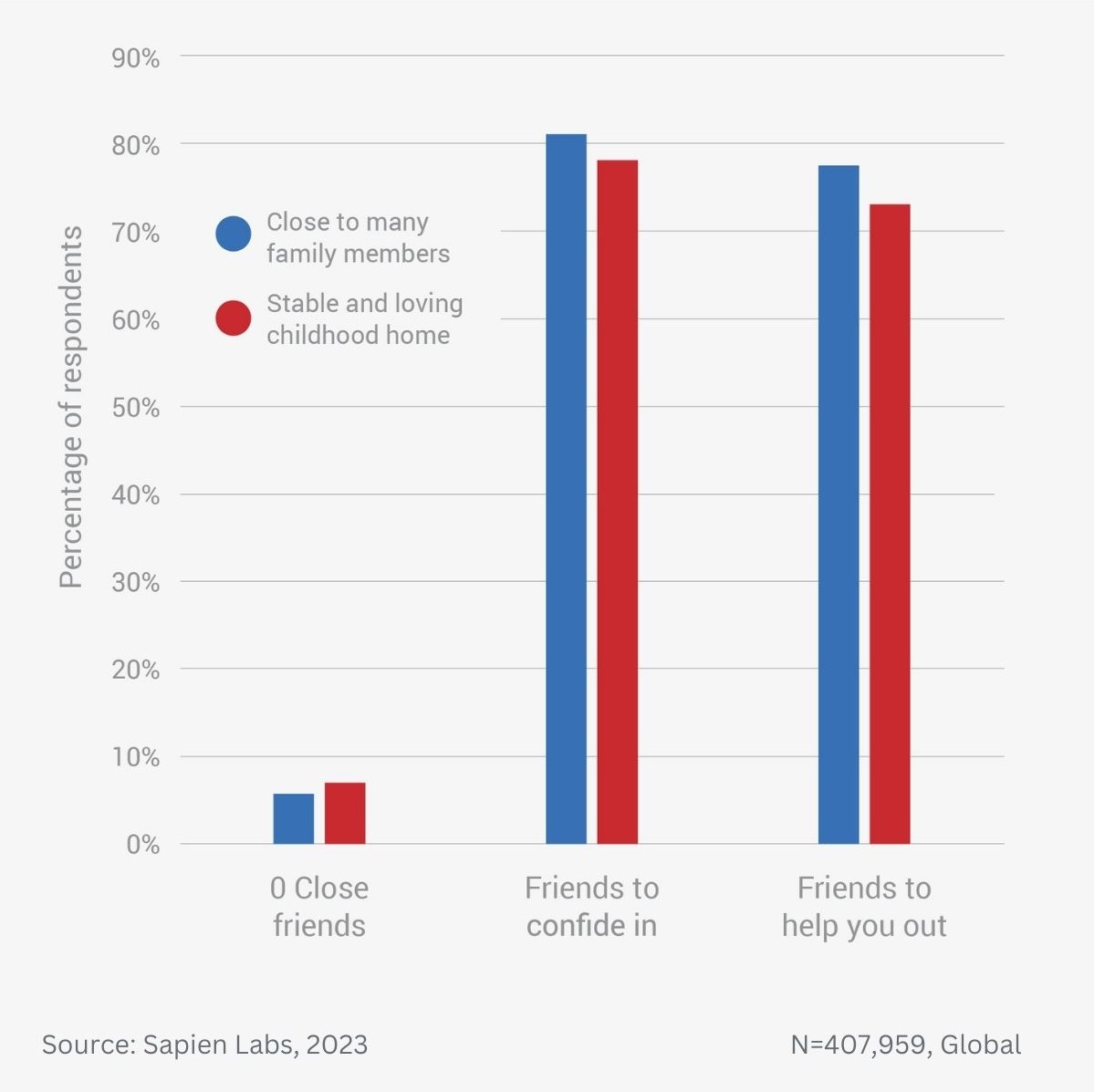
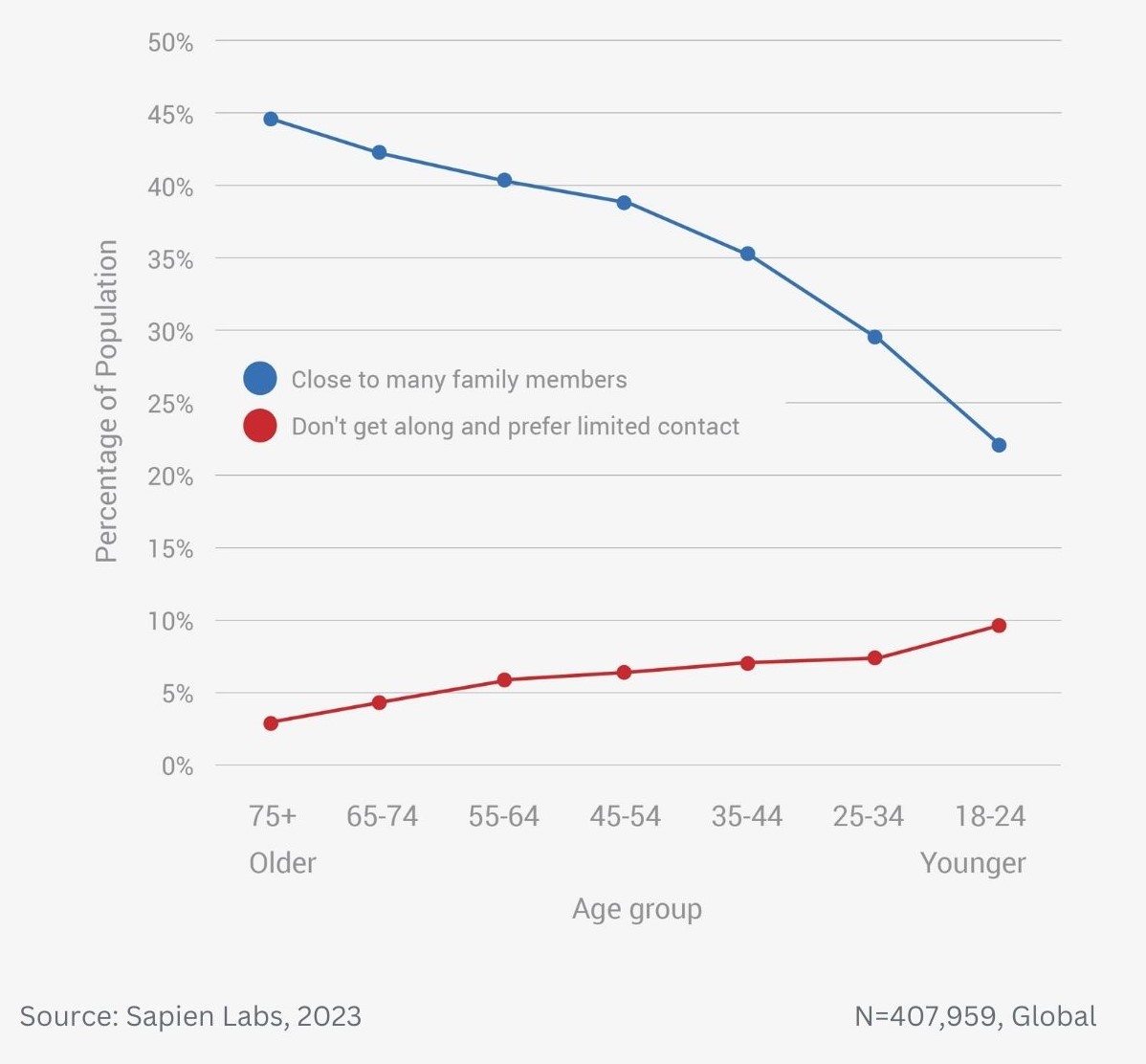
Older adults are twice as likely to be close to many of their adult family members as the youngest adults
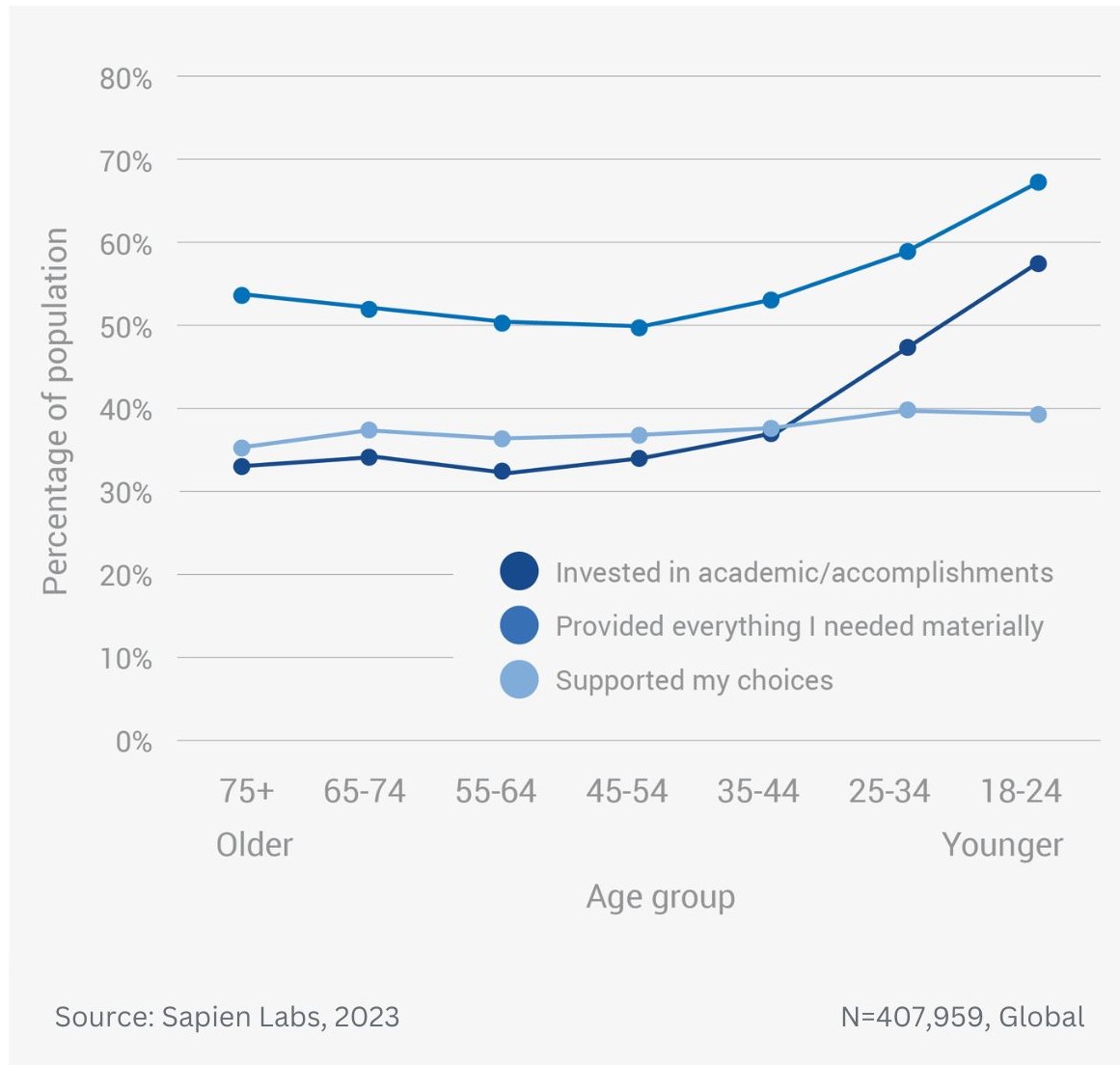
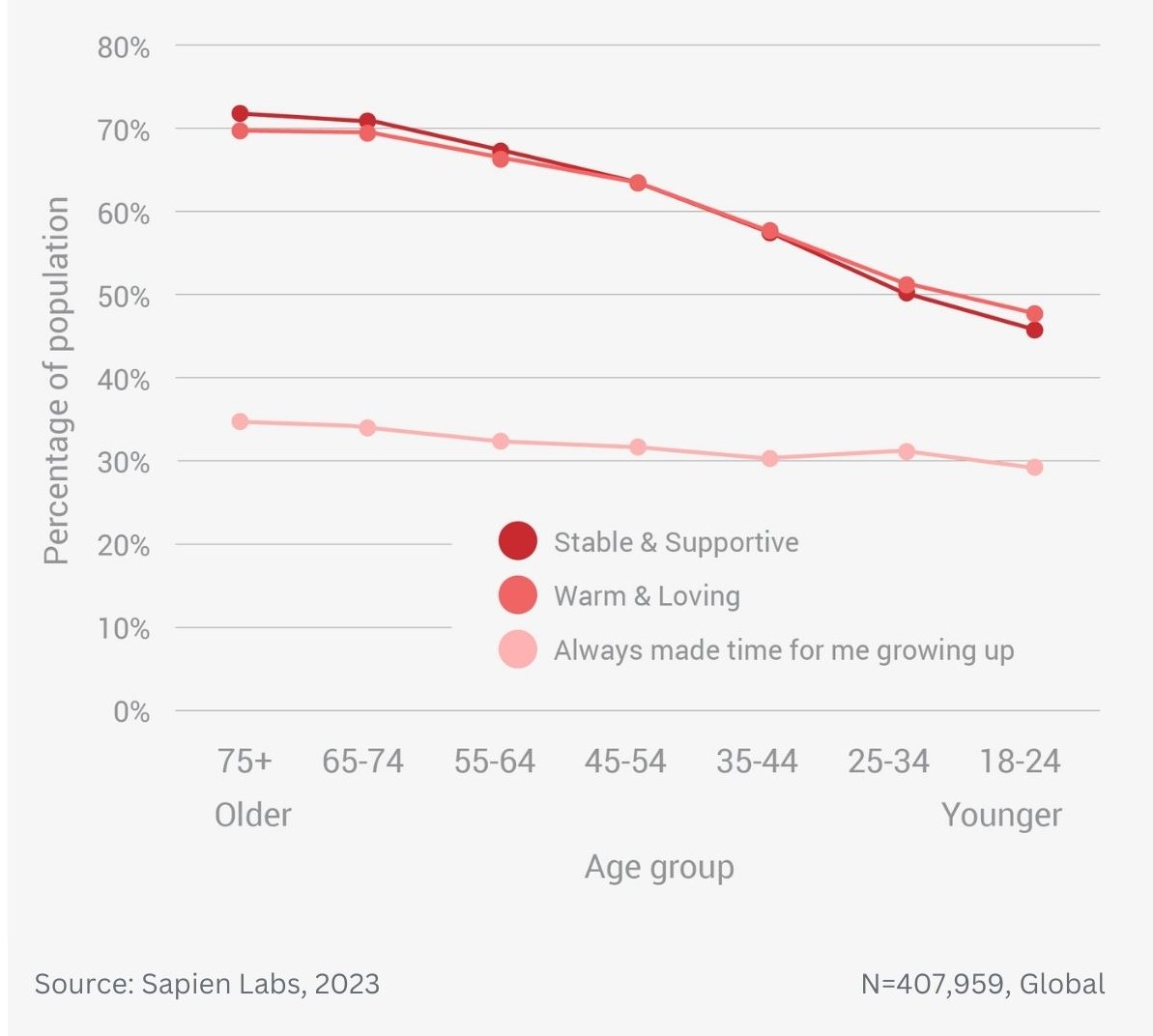
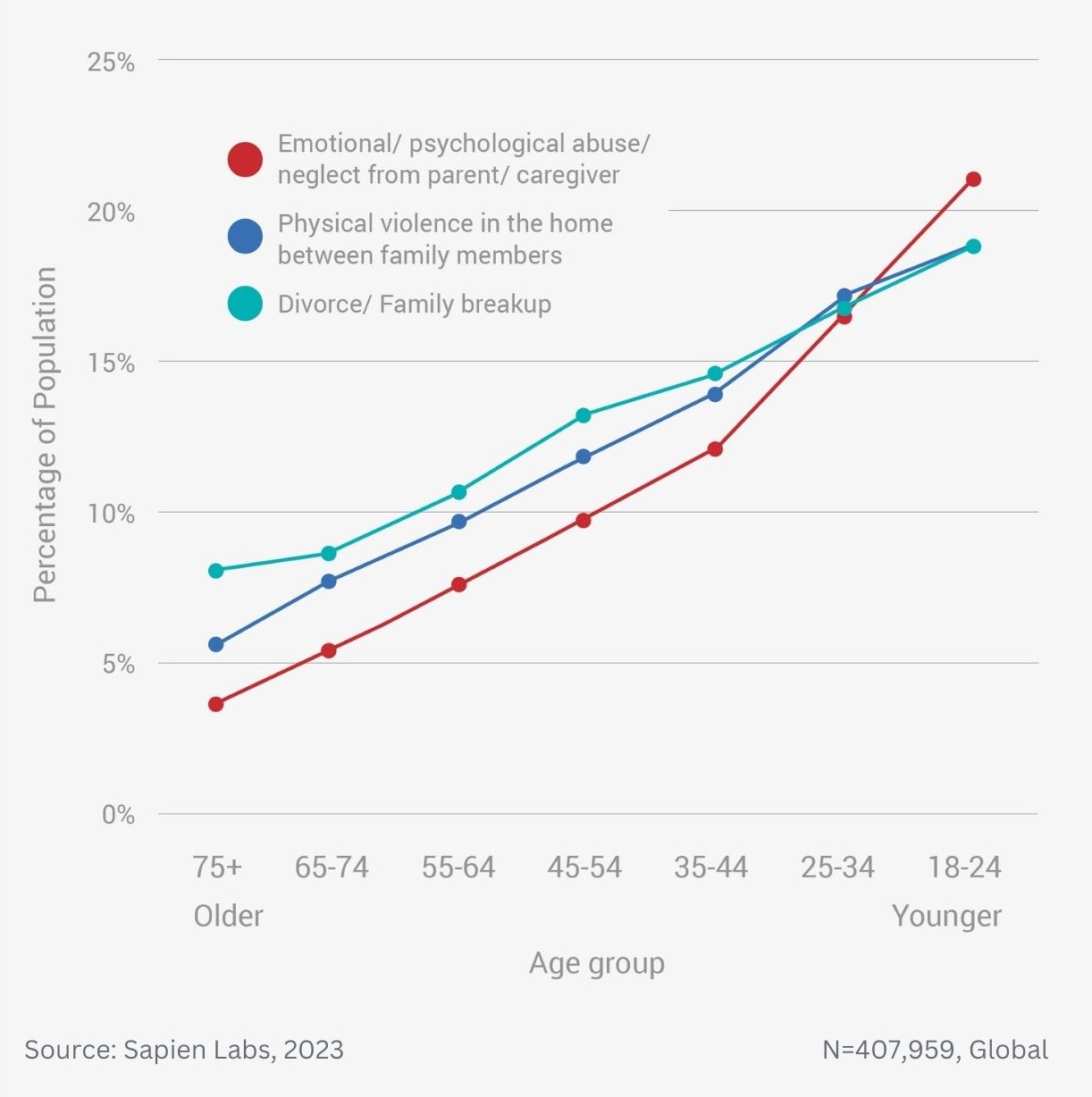
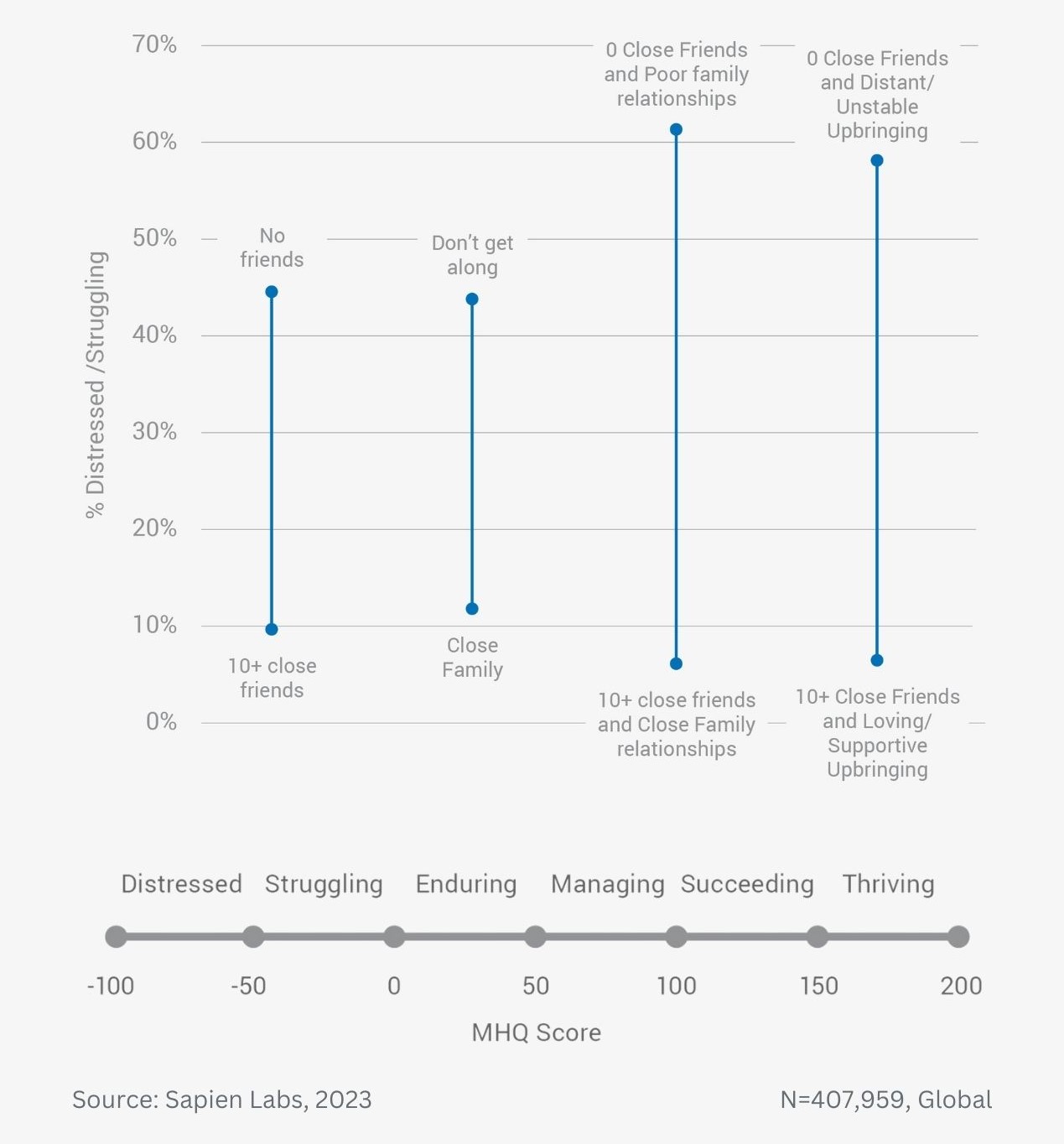
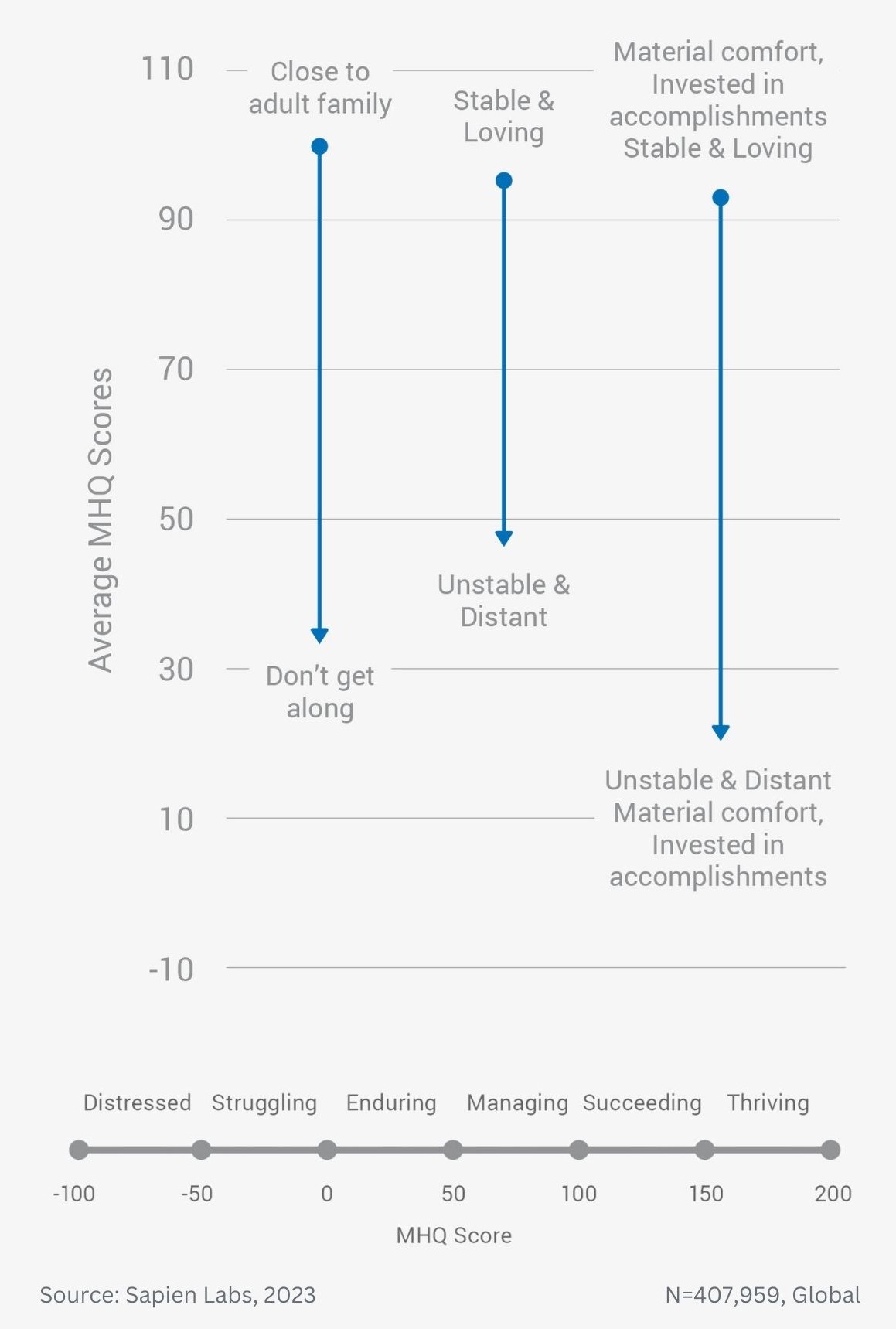
Difference in mental wellbeing based on childhood home and adult family relationships – average MHQ score
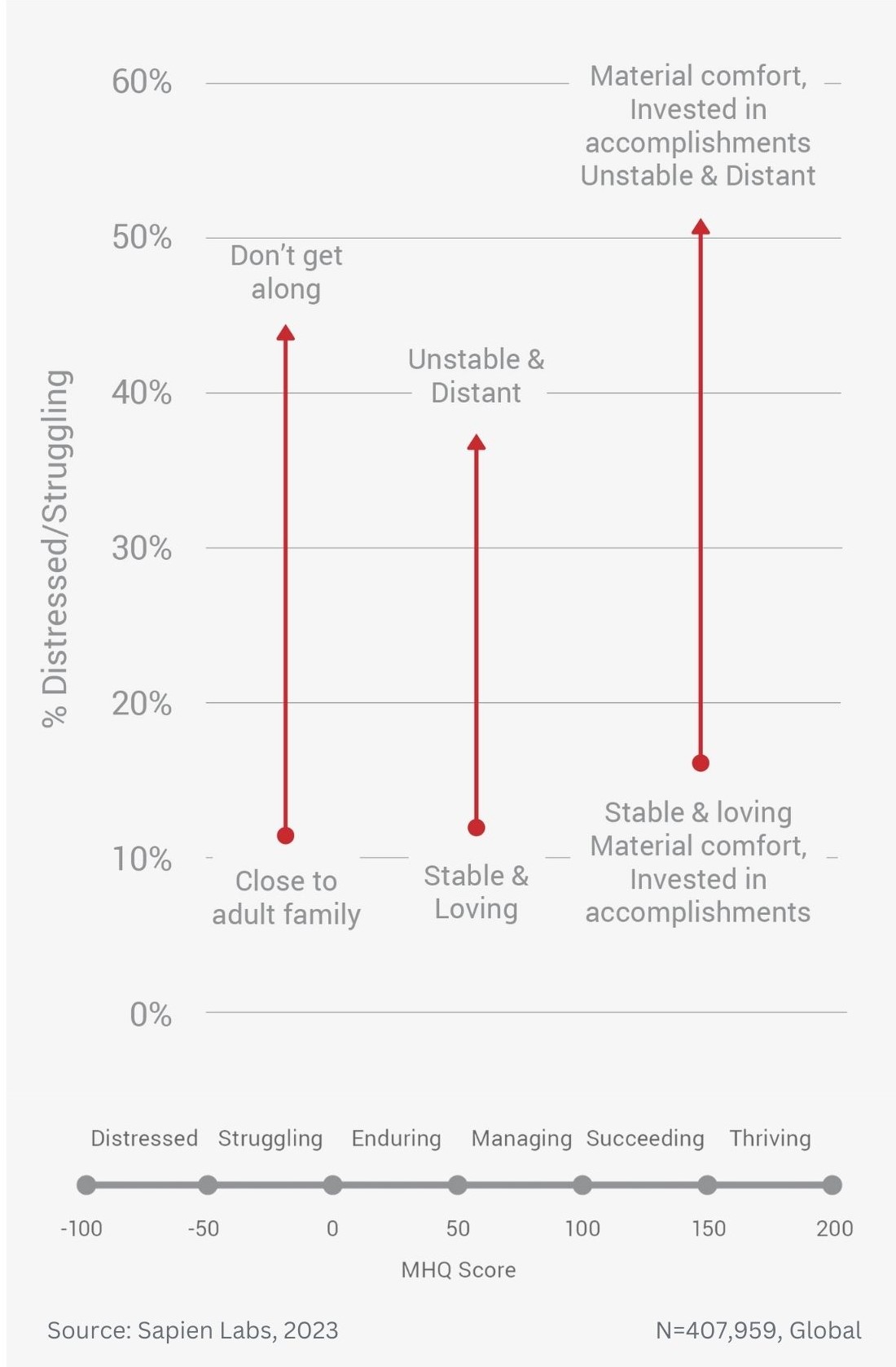
Difference in mental wellbeing based on childhood home and adult family relationships – % Distressed or Struggling
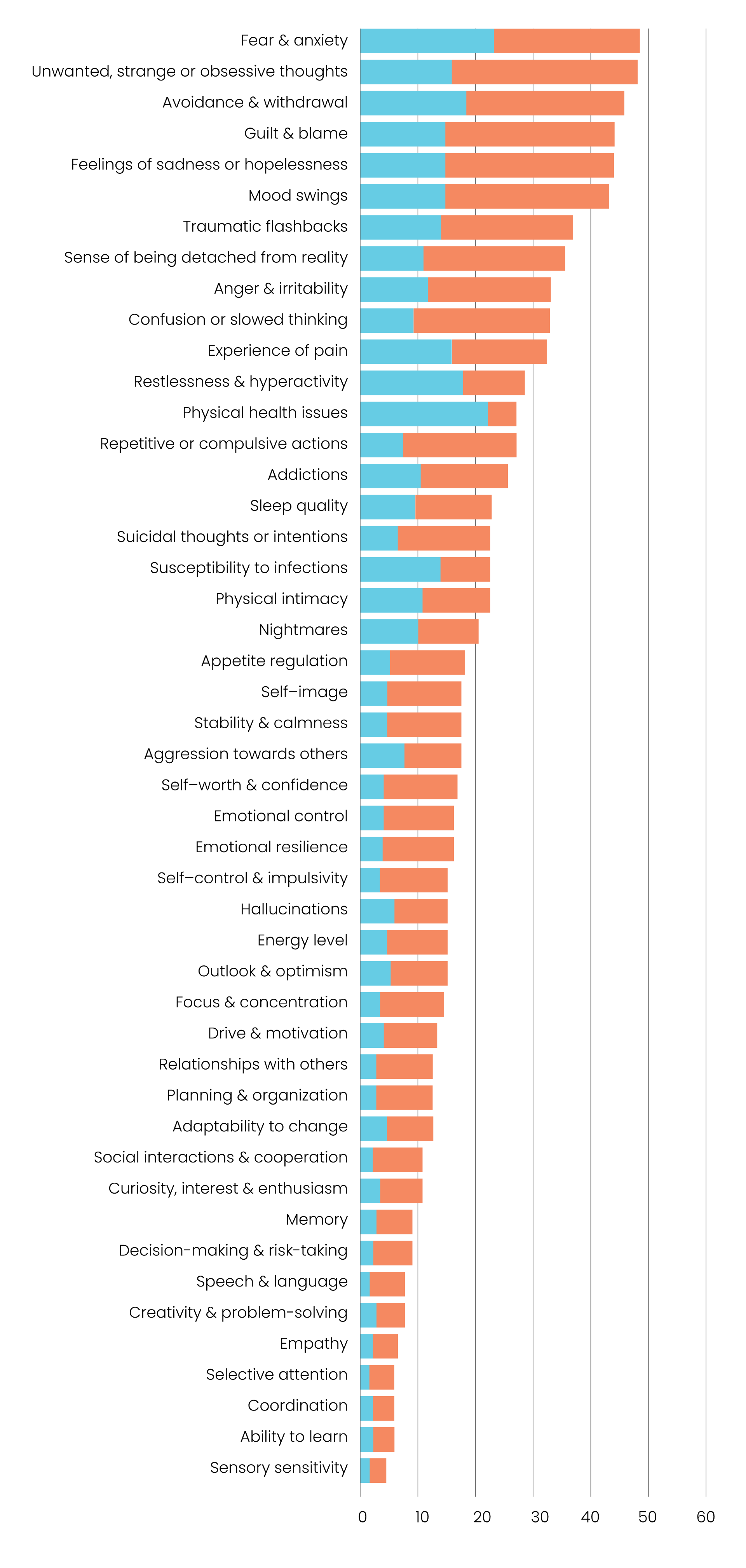
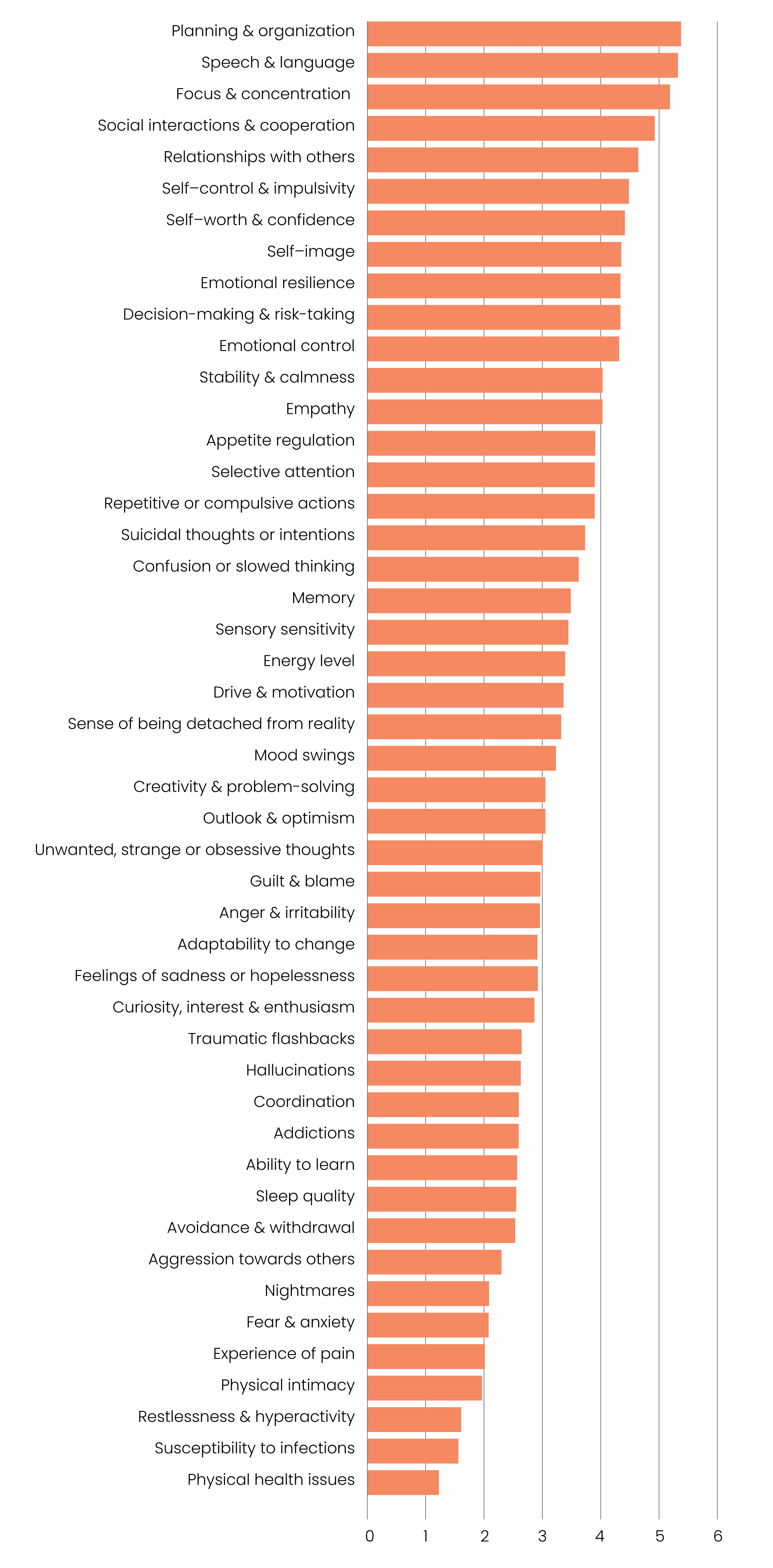
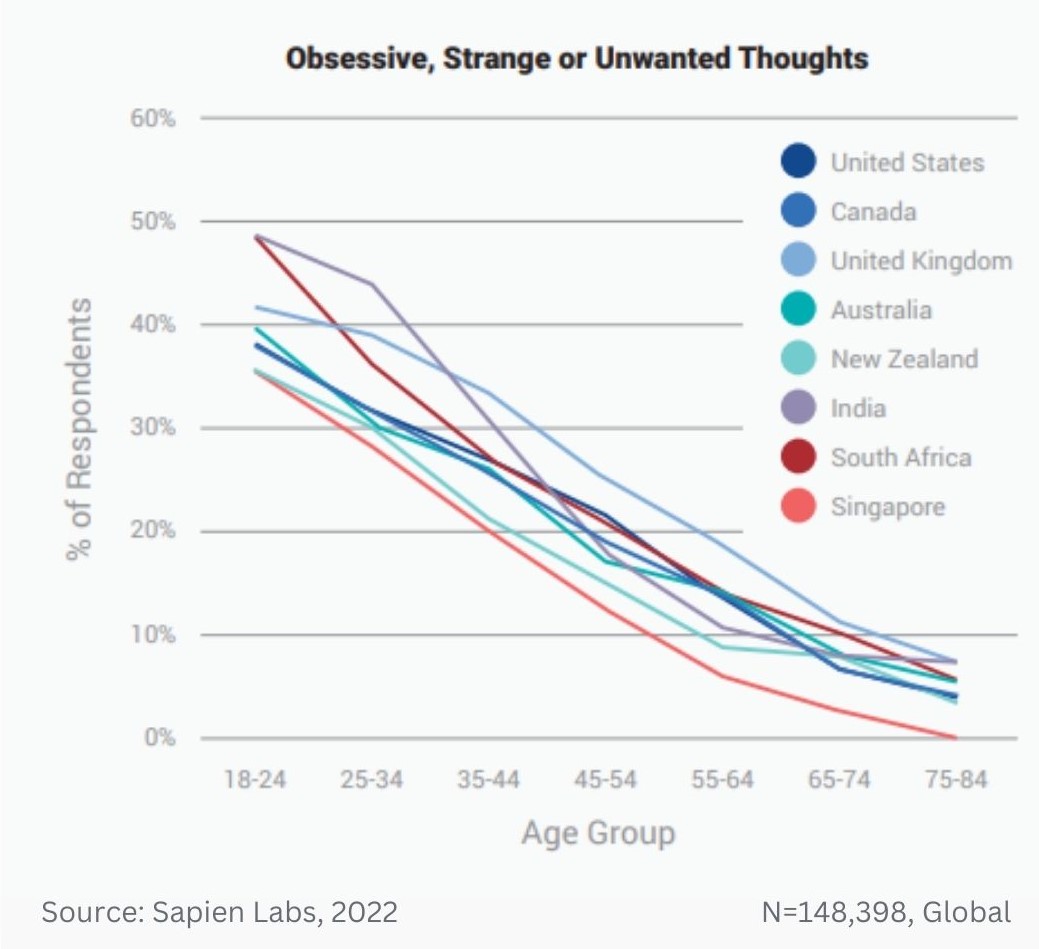
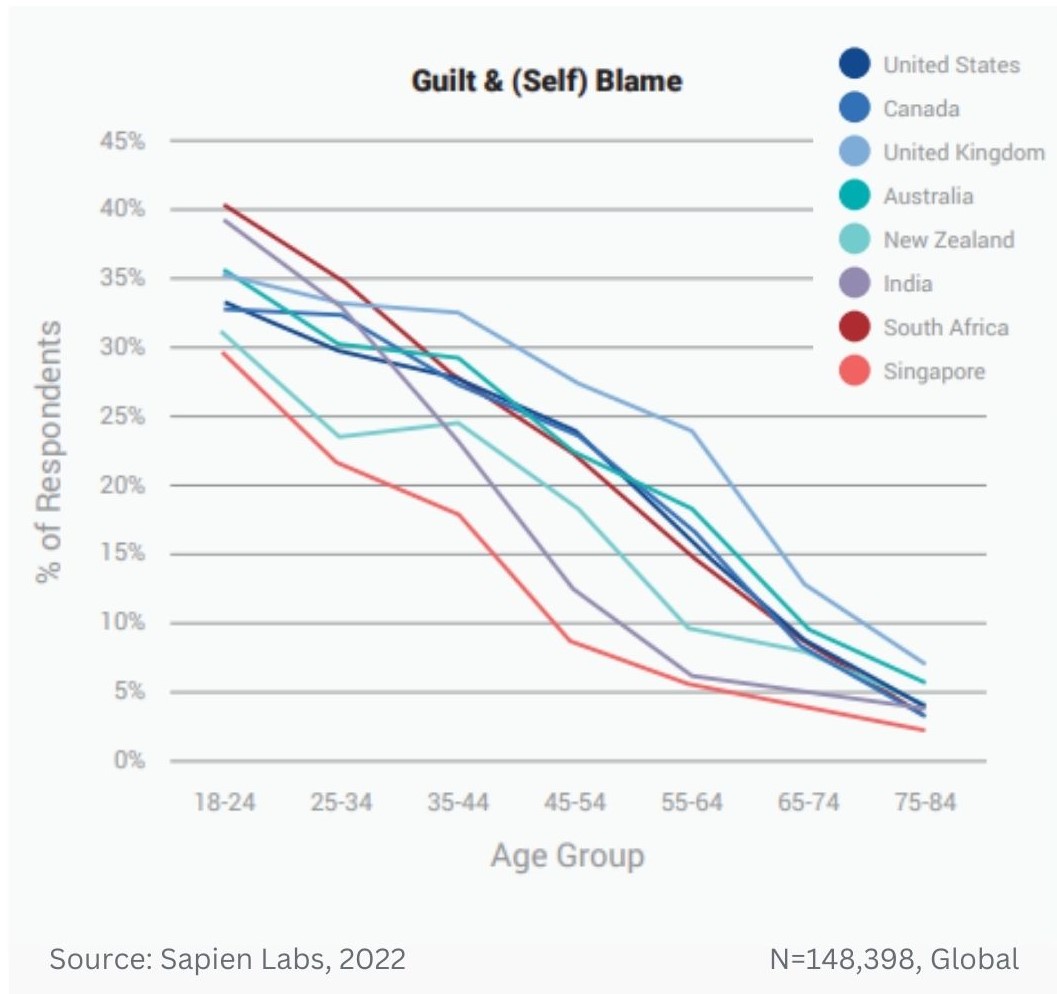
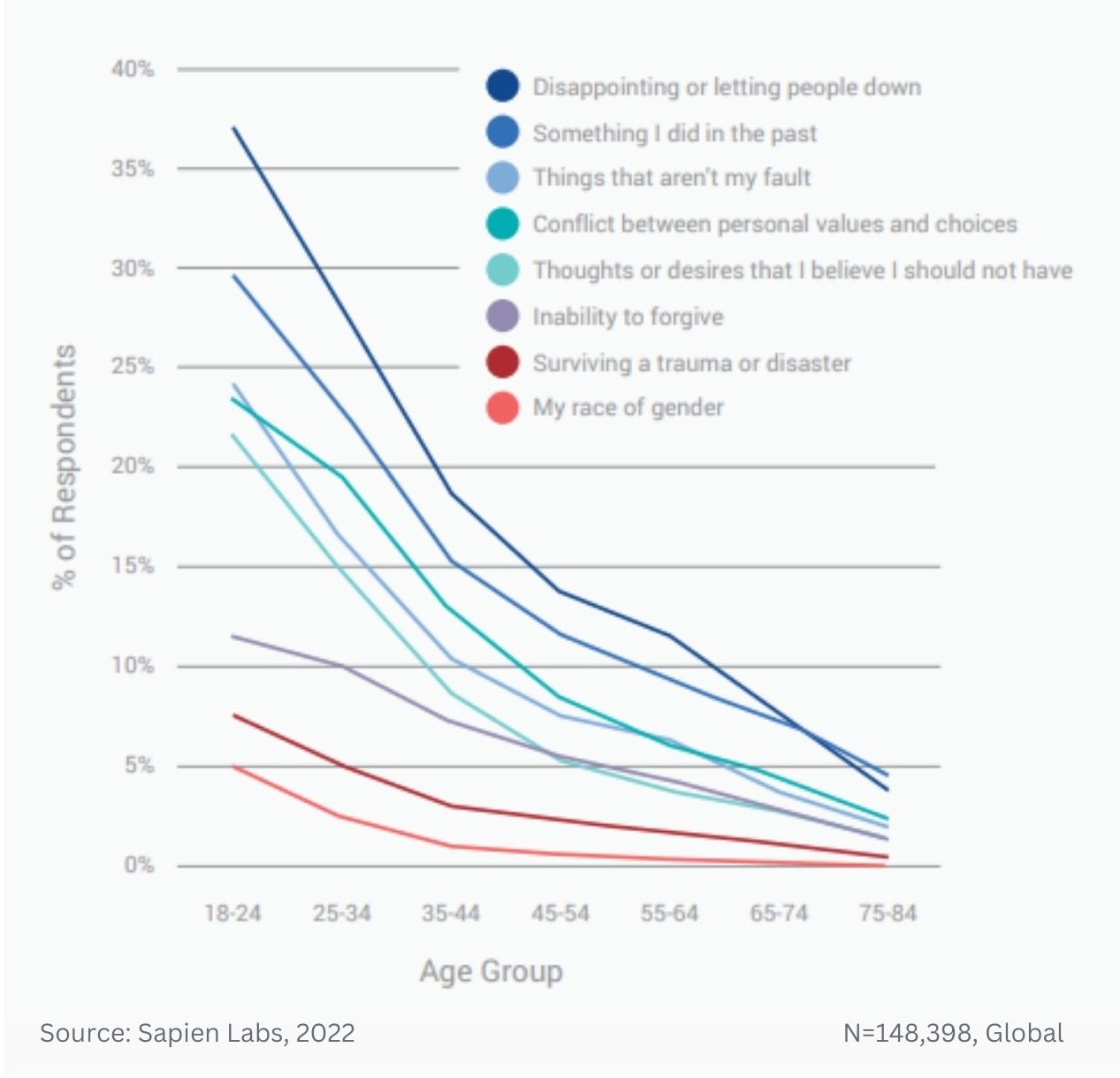
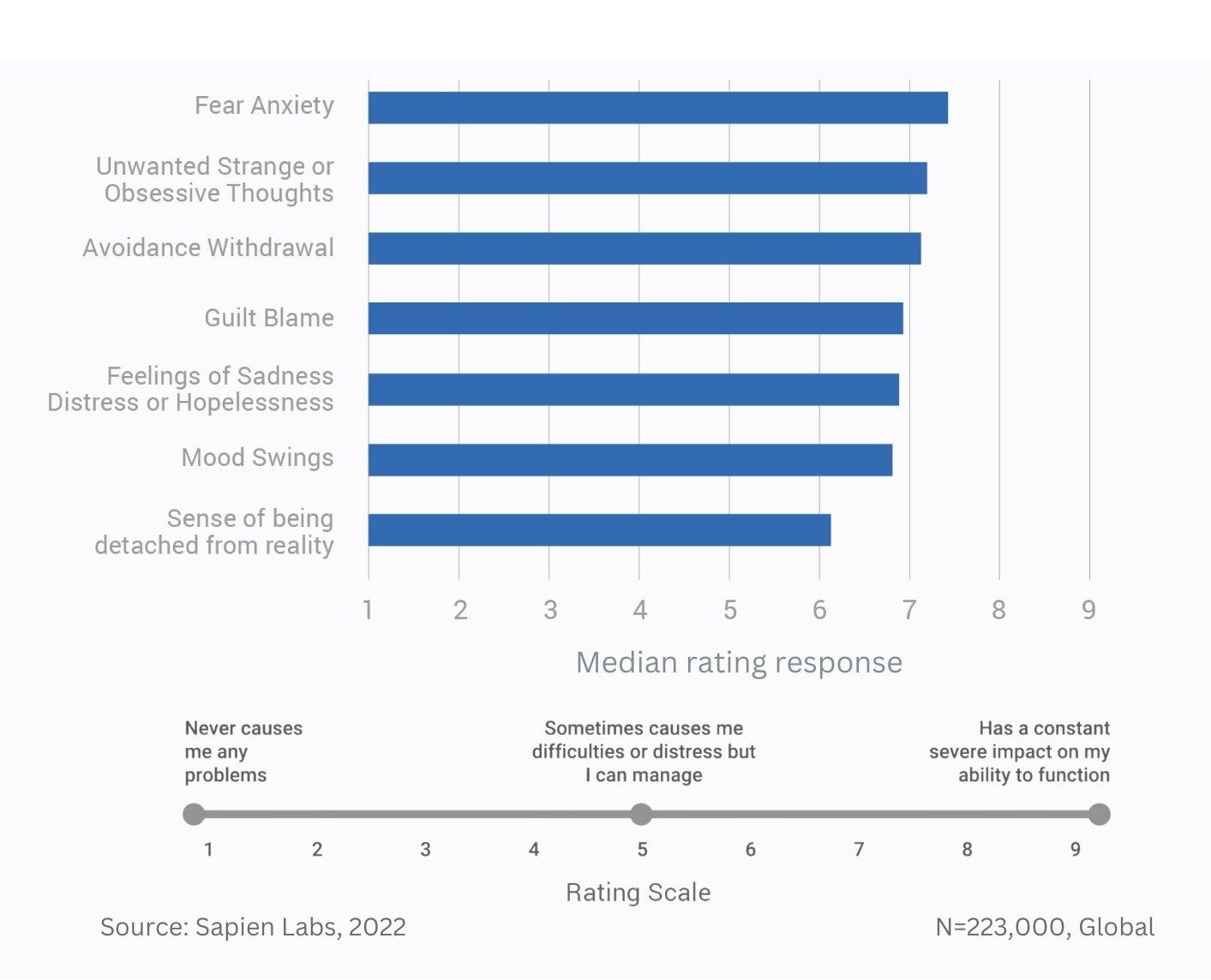
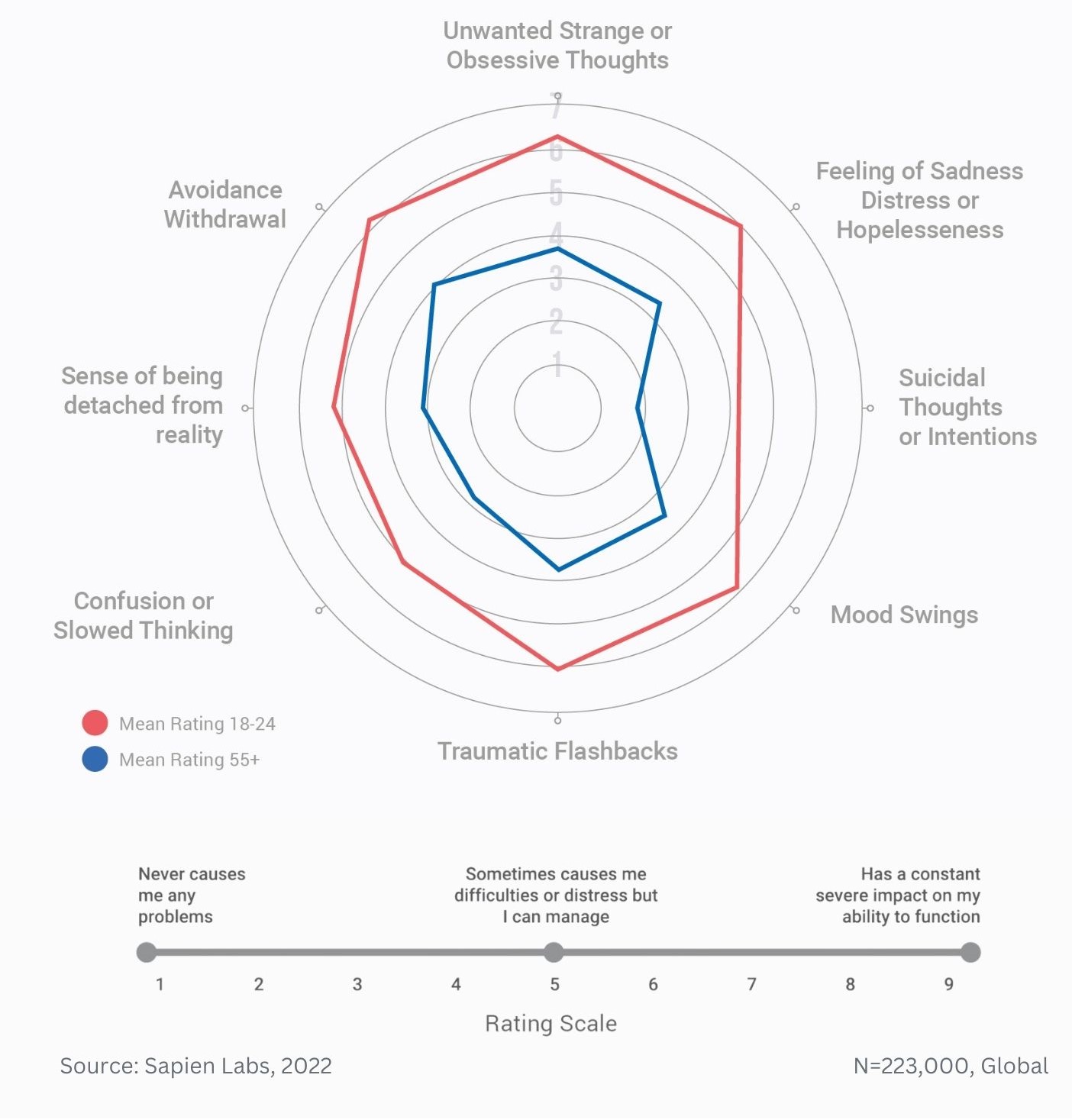
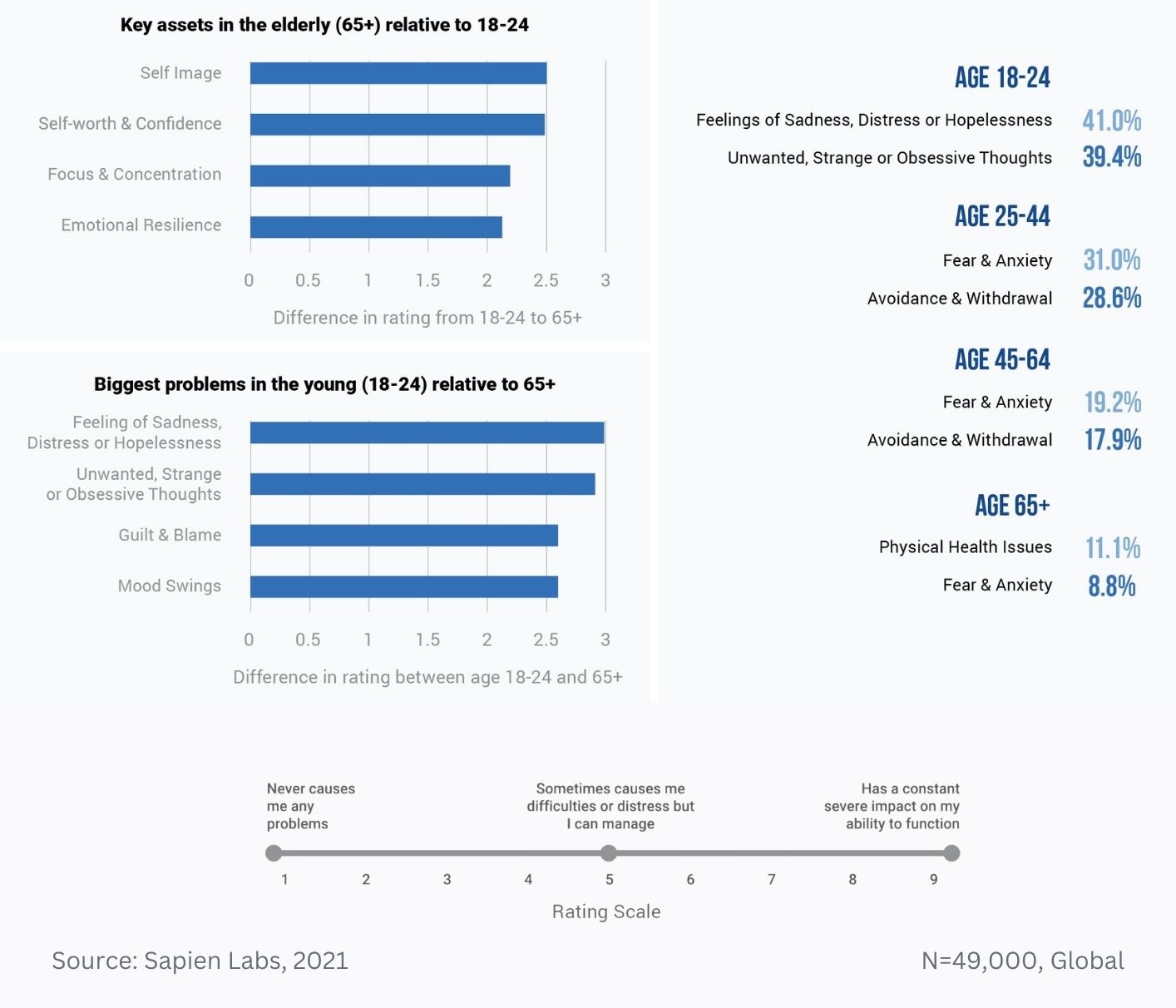
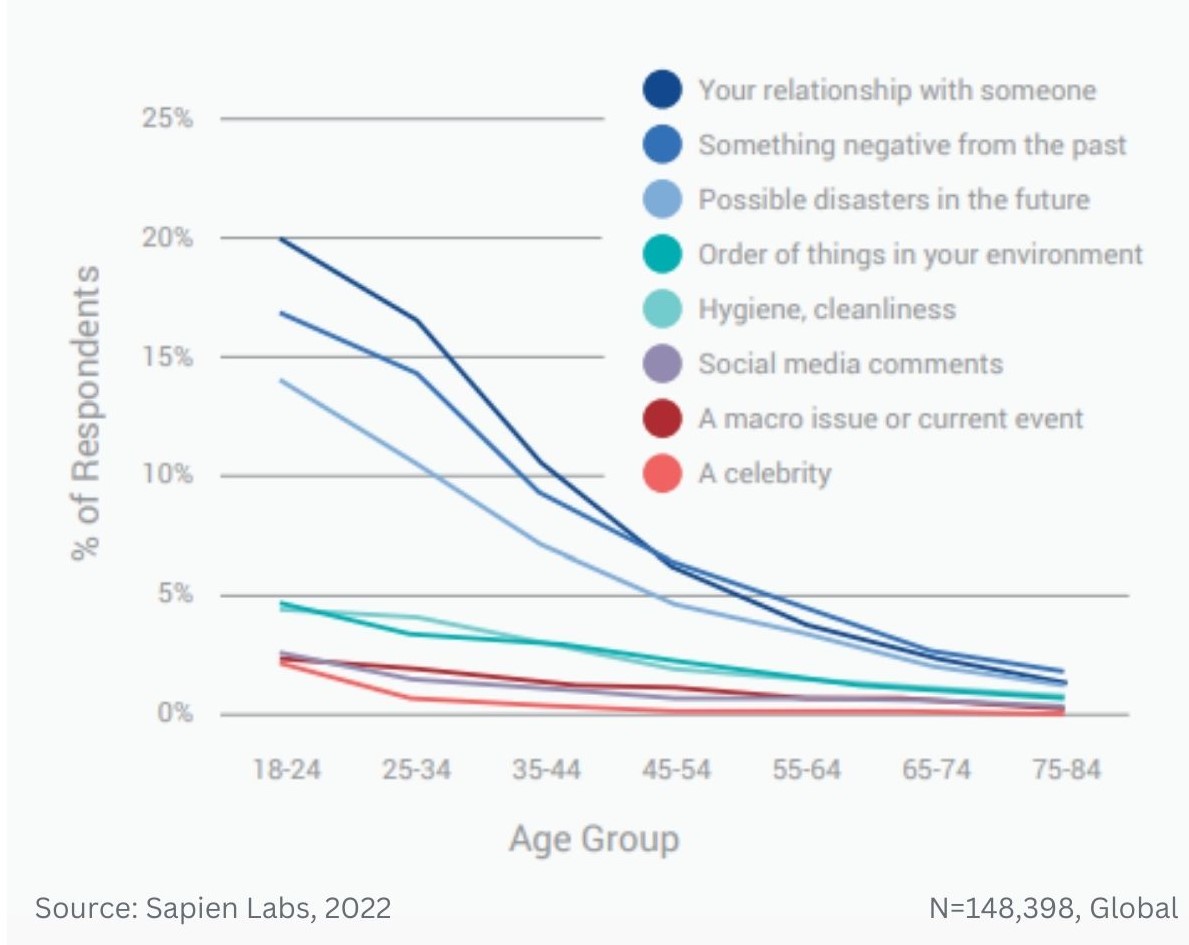
Prevalence of different types of debilitating obsessive, strange, and unwanted thoughts across age groups
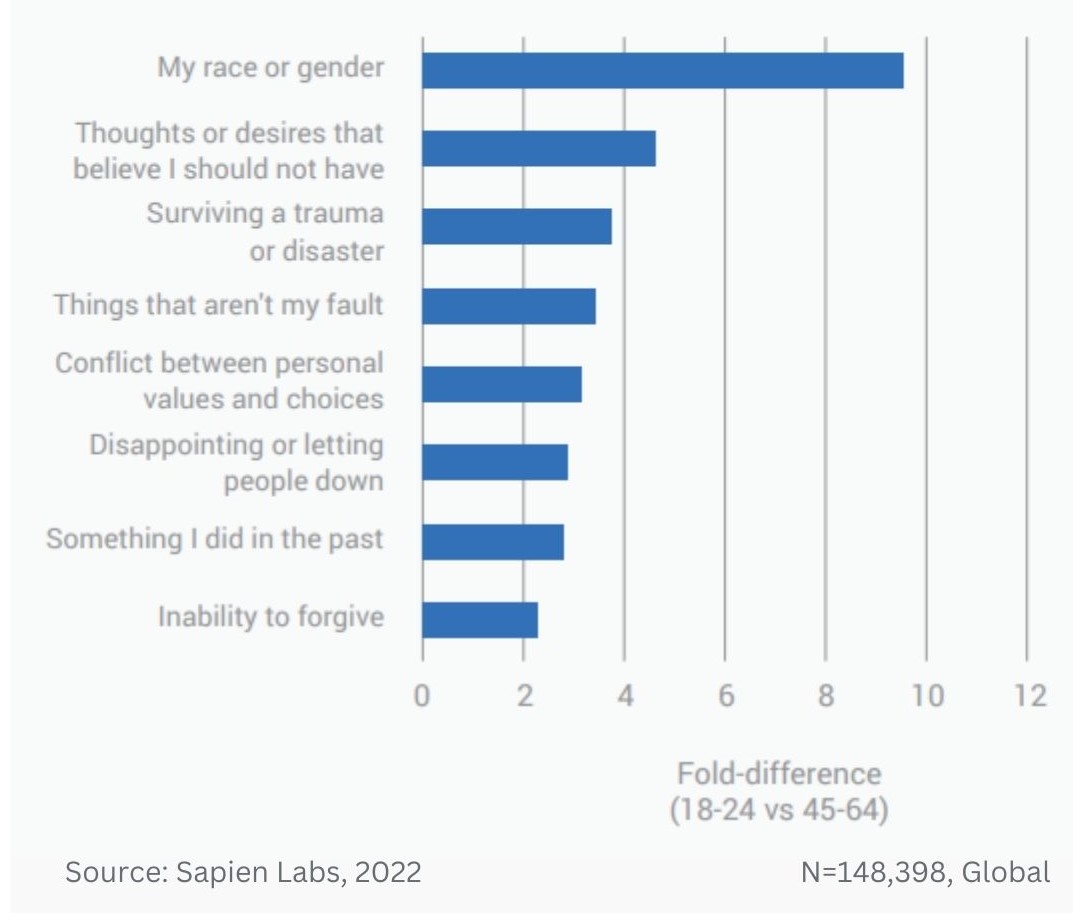
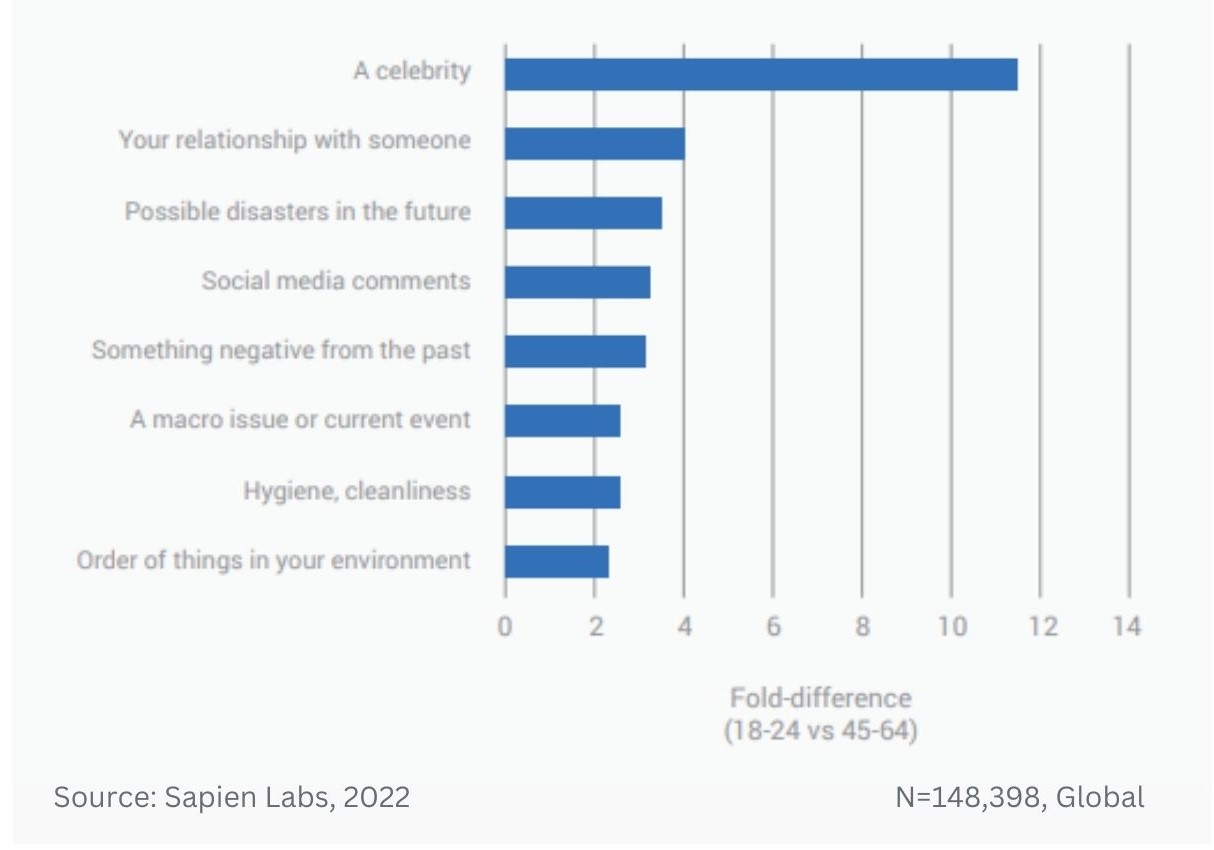
Magnitude difference in prevalence of debilitating obsessive, strange, and unwanted thoughts between younger and older adults
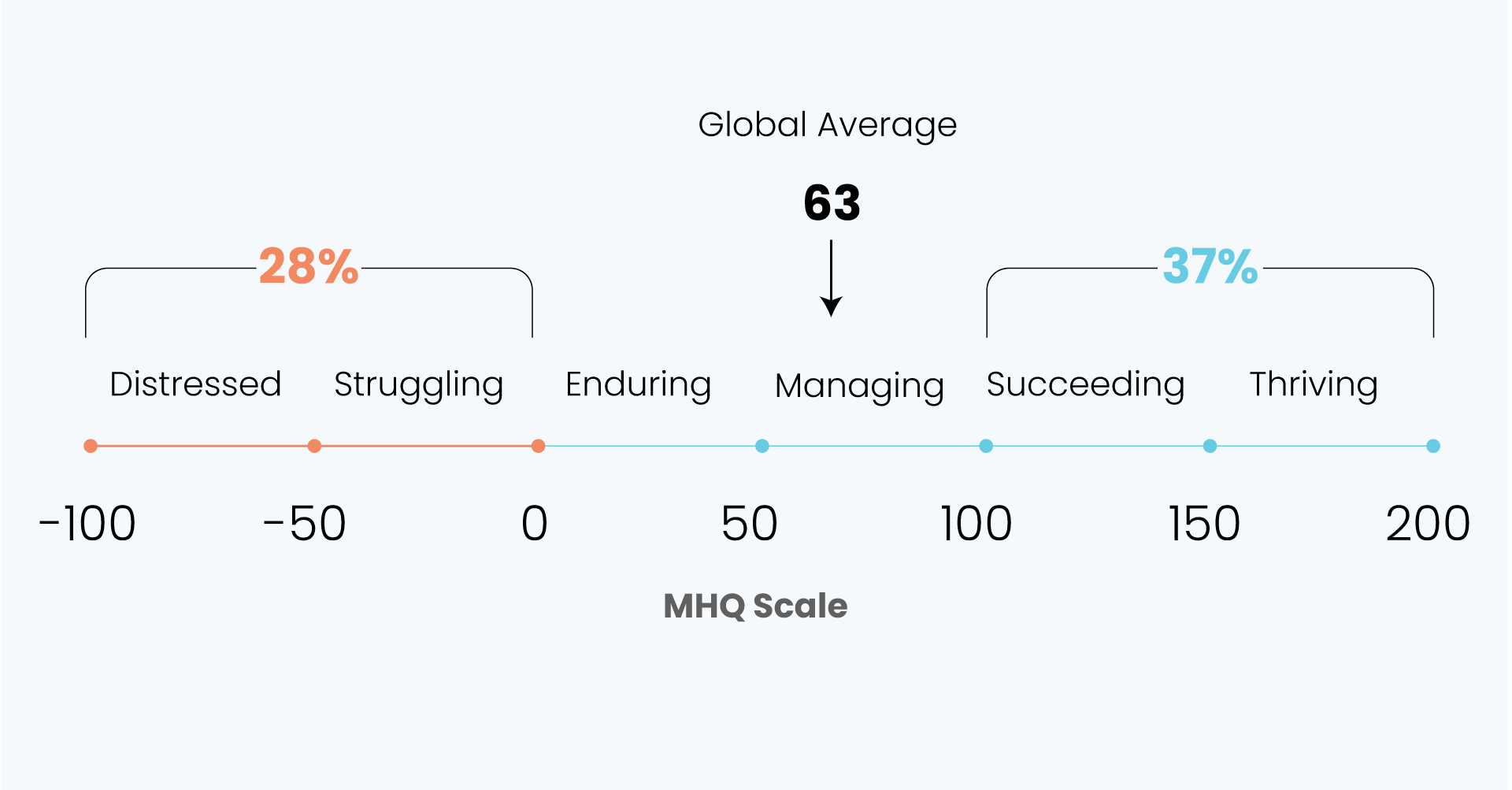
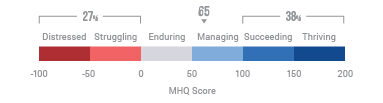
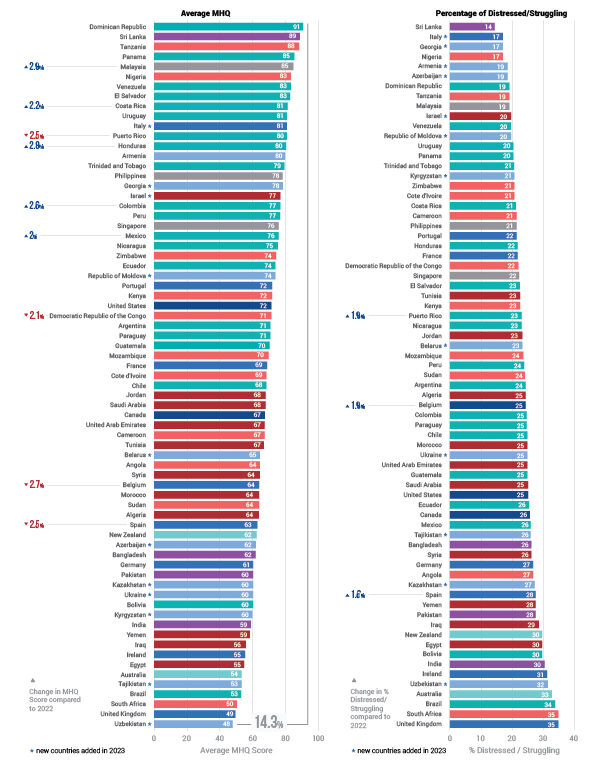
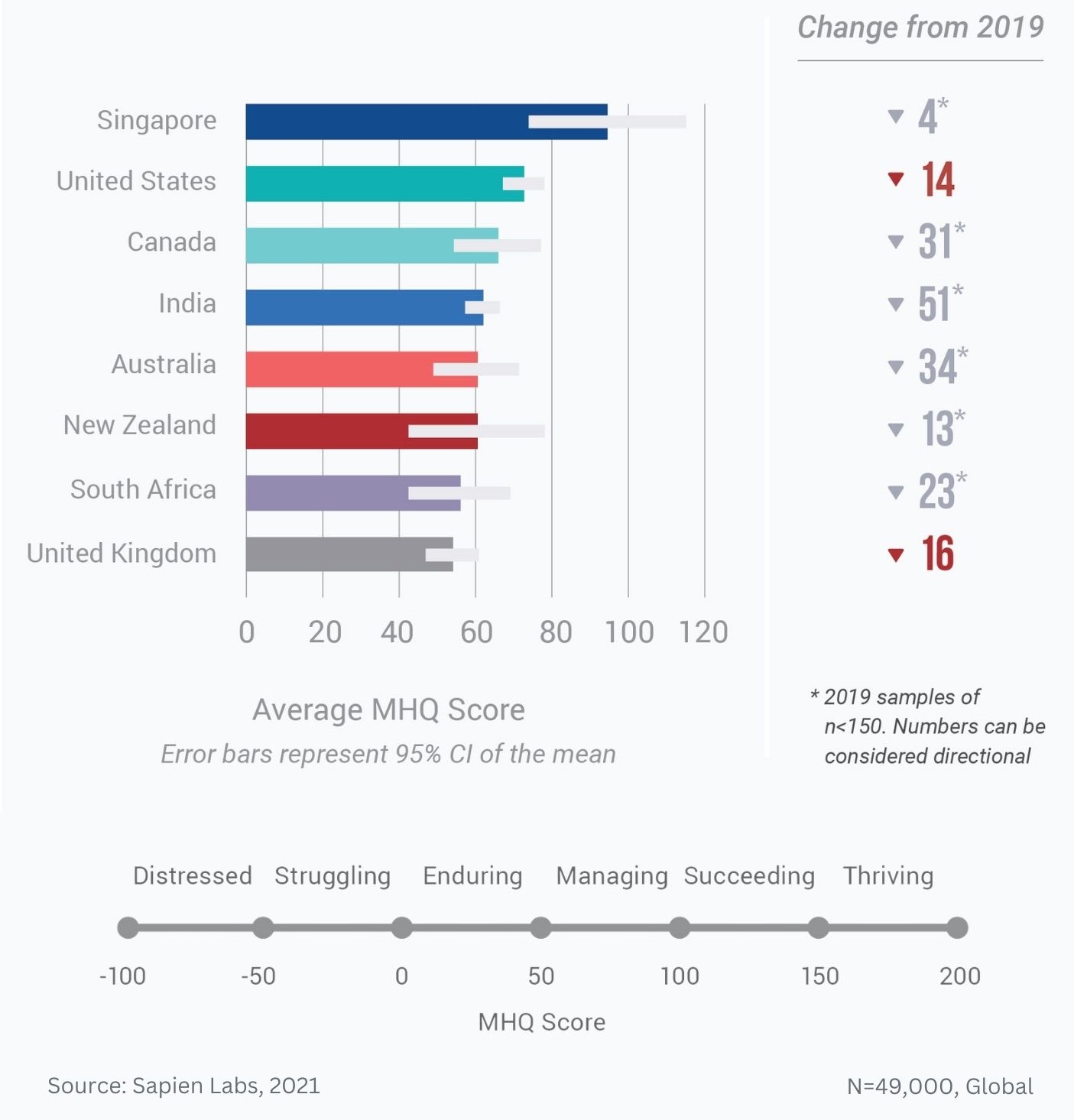
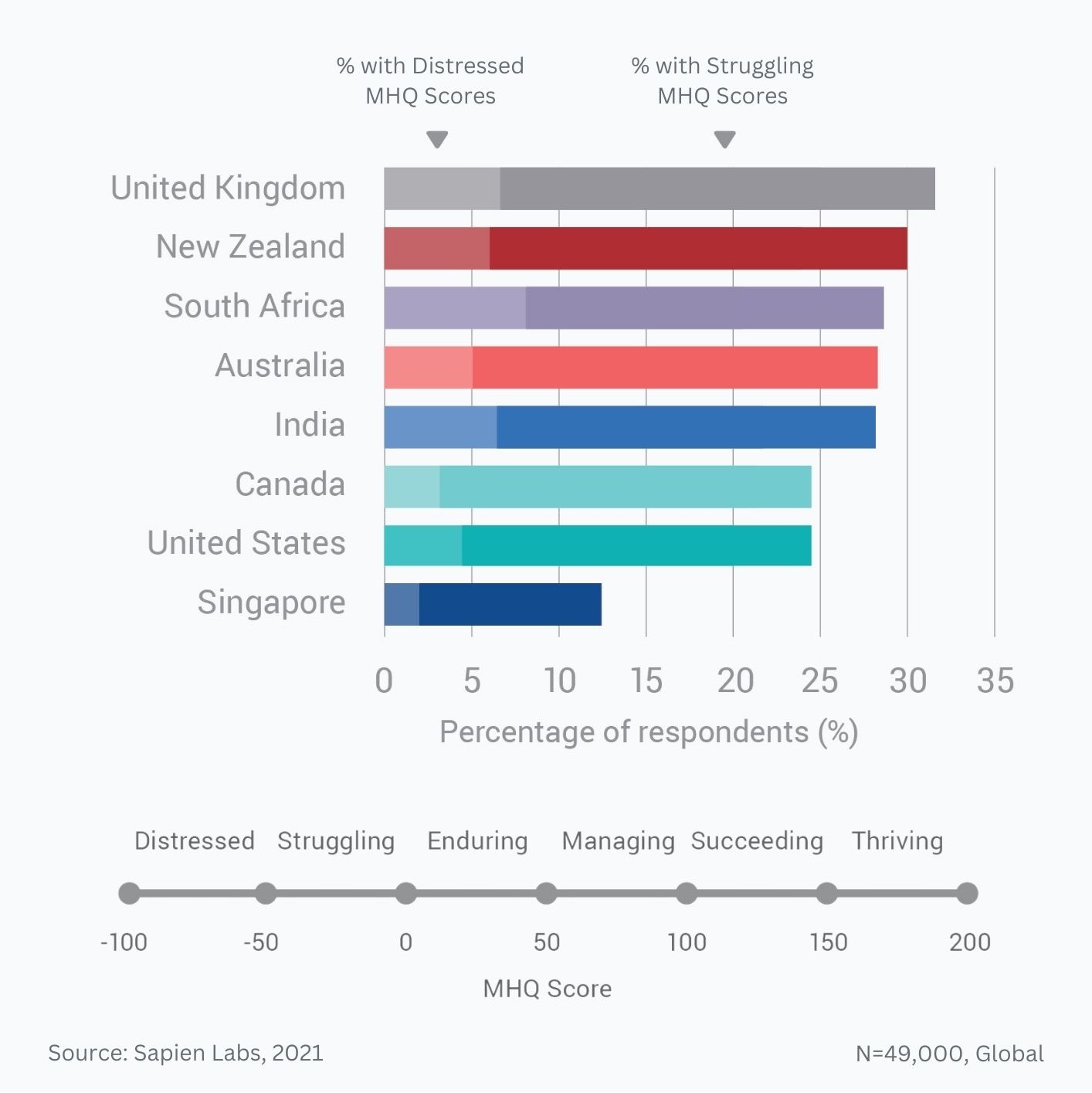
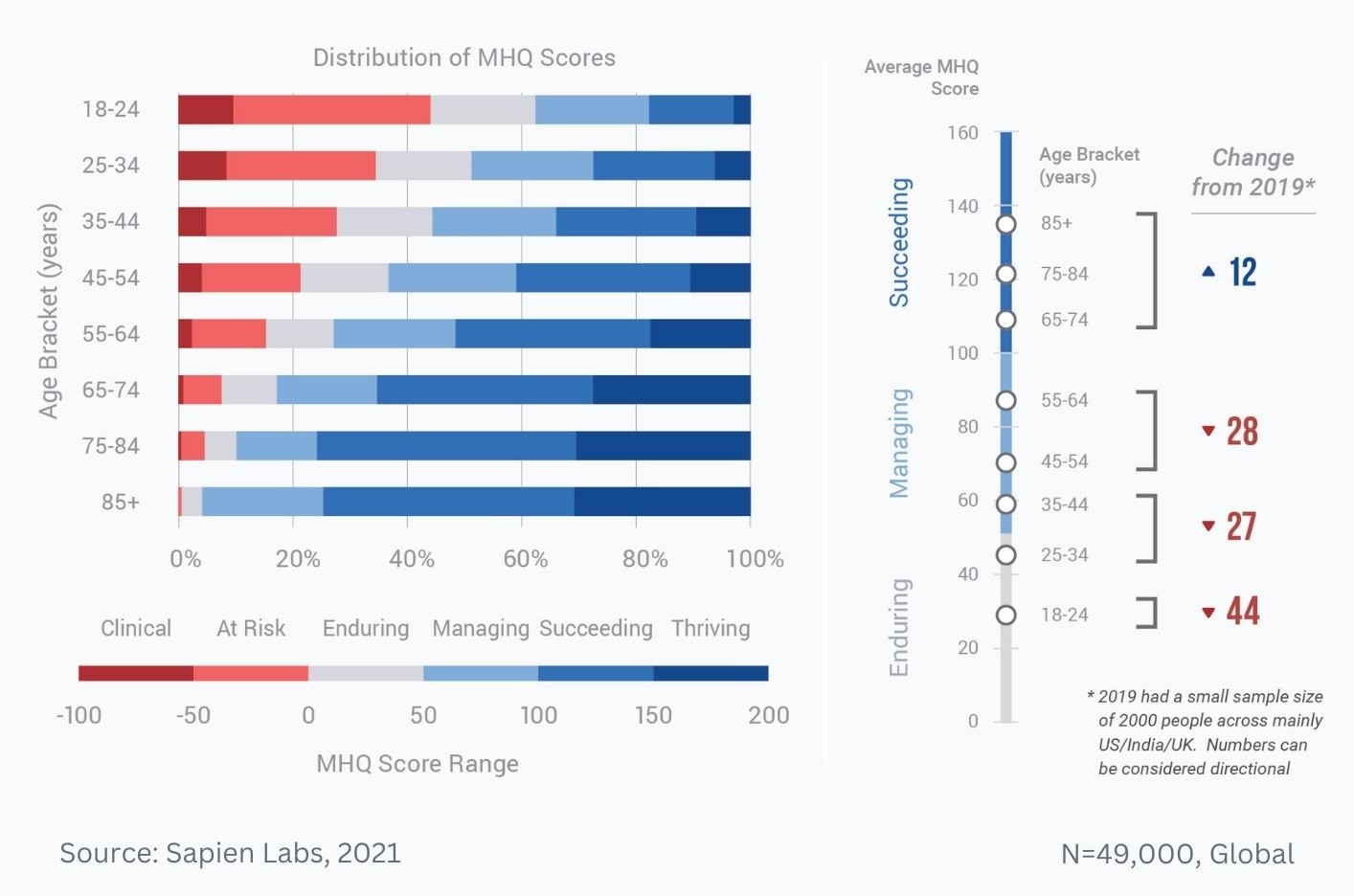
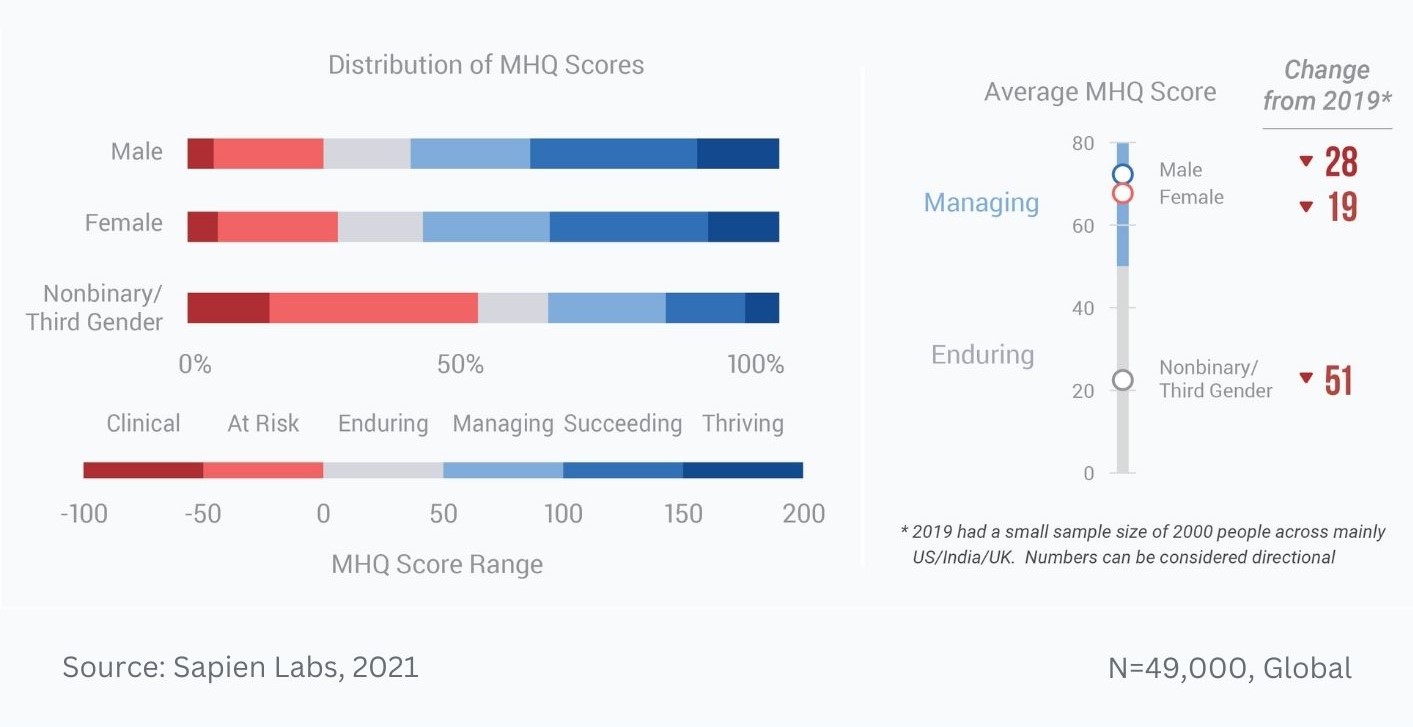
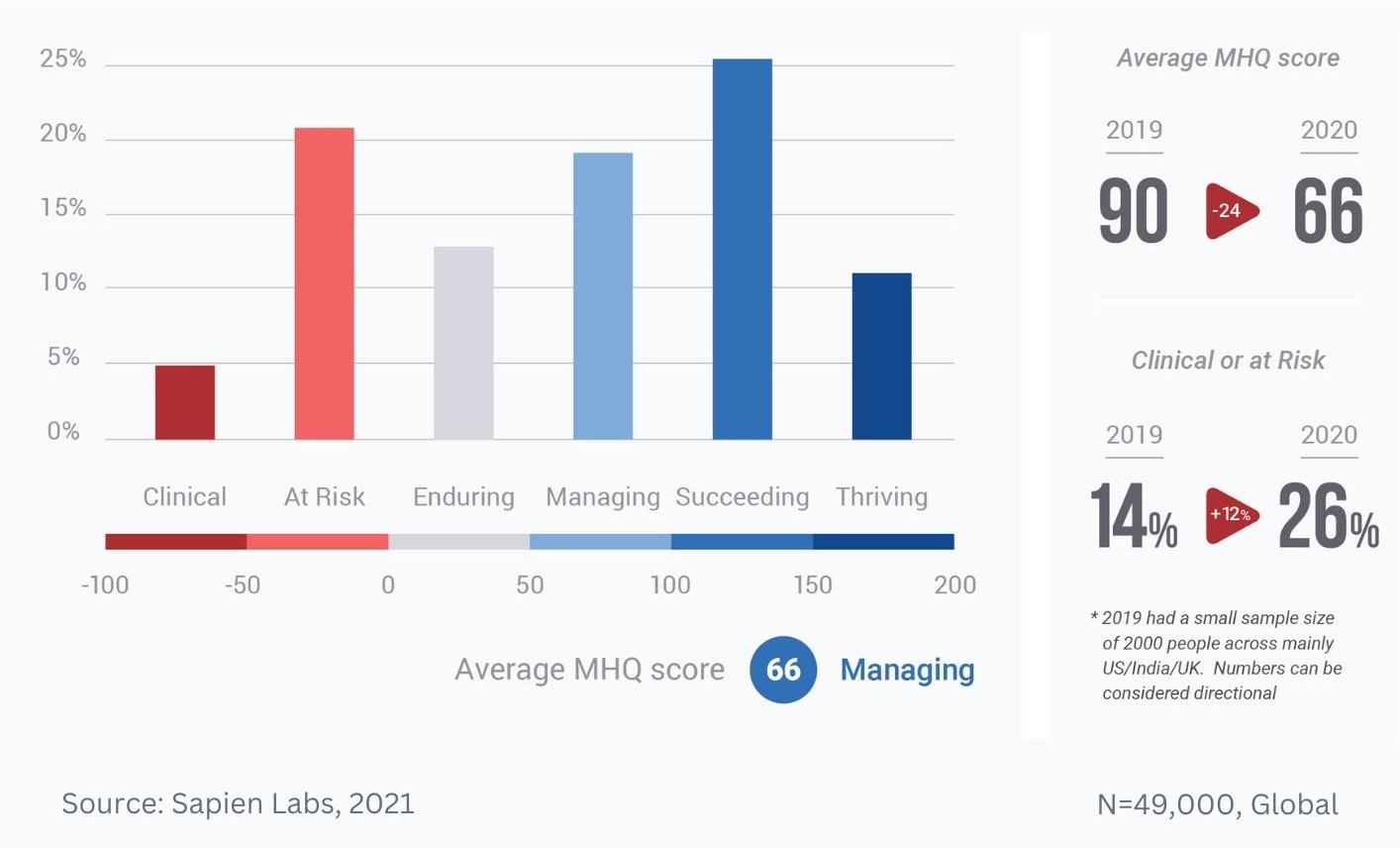
Distribution of MHQ Scores in 2020 across the English speaking population and changes relative to 2019
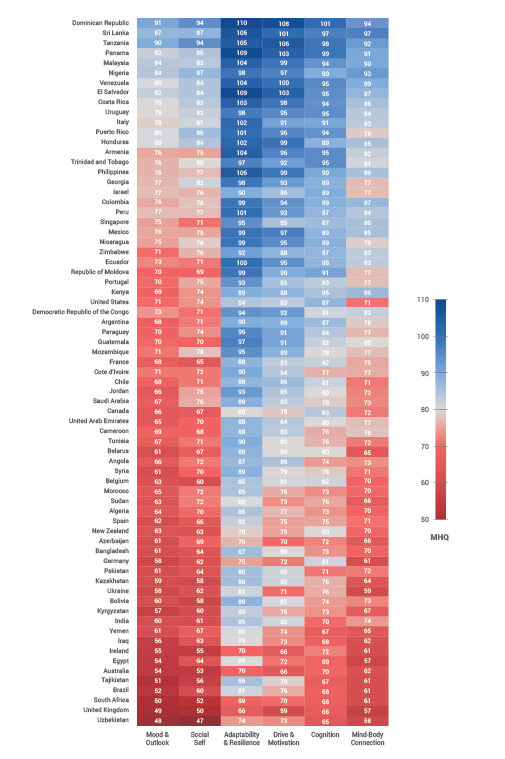
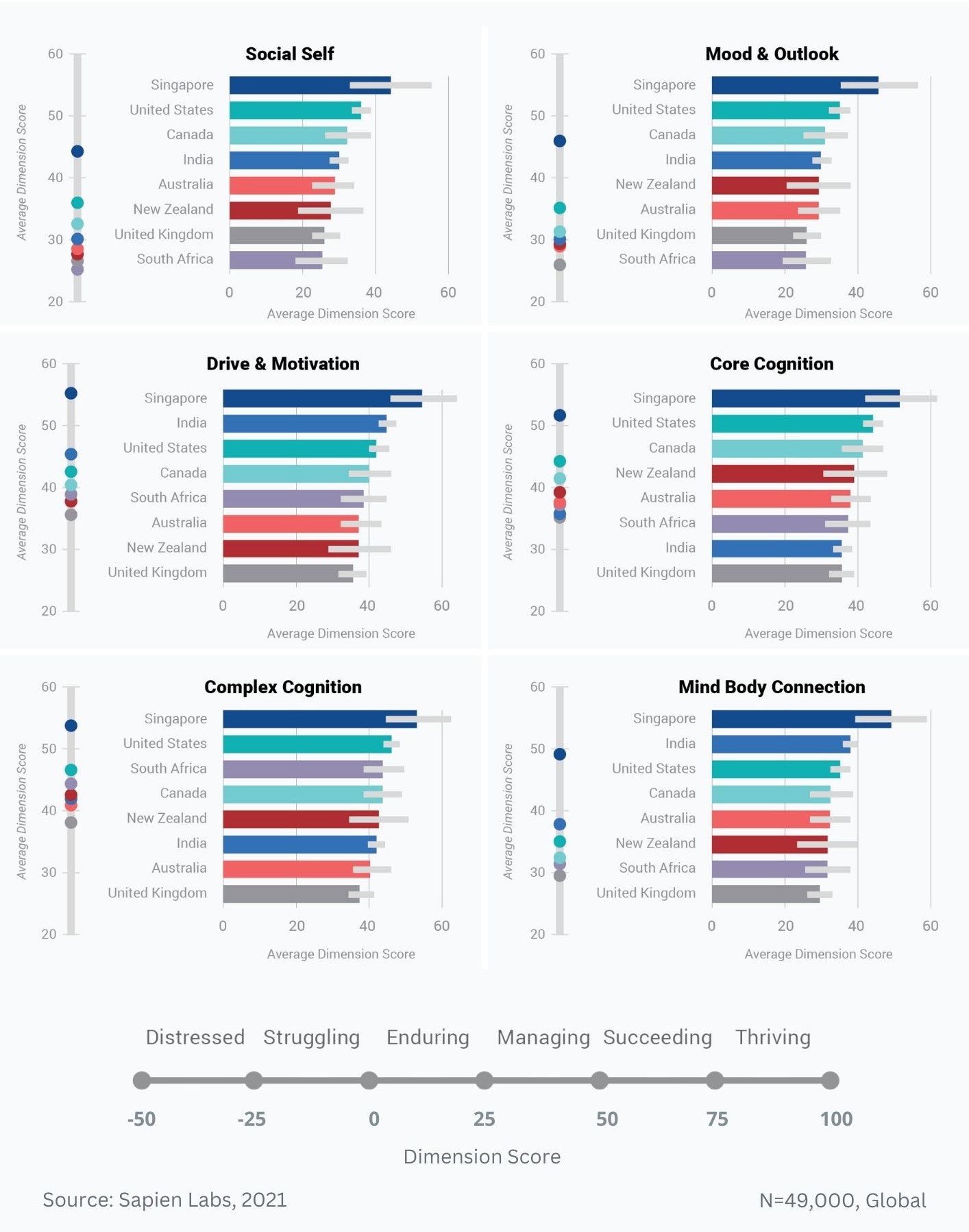
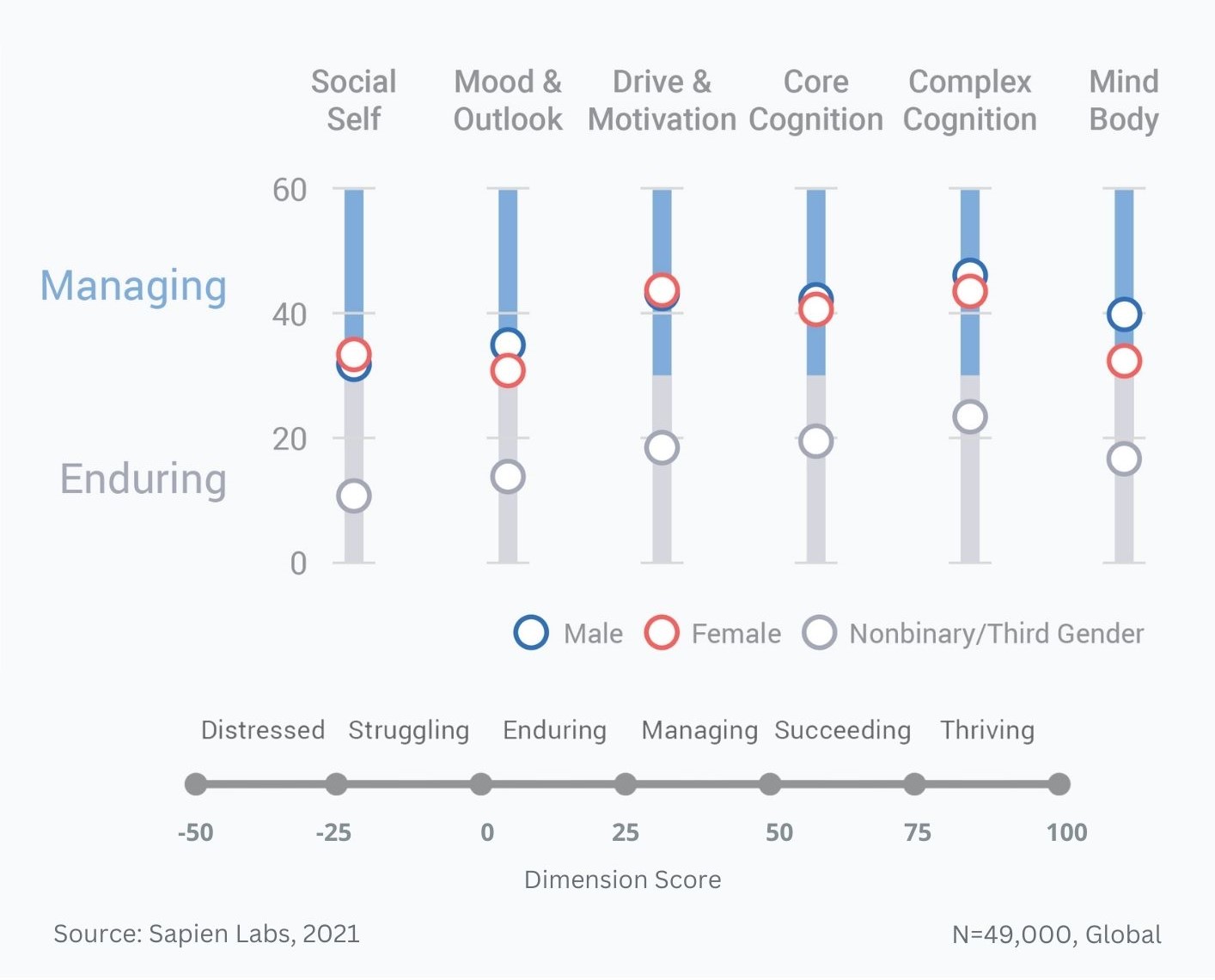
MHQ score distributions across the six functional dimensions of mental wellbeing and changes relative to 2019