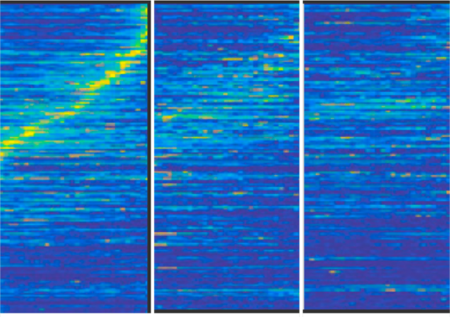
How do you compare and select the best Bayesian model in Dynamic Causal Modeling or DCM of EEG data? In the previous two blogs we […]
Lab Talk
Dynamic Causal Modelling (DCM): DCM – Neural Mass Models and Bayesian Inference
This post discusses the core components of neural mass models and Bayesian inference in DCM applied to EEG.
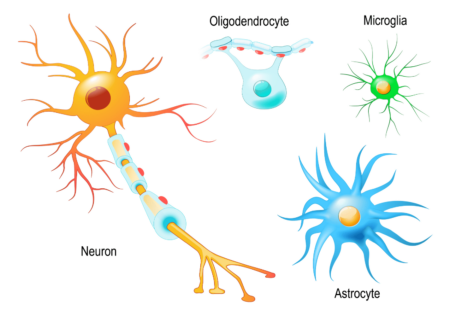
Glia As Key Players in Network Activity and Plasticity
After decades of being ignored, the important role of glia in shaping network activity and behavior is redefining how we understand the brain. For decades […]
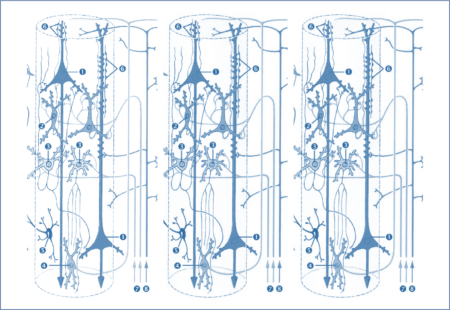
Dynamic Causal Modeling and the Application of Bayes Theorem
Dynamic Causal Modeling (DCM) takes a probabilistic Bayesian framework to infer effective or causal connectivity, essentially to model how a stimulus would influence the connectivity […]
Perspectives on the Future of EEG from EEG2021
Where is the future of EEG? The EEG 2021 Symposium held last week discussed various aspects of the field and where it is going. Here are some highlights.
A Primer on Bayes Theorem (for Neuroimaging)
A Bayesian framework, one that works with conditional probabilities, has numerous applications in Neuroimaging in general and in EEG specifically. But first, a primer on Bayes theorem and how it works.
Drifting Neuronal Representations of Function
Neurons do not stably participate in the representation of tasks and behaviors. Called representational drift, this calls for new thinking in how the brain represents […]
What Can Your Blood Tell You About Your Brain?
The blood may hold many clues to damage and degeneration in the brain. New findings bring a blood test for brain disorders closer to reality. […]
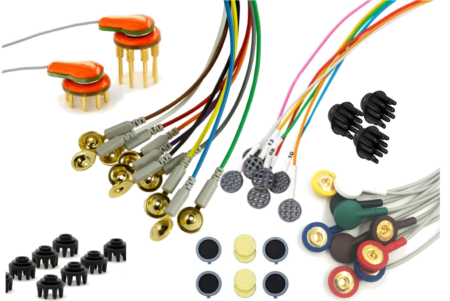
EEG Signal Quality in Wet Versus Dry Electrodes
Dry electrodes have some clear advantages but how does their signal quality compare to wet electrodes? Choosing one over the other may be a tradeoff between time, signal quality and stability.
Wet and Dry Electrodes for EEG
EEG recording technology remains similar in principle since its first use in 1923. However, a vast array of electrode types, both wet and dry, are […]