Power line noise at 50 and 60 Hz is bang in the middle of the spectrum of brain activity and is often picked up by…
Lab Talk
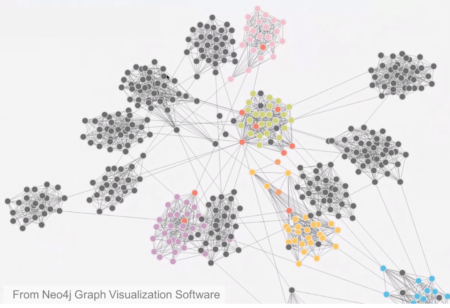
A Primer on the Application of Graph Theory to EEG
Graph theory has been most commonly used to understand the structure of social networks and has gained traction in the last decade as an important…
Alpha Energy – Specifically Estimating the Alpha Oscillatory Component in the EEG
The Alpha Energy metric specifically characterizes the periodic alpha components of the EEG that shows up as a peak above the background decay of the…
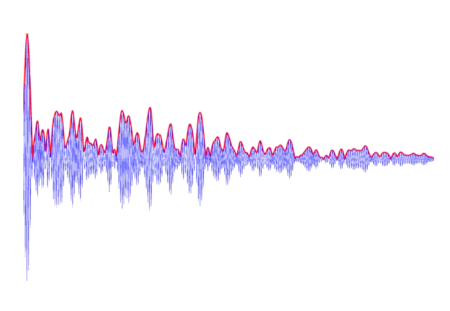
A New Metric of Waveform Complexity in EEG Analysis
It is yet unclear which features of the EEG signal are the most informative about brain states and outcomes. A new complexity measure with different…
Measuring a Thought
We all intuitively recognize a thought when we have one but a thought is hard to describe as measurable or observable factors. We all have…
Dead or Alive? Rethinking the Flat Line EEG
Death is commonly declared with the observation of a flat line or isoelectric EEG that is irreversible. Yet there are many caveats, challenges and ambiguities…
Computing Correlation Dimension in EEG
Correlation dimension is a method of computing the dimension of an attractor and has been applied to time series such as EEG with some luck…
The Lyapunov Exponent in EEG
Here we provide a background on the lyapunov exponent as a measure of nonlinearity and its application to EEG. Chaos in dynamical systems To understand…
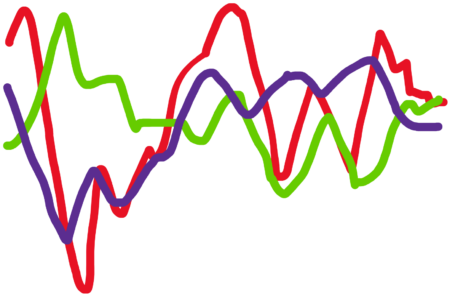
Social Synchronization in the EEG
Humans operate within a social context. The study of social synchronization or ‘hyperscanning’ using EEG is beginning to reveal insight into human interactions. Humans are…
Common Average vs Infinity Reference in EEG
How do the average and infinity references in EEG compare, and what are other reference free approaches? In the previous blogpost, we looked at how…