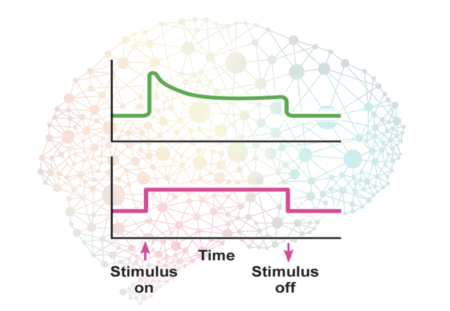
We constantly change our behavior between things like driving a car to chopping an onion. How does the brain switch quickly between different sensory-motor pathways…
Lab Talk
Computing Correlation Dimension in EEG
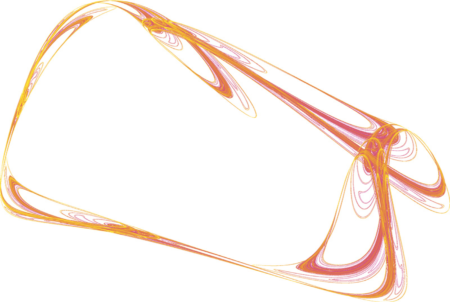
Correlation dimension is a method of computing the dimension of an attractor and has been applied to time series such as EEG with some luck…
Finding an Alternative to Connectionism
Mainstream theory of brain function revolves around patterns of connectivity. Could the adaptations of neurons be an alternative anchor that provides greater insight? Today’s mainstream…
The Lyapunov Exponent in EEG
Here we provide a background on the lyapunov exponent as a measure of nonlinearity and its application to EEG. Chaos in dynamical systems To understand…
Human Brain Organoids: What They Are and Aren’t
Human brain organoids are human brain cells derived from stem cells and grown in 3-D. How much like a real brain are they? Much of…
Predicting Human Behavior with Diffusion Models
Random walk or diffusion models have been successful at predicting human decision making and guiding experiments. Here’s why. In my last post I described two…
Transport of Proteins, RNA and DNA among Brain Cells
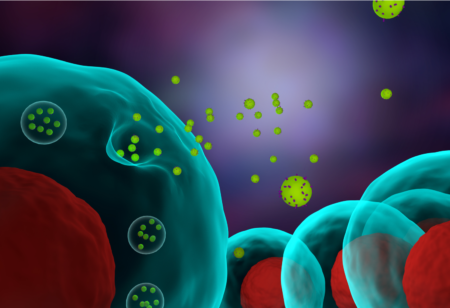
The discoveries of exosomes and tunneling nanotubes that allow intercellular transport of proteins, RNA and DNA among neurons and glia change how we think about…
Social Synchronization in the EEG
Humans operate within a social context. The study of social synchronization or ‘hyperscanning’ using EEG is beginning to reveal insight into human interactions. Humans are…
Two Successful Theories in Biology
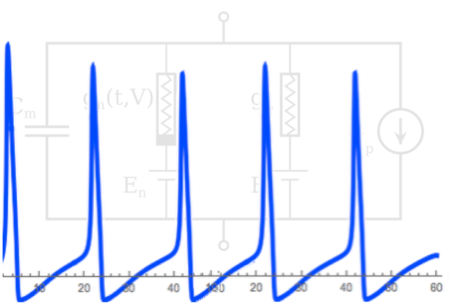
The theory of evolution and the Hodgkin-Huxley model of the action potential are two successful theories in biology that are relevant to the brain. Why…
Common Average vs Infinity Reference in EEG
How do the average and infinity references in EEG compare, and what are other reference free approaches? In the previous blogpost, we looked at how…