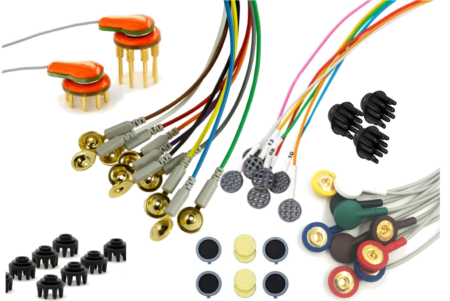
What are the common approaches to measuring depth of anesthesia in clinical application and how do we evaluate the algorithms used? Monitoring the depth of…
Lab Talk
Bayesian Model Selection For DCM Using EEG
How do you compare and select the best Bayesian model in Dynamic Causal Modeling or DCM of EEG data? In the previous two blogs we…
Dynamic Causal Modeling and the Application of Bayes Theorem
Dynamic Causal Modeling (DCM) takes a probabilistic Bayesian framework to infer effective or causal connectivity, essentially to model how a stimulus would influence the connectivity…
Perspectives on the Future of EEG from EEG2021
Where is the future of EEG? The EEG 2021 Symposium held last week discussed various aspects of the field and where it is going. Here are some highlights.
A Primer on Bayes Theorem (for Neuroimaging)
A Bayesian framework, one that works with conditional probabilities, has numerous applications in Neuroimaging in general and in EEG specifically. But first, a primer on Bayes theorem and how it works.
EEG Signal Quality in Wet Versus Dry Electrodes
Dry electrodes have some clear advantages but how does their signal quality compare to wet electrodes? Choosing one over the other may be a tradeoff between time, signal quality and stability.
Wet and Dry Electrodes for EEG
EEG recording technology remains similar in principle since its first use in 1923. However, a vast array of electrode types, both wet and dry, are…
Education and Travel in the EEG
Education and travel both increase the scope for more complex, novel stimulus to the brain. In turn the complexity of the brain EEG signal increases…
EEG Complexity Increases in Lockstep with Stimulus Consumption
More complex environments with expanded scope for stimulii to the brain have far reaching impact on various aspects of the brain. Sapien Labs’ Human Brain…
BCI Using Steady State Visual Evoked Potentials
Steady State Visual Evoked Potentials uses different frequencies of visual stimulii to distinguish between objects in BCI applications and have relatively high information transfer rates….