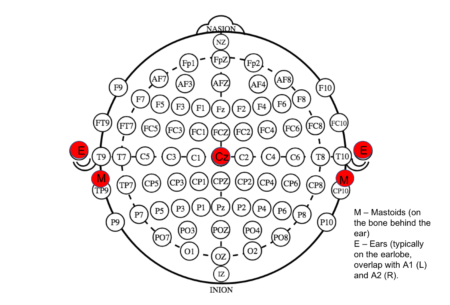
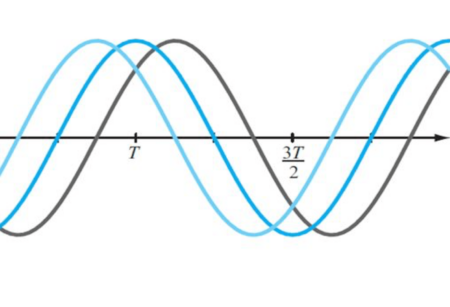
Humans operate within a social context. The study of social synchronization or ‘hyperscanning’ using EEG is beginning to reveal insight into human interactions. Humans are…
Lab Talk
Common Average vs Infinity Reference in EEG
How do the average and infinity references in EEG compare, and what are other reference free approaches? In the previous blogpost, we looked at how…
Effect of EEG Reference Choice on Outcomes
In EEG, voltages recorded at each electrode are computed with reference to another electrode. The choice of this electrode reference impacts a number of EEG measures….
EEG Connectivity Using Phase Lag Index
Phase Lag Index is a tool to estimate connectivity in EEG in a way that eliminates volume conduction effects. However, it is also likely to…
Assessing Connectivity with Phase Locking Value
Assessing phase locking in the signal between two electrodes is often used as a method to assess functional connectivity. Here is a look at how…
Why Do Brains Have Spontaneous Activity?
The brain spontaneously produces activity regardless of mental activity and stimulus input. Current theories treat this activity as noise or simply ignore it. What does…
Tracking Anesthesia
With multifaceted effects from analgesia, amnesia, paralysis and loss of consciousness the mechanisms of anesthesia are still a mystery. Can tracking with EEG provide deeper…
Factors that Impact Coherence in the EEG
Coherence is a commonly used measure in EEG analysis. What is Coherence and what are the practical considerations, limitations and interpretations of this measure when…
Neuronal Avalanches: What are They and What do They Mean?
Neuronal avalanches are a structure of organization of cascades of synchronized of activity in the cortex that have several surprising implications for how we understand…
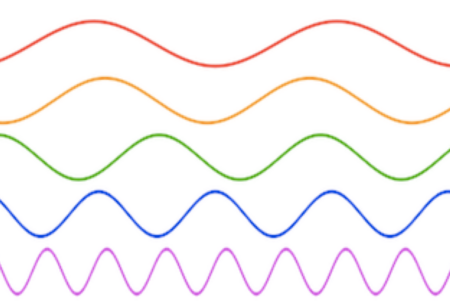
Brain Waves, Sine Waves and the Fourier Transform
The most popular method of analyzing brain signals is to decompose it into its component sinusoids using the fourier transform. However a non-sinusoidal physiology poses…