Identifying the source within the brain from which an EEG signal element originates is a complex problem that requires a model of the head and…
Lab Talk
The Inverse Problem in EEG – Assumptions and Pitfalls
Solving the inverse problem in EEG to identify the source of a signal requires a number of assumptions to constrain the solution space. These assumptions…
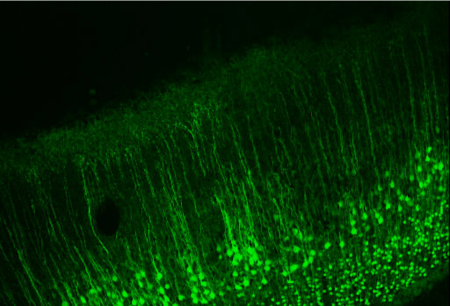
Brain in a Dish
Pieces of brain in a dish can give rise to synchronous electrical activity with similar characteristics to that measured in the intact brain. What aspect…
Understanding Multiscale Entropy
Multiscale entropy extends sample entropy to multiple time scales or signal resolutions to provide an additional perspective when the time scale of relevance is unknown….
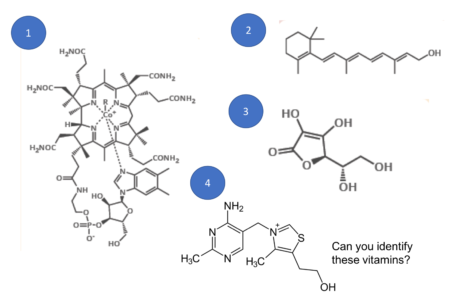
Vitamins for the Brain
Vitamins play a crucial role in building axon fiber and facilitating synaptic transmission but have to be ingested to become available to the brain. Surprisingly,…
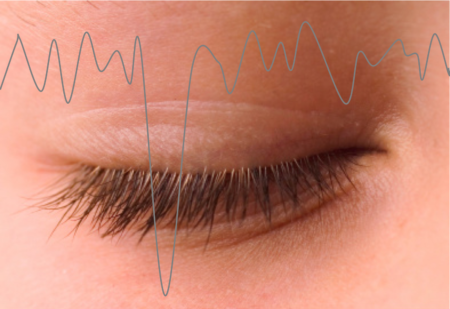
Getting Rid of Eye Blink in the EEG
The eye blink is one of the most common contaminants of the EEG signal. Here we discuss some common techniques used to remove it including…
Many Ways to Measure Attention
Attention is a multifaceted, multisensory cognitive phenomenon that can be studied in many ways. Here we describe a few methods used in the lab to…
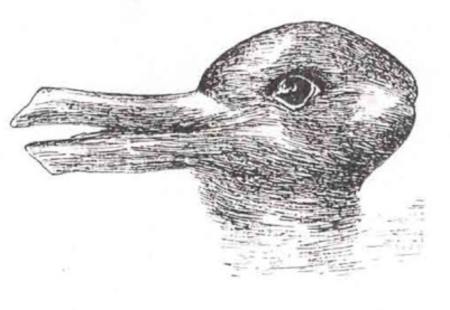
The Illusion of Reality
Optical illusions demonstrate how our brains filter sensory stimulii and fit it into a construct that ‘makes sense’ to us. Can we measure our…
Alpha, Alpha Everywhere: What Does it Mean?
Activity in the alpha band has been a subject of much interest since the first recording of EEG. However methodological inconsistencies and confounding changes across…
Detrended Fluctuation Analysis: A Glimpse at Memory in the EEG
DFA is a method to identify self-similarity of signals in time – a way of quantifying an aspect of memory. How does it work, how…